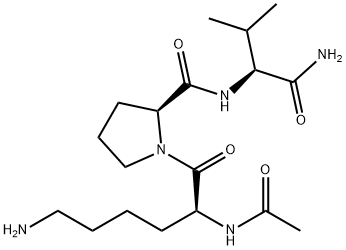
Melanotan-1
- CAS NO.:75921-69-6
- Empirical Formula: C78H111N21O19
- Molecular Weight: 1646.85
- MDL number: MFCD00151715
- EINECS: 211-519-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-26 17:28:21
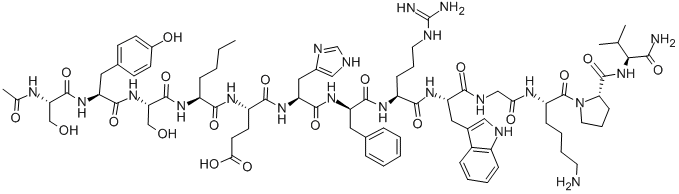
What is Melanotan-1 ?
Absorption
Afamelanotide is administered as a subcutaneous implant that slowly elutes active drug. Most of the dose is released within the first 48 hours, with >90% released by day 5. Plasma levels of afamelanotide decrease slowly over the course of several days following administration - by day 10, plasma levels were undetectable in most clinical trial subjects. Following administration of a single subcutaneous implant, the median Tmax was 36 hours, the mean Cmax was 3.7 ± 1.3 ng/mL, and the mean AUC0-∞ was 138.9 ± 42.6 hr.ng/mL.
Toxicity
Data regarding symptoms or treatment of afamelanotide overdose are currently unavailable.
The Uses of Melanotan-1
[Nle4, D-Phe7]-α-Melanocyte Stimulating Hormone trifluoroacetate salt has been used to detect its effect on O2 consumption and CO2 production in C57BL/6 mice.1It is also used to determine its effect on leptin secretion in the primary cultures of differentiated adipocytes.
Indications
Afamelanotide is indicated for the prevention of phototoxicity in adult patients with erythropoietic protoporphyria (EPP).
Background
Afamelanotide is a first-in-class, synthetic, 13-amino acid peptide analogue of the endogenous alpha melanocyte-stimulating hormone (α-MSH). It differs structurally from its endogenous counterpart by only two amino acids - these structural differences improve biological efficacy by imparting a greater affinity for its target and a longer biological half-life. Afamelanotide is currently the only approved drug therapy used in the management of erythropoietic protoporphyria, having received approval in the EU in December 2014 and subsequent FDA approval in October 2019. Despite its relatively recent approval, afamelanotide has been available for use as an orphan drug in both the US and EU since 2008.
Definition
ChEBI: Afamelanotide is a polypeptide comprising of 13 amino acids which is an analogue of alpha-melanocyte stimulating hormone. It is approved as a dermatologic drug for the prevention of phototoxicity in adult patients with erythropoietic protoporphyria. It has a role as a dermatologic drug.
Origin
Melanotan 1, an alpha MSH analog (Nle4DPhe7-Melanocyte-Stimulating Hormone), is a potent melanocortin developed in the 1980s. Melanotan 2 is a shorter cyclic variant of Melanotan 1 produced in the 1990s. Melanotan 2 was found to increase skin pigmentation at lower cumulative doses than Melanotan 1. However, in clinical trials it was found to have more side effects including nausea somnolence and penile erections[1].
References
[1] Robert T Dorr. “Effects of a superpotent melanotropic peptide in combination with solar UV radiation on tanning of the skin in human volunteers.” Archives of dermatology 140 7 (2004): 827–35.
General Description
[Nle4, D-Phe7]-α-melanocyte stimulating hormone is a potent analogue of α;-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (α -MSH). αMSH is a tridecapeptide, mostly produced by the cells in the brain, pituitary and in circulation.
Biochem/physiol Actions
[Nle4, D-Phe7]-α-melanocyte stimulating hormone is 100 times more potent than α-MSH in stimulating melanoma tyrosinase, which is a rate limiting enzyme in melanin biosynthesis and is 26 times as potent as α-MSH in S91adenylate cyclase assay. α –MSH has an essential role to play in melanin production in animals. It also regulates development of several skin diseases, including cutaneous inflammation and hyper-proliferative skin diseases.
Pharmacokinetics
Afamelanotide increases the production of eumelanin, an endogenous photoprotective agent, to attenuate UV-induced skin damage in patients with a condition that predisposes them to phototoxicity. It has a relatively long duration of therapeutic effect despite its short half-life due to its ability to increase melanosome density and therefore skin pigmentation. As afamelanotide may darken pre-existing skin pigmentary lesions, patients receiving afamelanotide should undergo a full body skin examination every 6 months to monitor for progression or worsening of any skin abnormalities. Standard sun safety measures should continue to be employed during afamelanotide therapy.
Side Effects
The TGA has previously warned consumers against the use of Melanotan-I and Melanotan-II for tanning and weight loss. Side-effects include darkened skin, increased moles and freckles, nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, flushing of the face, involuntary stretching and yawning, and spontaneous erections.
Metabolism
Details regarding the metabolism and metabolites of afamelanotide are sparse. The drug is more resistant to degradation by serum and proteolytic enzymes than its endogenous counterpart, α-MSH, but presumably undergoes a relatively rapid hydrolysis given its short half-life. It has been suggested that afamelanotide may be degraded in the same manner as α-MSH but at a much slower rate, or may instead be degraded intracellularly via endocytosis or non-specific proteases.
storage
Store at -20°C
Properties of Melanotan-1
| Density | 1.46±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| RTECS | OS1830200 |
| storage temp. | −20°C |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 4.43±0.10(Predicted) |
| color | White to off-white |
| Water Solubility | Soluble to 0.60 mg/ml in sterile water |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 75921-69-6(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Melanotan-1
Computed Descriptors for Melanotan-1
| InChIKey | UAHFGYDRQSXQEB-LEBBXHLNSA-N |
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate (S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 4-Hydrazinobenzoic acid 3,4-Dibenzyloxybenzaldehyde Electrolytic Iron Powder 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 4-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 3-(Hydroxymethyl)benzoate N-Boc-2-chloroethylamine 1-Bromo-2-methoxy-3-nitrobenzene N-Methyl-3-cyclopenten-1-amine 2-Bromo-3-hydroxybenzaldehyde 1H-indazole-5-carboxamideRelated products of tetrahydrofuran




You may like
-
![[Nle4, D-Phe7]-α-Melanocyte Stimulating Hormone trifluoroacetate salt CAS 75921-69-6](https://img.chemicalbook.in//Content/image/CP5.jpg) [Nle4, D-Phe7]-α-Melanocyte Stimulating Hormone trifluoroacetate salt CAS 75921-69-6View Details
[Nle4, D-Phe7]-α-Melanocyte Stimulating Hormone trifluoroacetate salt CAS 75921-69-6View Details
75921-69-6 -
 7441-43-2 98%View Details
7441-43-2 98%View Details
7441-43-2 -
 1260741-78-3 6-Bromo-3-iodo-1-methyl-1H-indazole 98%View Details
1260741-78-3 6-Bromo-3-iodo-1-methyl-1H-indazole 98%View Details
1260741-78-3 -
 4-bromo-3,5-dimethylbenzenesulfonyl chloride 1581266-79-6 98%View Details
4-bromo-3,5-dimethylbenzenesulfonyl chloride 1581266-79-6 98%View Details
1581266-79-6 -
 2490430-37-8 98%View Details
2490430-37-8 98%View Details
2490430-37-8 -
 N-(5-Amino-2-methylphenyl)acetamide 5434-30-0 98%View Details
N-(5-Amino-2-methylphenyl)acetamide 5434-30-0 98%View Details
5434-30-0 -
 124371-59-1 98%View Details
124371-59-1 98%View Details
124371-59-1 -
 53857-52-2 98%View Details
53857-52-2 98%View Details
53857-52-2