Maytansine
- CAS NO.:35846-53-8
- Empirical Formula: C34H46ClN3O10
- Molecular Weight: 692.2
- MDL number: MFCD28127038
- EINECS: 252-754-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 23:02:33
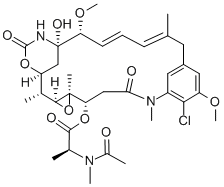
What is Maytansine?
Description
This novel ansa macrolide alkaloid occurs in a number of May tan us species. The structure given has been elucidated from chemical and spectroscopic data. In low doses (25-50 mcg/kg), maytansine prolonged the survival of mice bearing vincristine-sensitive P388 leukemia but not those bearing vincristine-resistant tumour lines. In vitro, it suppressed the growth of U21 0, LSl78Y and P388 leukemia cells with ED50 of 2 X 10-9 , 1.5 X 10-9 and 6 X 10-10M respectively and elevated the mitotic index in L 121 0 cells. From labelling studies it was shown that the alkaloid inhibited DNA formation by P388 cells to a greater extent than RNA and protein synthesis. Maytensine did not inhibit RNA polymerase from Escherichia coli at levels as high as 1 X 10-4M.
The Uses of Maytansine
Antineoplastic.
Definition
ChEBI: An organic heterotetracyclic compound and 19-membered macrocyclic lactam antibiotic originally isolated from the Ethiopian shrub Maytenus serrata but also found in other Maytenus species. It exhibits cytotoxicity against many tumo r cell lines.
Biological Functions
Maytansine is a potent microtubule-targeted compound that inhibits proliferation of cells at mitosis. Antibody-maytansinoid conjugates consisting of maytansinoids (DM1 and DM4) attached to tumor-specific antibodies have shown promising clinical results The microtubule-targeting maytansinoids accumulate in cells and induce mitotic arrest at 250- to 1000-fold lower concentrations than those required for their association with tubulin or microtubules.
Toxicology
Maytansine, an ansa macrolide isolated from African plants of the genera Maytenus and Putterlickia was first described almost two decades ago. It had been reported to be active against several forms of cancer, but a later phase II evaluation suggested no major role for this drug in tumor treatment. Although the toxic side effects were moderate, the antitumor activity was also not impressive.
Maytansine binds to tubulin rapidly and reversibly. Competitive inhibition of binding between maytansine and the vinca alkaloids has been observed, suggesting that maytansine must occupy at least one of vinblastine's binding sites on the tubulin molecule. The number of the maytansine binding sites is not known. Assembly of MT is inhibited at maytansine concentrations below 1μM. This suggests a substoichiometric poisoning mechanism as in the cases of colchicine, vinblastine and podophyllotoxin, but the details are not known. In contrast to many other MT-interacting toxins,maytansine does not promote the formation of aberrant tubulin polymers, even at millimolar concentrations. In fact, low concentrations of maytansine even inhibit vinblastine-induced formation of aberrant polymers.
Mode of action
Maytansine is a new drug undergoing clinical investigation. It has functional similarities to vincristine.
Maytansine, an ansa macrolide of considerable antitumor potency, is obtained from plants of the genera Maytenus and Putterlickia. Maytansine binds rapidly and reversibly to tubulin, and is a competitive inhibitor of vinca alkaloid binding. Colchicine has no effect on maytansine binding. Maytansine and the vinca alkaloids have comparable binding constants, share a common binding site, although an additional site or attachment position specific for maytansine appears to be present. Maytansine may inhibit tubulin polymerization by interfering with certain critical-SH groups necessary for assembly. Like the vincas, it inhibits assembly substroichiometric. Unlike the vincas, as well as colchicine and podophyllotoxin, maytansine appears capable of inducing rapid microtubule disassembly in vitro when added to microtubules at end state. Furthermore, maytansine enhances alkylation by iodoacetamide,an effect opposite to that obtained with V BL, suggesting that maytansine may have different conformation effects on tubulin.
References
Walpert-Defillipes et al., Biochem. Pharmacol., 24, 751 (1975)
Properties of Maytansine
| Melting point: | 183.5-184℃ |
| Boiling point: | 895.1±65.0 °C(Predicted) |
| alpha | D26 -145° (c = 0.055 in chloroform) |
| Density | 1.1049 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.6000 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | Store at -20°C |
| solubility | DMF: 1 mg/ml; DMSO: 10 mg/ml; Ethanol: 2 mg/ml; PBS (pH 7.2): insol |
| form | A solid |
| pka | 9.82±0.70(Predicted) |
| Stability: | Light Sensitive |
Safety information for Maytansine
Computed Descriptors for Maytansine
| InChIKey | WKPWGQKGSOKKOO-YHBUUTGONA-N |
New Products
4-Fluorophenylacetic acid 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate (6-METHYL-[1,3]DITHIOLO[4,5-b]QUINOXALIN-2-ONE INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
![3-[2-(dimethylamino)ethoxy]-N,N-dimethylpropylamine](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/34745-96-5.gif)
You may like
-
 Maytansine CAS 35846-53-8View Details
Maytansine CAS 35846-53-8View Details
35846-53-8 -
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1