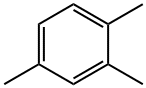
Mesitylene
Synonym(s):1,3,5-Trimethylbenzene;Mesitylene solution
- CAS NO.:108-67-8
- Empirical Formula: C9H12
- Molecular Weight: 120.19
- MDL number: MFCD00008538
- EINECS: 203-604-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:49:53
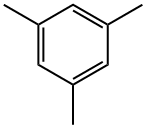
What is Mesitylene?
Description
Mesitylene is a clear, colorless liquid with a distinctive, aromatic odor. Molecular weight= 120.21; Specific gravity (H2O:1)= 0.86;Boiling point=165℃; Freezing/Melting point=45℃; Vapor pressure= 2 mmHg at 20℃; Flash point=50℃ (cc); Autoignition temperature=559℃. Hazard Identification (based on NFPA-704 M Rating System): Health 0, Flammability 2, Reactivity 0. Practically insoluble in water; solubility= 0.002%.
Chemical properties
Aromatic-herbaceous, ethereal odor, comparatively diffusive, reminiscent of Thyme, overall pleasant, not as gassy as Cymene.
Chemical properties
Mesitylene is a clear, colorless liquid. Distinctive, aromatic odor.
Physical properties
Colorless liquid with a peculiar odor. An odor threshold concentration of 170 ppbv was reported by Nagata and Takeuchi (1990).
The Uses of Mesitylene
Mesitylene is used to make plastics and dyes. It acts as a solvent, ligand in organometallic chemistry and precursor to 2,4,6-trimethylaniline. It is also used as a developer for photopatternable silicones due to its solvent properties in the electronics industry. It is used as an internal standard in nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) samples due to the presence of three equivalent protons in it. It is involved in the production of trimesic acid and antioxygen, epoxy firming agent and polyester resin stabilizers. Further, it is used as an additive and component in aviation gasoline blends.
The Uses of Mesitylene
Intermediate, including anthraquinone vat dyes, UV oxidation stabilizers for plastics.
What are the applications of Application
1,3,5-Trimethylbenzene is a precursor to 2,4,6-trimethylaniline
Definition
ChEBI: A trimethylbenzene carrying methyl substituents at positions 1, 3 and 5.
Synthesis Reference(s)
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 92, p. 3232, 1970 DOI: 10.1021/ja00713a078
The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 19, p. 923, 1954 DOI: 10.1021/jo01371a008
General Description
A colorless liquid with a peculiar odor. Insoluble in water and less dense than water. Flash point near 123°F. May be toxic by ingestion and inhalation. Used to make plastics and dyes.
Air & Water Reactions
Flammable. Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
TRIMETHYLBENZENE is incompatible with the following: Oxidizers, nitric acid .
Hazard
Moderate fire hazard. Toxic by inhalation. Central nervous system impairment, asthma, and hematologic effects.
Health Hazard
May cause toxic effects if inhaled or absorbed through skin. Inhalation or contact with material may irritate or burn skin and eyes. Fire will produce irritating, corrosive and/or toxic gases. Vapors may cause dizziness or suffocation. Runoff from fire control or dilution water may cause pollution.
Fire Hazard
HIGHLY FLAMMABLE: Will be easily ignited by heat, sparks or flames. Vapors may form explosive mixtures with air. Vapors may travel to source of ignition and flash back. Most vapors are heavier than air. They will spread along ground and collect in low or confined areas (sewers, basements, tanks). Vapor explosion hazard indoors, outdoors or in sewers. Runoff to sewer may create fire or explosion hazard. Containers may explode when heated. Many liquids are lighter than water.
Safety Profile
Poison by inhalation. Moderately toxic by intraperitoneal route. Human systemic effects by inhalation: sensory changes involving peripheral nerves, somnolence (general depressed activity), and structural or functional change in trachea or bronchi. Reports of leukopenia and thrombocytopenia in experimental animals. A mild skin and eye irritant. A flammable liquid when exposed to heat or flame; can react vigorously with oxidizing materials. Violent reaction with HNO3. To fight fire, use water spray, fog, foam, CO2. Emitted from modern buildmg materials (CENEAR 69,22,91). When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes.
Potential Exposure
Mesitylene is used as raw material in chemical synthesis and as ultraviolet stabilizer; as a paint thinner, solvent, and motor fuel component; as an intermediate in organic chemical manufacture.
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts theskin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediately with soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure, begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR if heart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medical facility. When this chemical has been swallowed, get medical attention. Give large quantities of water and induce vomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit.
Source
Detected in distilled water-soluble fractions of 87 octane gasoline (0.34 mg/L), 94 octane
gasoline (1.29 mg/L), Gasohol (0.48 mg/L), No. 2 fuel oil (0.08 mg/L), jet fuel A (0.09 mg/L),
diesel fuel (0.03 mg/L), and military jet fuel JP-4 (0.09 mg/L) (Potter, 1996). Schauer et al. (1999)
reported 1,3,5-trimethylbenzene in a diesel-powered medium-duty truck exhaust at an emission
rate of 260 μg/km.
California Phase II reformulated gasoline contained 1,3,5-trimethylbenzene at a concentration of
7.45 g/kg. Gas-phase tailpipe emission rates from gasoline-powered automobiles with and without
catalytic converters were 1.98 and 210 mg/km, respectively (Schauer et al., 2002).
Thomas and Delfino (1991) equilibrated contaminant-free groundwater collected from
Gainesville, FL with individual fractions of three individual petroleum products at 24–25 °C for
24 h. The aqueous phase was analyzed for organic compounds via U.S. EPA approved test method
602. Average 1,3,5-trimethylbenzene concentrations reported in water-soluble fractions of
unleaded gasoline, kerosene, and diesel fuel were 333, 86, and 13 μg/L, respectively. When the
authors analyzed the aqueous-phase via U.S. EPA approved test method 610, average 1,3,5-
trimethylbenzene concentrations in water-soluble fractions of unleaded gasoline, kerosene, and
diesel fuel were greater, i.e., 441, 91, and 27 μg/L, respectively.
Drinking water standard: No MCLGs or MCLs have been proposed (U.S. EPA, 2000).
Environmental Fate
Biological. In anoxic groundwater near Bemidji, MI, 1,3,5-trimethylbenzene anaerobically
biodegraded to the intermediate tentatively identified as 3,5-dimethylbenzoic acid (Cozzarelli et
al., 1990).
Photolytic. Glyoxal, methylglyoxal, and biacetyl were produced from the photooxidation of
1,3,5-trimethylbenzene by OH radicals in air at 25 °C (Tuazon et al., 1986a). The rate constant for
the reaction of 1,3,5-trimethylbenzene and OH radicals at room temperature was 4.72 x 10-11
cm3/molecule?sec (Hansen et al., 1975). A rate constant of 2.97 x 10-8 L/molecule?sec was reported
for the reaction of 1,3,5-trimethylbenzene with OH radicals in the gas phase (Darnall et al., 1976).
Similarly, a room temperature rate constant of 6.05 x 10-11 cm3/molecule?sec was reported for the
vapor-phase reaction of 1,3,5-trimethylbenzene with OH radicals (Atkinson, 1985). At 25 °C, a
rate constant of 3.87 x 10-11 cm3/molecule?sec was reported for the same reaction (Ohta and
Ohyama, 1985).
Chemical/Physical. 1,3,5-Trimethylbenzene will not hydrolyze because it does not contain a
hydrolyzable functional group (Kollig, 1993).
Storage
Color Code—Red: Flammability Hazard: Store in a flammable liquid storage area or approved cabinet away from ignition sources and corrosive and reactive materials. Prior to working with this chemical you should be trained on its proper handling and storage. This chemical must be stored to avoid contact with oxidizers (such as perchlorates, peroxides, permanganates, chlorates, and nitrates) and strong oxidizers (such as chlorine, bromine, and fluorine), since violent reactions occur. Store in tightly closed containers in a cool, well-ventilated area away from heat. Sources of ignition, such as smoking and open flames are prohibited where this chemical is used, handled, or stored in a manner that could create a potential fire or explosion hazard. Metal containers involving the transfer of 5 gallons or more of this chemical should be grounded and bonded. Drums must be equipped with self-closing valves, pressure vacuum bungs, and flame arresters. Use only nonsparking tools and equipment, especially when opening and closing containers of this chemical.
Shipping
UN1993 Flammable liquids, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 3; Labels: 3-Flammable liquid, Technical Name Required.
Purification Methods
Dry it with CaCl2 and distil it from Na in a glass helices-packed column. Treat it with silica gel and redistil it. Alternative purifications include vapour-phase chromatography, or fractional distillation followed by azeotropic distillation with 2-methoxyethanol (which is subsequently washed out with H2O), drying and fractional distilling. More exhaustive purification uses sulfonation by dissolving in two volumes of conc H2SO4, precipitating with four volumes of conc HCl at 0o, washing with conc HCl and recrystallising from CHCl3. The mesitylene sulfonic acid is hydrolysed with boiling 20% HCl and steam distilled. The separated mesitylene is dried (MgSO4 or CaSO4) and distilled. It can also be fractionally crystallised from the melt at low temperatures. [Beilstein 5 IV 1016.]
Incompatibilities
Vapors forms explosive mixture with air. Violent reaction with nitric acid. Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides
Waste Disposal
Dissolve or mix the material with a combustible solvent and burn in a chemical incinerator equipped with an afterburner and scrubber. All federal, state, and local environmental regulations must be observed.
Properties of Mesitylene
| Melting point: | -45 °C |
| Boiling point: | 163-166 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 0.864 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| vapor density | 4.1 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 14 mm Hg ( 55 °C) |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | 112 °F |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Miscible with alcohol, benzene, ether (Windholz et al., 1983), and trimethylbenzene isomers. |
| appearance | Colorless liquid |
| form | Liquid |
| pka | >14 (Schwarzenbach et al., 1993) |
| color | Clear colorless |
| Odor Threshold | 0.17ppm |
| explosive limit | 0.88-6.1%, 100°F |
| Water Solubility | 2.9 g/L (20 ºC) |
| Merck | 14,5907 |
| BRN | 906806 |
| Henry's Law Constant | 4.03, 4.60, 5.71, 6.73, and 9.63 at 10, 15, 20, 25, and 30 °C, respectively (EPICS, Ashworth et al.,1988) |
| Exposure limits | NIOSH REL: TWA 25 ppm (125 mg/m3); ACGIH TLV: TWA for mixed
isomers 25 ppm (adopted). |
| Dielectric constant | 3.4(Ambient) |
| Stability: | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 108-67-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Benzene, 1,3,5-trimethyl-(108-67-8) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 1,3,5-Trimethylbenzene (108-67-8) |
Safety information for Mesitylene
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H226:Flammable liquids H304:Aspiration hazard H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H332:Acute toxicity,inhalation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation H411:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P331:Do NOT induce vomiting. P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. P303+P361+P353:IF ON SKIN (or hair): Remove/Take off Immediately all contaminated clothing. Rinse SKIN with water/shower. |
Computed Descriptors for Mesitylene
| InChIKey | AUHZEENZYGFFBQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Mesitylene manufacturer
JSK Chemicals
Triveni Interchem Private Limited (Group Of Triveni Chemicals)
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
![(-)-2-[METHYLAMINO]-1-PHENYLPROPANE](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/33817-09-3.gif)


You may like
-
 MESITYLENE 99%View Details
MESITYLENE 99%View Details -
 Mesitylene extrapure CAS 108-67-8View Details
Mesitylene extrapure CAS 108-67-8View Details
108-67-8 -
 Mesitylene 95% CAS 108-67-8View Details
Mesitylene 95% CAS 108-67-8View Details
108-67-8 -
 Mesitylene CAS 108-67-8View Details
Mesitylene CAS 108-67-8View Details
108-67-8 -
 1,3,5-Trimethylbenzene CAS 108-67-8View Details
1,3,5-Trimethylbenzene CAS 108-67-8View Details
108-67-8 -
 MESITYLENE For Synthesis CAS 108-67-8View Details
MESITYLENE For Synthesis CAS 108-67-8View Details
108-67-8 -
 Mesitylene CAS 108-67-8View Details
Mesitylene CAS 108-67-8View Details
108-67-8 -
 Mesitylene (C9H12) 108-67-8, 97%, Industrial GradeView Details
Mesitylene (C9H12) 108-67-8, 97%, Industrial GradeView Details
108-67-8
