MERCURIC CYANIDE
Synonym(s):Mercuric cyanide
- CAS NO.:592-04-1
- Empirical Formula: C2HgN2
- Molecular Weight: 252.62
- MDL number: MFCD00011037
- EINECS: 209-741-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:08:52
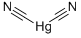
What is MERCURIC CYANIDE?
Description
Mercuric cyanide is an odorless, white crystalline solid; turns gray to dark brown when exposed to light. Molecular weight= 252.63; Decomposes at 319℃. Hazard Identification (based on NFPA-704 M Rating System): Health 3, Flammability 0, Reactivity 0. Soluble in water.
Chemical properties
WHITE FINE CRYSTALLINE POWDER
Chemical properties
Mercuric cyanide is an odorless, white crystalline solid; turns gray to dark brown when exposed to light
The Uses of MERCURIC CYANIDE
Mercuric cyanide finds veterinary application as a topical antiseptic for cats and other animals.
The Uses of MERCURIC CYANIDE
Medicine (antiseptic), germicidal soaps, manufacturing cyanogen gas, photography.
Definition
ChEBI: Mercury dicyanide is a mercury coordination entity.
General Description
Odorless tetragonal crystals or white powder. Toxic by inhalation (dust, and the hydrogen cyanide from decomposition) and by ingestion. Toxic oxides of nitrogen are produced in fires. It is used in medicine, germicidal soaps, photography, and in making cyanogen gas.
Air & Water Reactions
Soluble in water. Gradually decomposed by water to give off hydrogen cyanide, a flammable poison gas.
Reactivity Profile
MERCURIC CYANIDE is rapidly decomposed by acids to give off hydrogen cyanide, a flammable poison gas. Decomposed in the light. May tend to explosive instability. Capable of violent reaction with oxidizing agents. Fusion with metal chlorates, perchlorates, nitrates or nitrites can cause a violent explosion [Bretherick 1979. p. 101].
Hazard
Toxic by ingestion, inhalation, and skin absorption.
Health Hazard
Symptoms of both cyanide and mercury intoxication can occur. Acute poisoning has resulted from inhaling dust concentrations of 1.2-8.5 mg/m 3 of air; symptoms include tightness and pain in chest, coughing, and difficul ty in breathing; cyanide poisoning can cause anxiety, confusion, dizziness, and shortness of breath, with possible unconsciousness, convulsions, and paralysis; breath may smell like bitter almonds. Ingestion causes necrosis, pain, vomiting, an d severe purging, plus the above symptoms. Contact with eyes causes ulceration of conjunctiva and cornea. Contact with skin causes irritation and possible dermatitis; systemic poisoning can occur by absorption through skin.
Health Hazard
Mercuric cyanide is a highly poisonous compound. Its components, mercury(II) and the cyanide ions, are both highly toxic. Its toxicity, however, is lower than that of sodium and potassium cyanides.
Acute toxic symptoms from oral intake of this compound in humans are hypermotility, diarrhea, nausea or vomiting, and injury to kidney and bladder. Toxic symptoms may be manifested in humans from consuming 15–20 g of this compound. Lower doses may produce somnolence. An intraperitoneal dosage of 7.5 mg/kg was fatal to rats.
LD50 value, oral (mice): 7.5 mg/kg.
Fire Hazard
Special Hazards of Combustion Products: Fumes from fire may contain toxic mercury and hydrogen cyanide.
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion, subcutaneous, intravenous, and intraperitoneal routes. Human systemic effects by ingestion: nausea or vomiting, hypermotility, dlarrhea, kidney changes, somnolence. Hydrolyzes to toxic fumes. A frictionand impact-sensitive explosive. It may initiate detonation of liquid hydrogen cyanide. Incompatible with fluorine, magnesium, sodium nitrite. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of Hg, NOx, and CN-. See also CYANIDE and MERCURY COMPOUNDS.
Potential Exposure
Mercuric cyanide is used in medicine, germicidal soaps, photography and in making cyanogen gas
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove any contact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least 15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts the skin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediately with soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure, begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR if heart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medical facility. When this chemical has been swallowed, get medical attention. Give large quantities of water and induce vomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit. Antidotes and special procedures for medical personnel: The drug NAP (n-acetyl penicillamine) has been used to treat mercury poisoning, with mixed success. Note to physician: For severe poisoning BAL [British AntiLewisite, dimercaprol, dithiopropanol (C3H8OS2)] has been used to treat toxic symptoms of certain heavy metals poisoning including mercury. Although BAL is reported to have a large margin of safety, caution must be exercised, because toxic effects may be caused by excessive dosage. Most can be prevented by premedication with 1-ephedrine sulfate (CAS: 134-72-5).
storage
Color Code—Blue: Health Hazard/Poison: Store in a secure poison location. Prior to working with this chemical you should be trained on its proper handling and storage. Mercuric cyanide must be stored to avoid contact with fluorine, magnesium, and sodium nitrite, since violent reactions occur. Mercuric cyanide should not contact acid or heat because it will release flammable hydrogen cyanide gas. Store in tightly closed containers in a cool, well-ventilated area away from light. Protect containers from physical damage.
Shipping
UN1636 Mercuric cyanide, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials
Purification Methods
Crystallise it from water. The solubility in H2O is 8% at ~20o and 33% at ~100o; in EtOH it is 8% at ~20o and in MeOH it is 25% at ~20o. [Blitz Z Anorg Allgem Chem 170 161 1928.] POISONOUS.
Incompatibilities
Violent reaction with fluorine, magnesium, sodium nitrite, acids. Heating or contact with acid releases toxic mercury and flammable hydrogen cyanide gas. Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides
Waste Disposal
Return to supplier for mercury recovery and deactivation.
Properties of MERCURIC CYANIDE
| Melting point: | 46.85°C |
| Density | 3.996 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| storage temp. | Poison room |
| solubility | Methanol (Slightly), THF (Soluble) |
| form | Fine Crystalline Powder |
| color | White |
| Specific Gravity | 3.996 |
| Water Solubility | g/100g solution H2O: 6.31 (0°C), 10.06±0.06 (25°C), 35.05 (101.1°C) [KRU93]; 1g dissolves in 13mL alcohol, 4mL methanol; slightly soluble ether; slowly soluble glycerol [MER06] |
| Merck | 13,5903 |
| BRN | 4652800 |
| Exposure limits | TLV-TWA 0.1 mg Hg/m3 (skin) (ACGIH). |
| Stability: | Acid Sensitive, Light Sensitive |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 592-04-1(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Mercuric cyanide (592-04-1) |
Safety information for MERCURIC CYANIDE
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H373:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P403+P233:Store in a well-ventilated place. Keep container tightly closed. |
Computed Descriptors for MERCURIC CYANIDE
New Products
4-Fluorophenylacetic acid 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate (6-METHYL-[1,3]DITHIOLO[4,5-b]QUINOXALIN-2-ONE INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 42831-50-5 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 98%View Details
42831-50-5 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 98%View Details
42831-50-5 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1