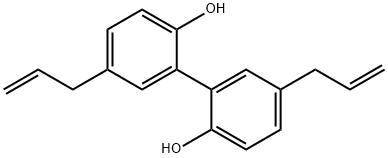
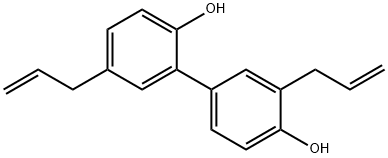
Magnolol
Synonym(s):2,2′-Bichavicol;5,5′-Diallyl-2,2′-biphenyldiol
- CAS NO.:528-43-8
- Empirical Formula: C18H18O2
- Molecular Weight: 266.33
- MDL number: MFCD00016658
- EINECS: 610-903-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 23:02:33
What is Magnolol?
Description
Magnolol is a bioactive compound isolated from the bark of M. officinalis that has been used in Asian traditional medicine for the treatment of anxiety, sleep disorders, and allergic diseases. Magnolol can activate cannabinoid (CB) receptors, behaving as a partial agonist with selectivity for the peripheral CB2 subtype (EC50 = 3.28 μM; Ki = 1.44 μM) versus central CB1 (EC50 = 18.3 μM; Ki = 3.15 μM).
Chemical properties
White or off-white powder
The Uses of Magnolol
Magnolol is the bioactive phytochemicals found in Magnolia officinalis (1). Magnolol has been used to treat anxiety, cough, headache and allergies (2). It also inhibits tumor necrosis factor-a-*induced ICAM-1 expression in human lung epithelial cells.
What are the applications of Application
Magnolol is an inhibitor of NO and TNF-α production
Definition
ChEBI: Magnolol is a member of biphenyls.
Hazard
Moderately toxic by ingestion.
Biological Activity
Magnolol, a natural lignan isolated from the stem bark of Magnolia officinalis, is a dual agonist of both RXRα and PPARγ, with EC50 values of 10.4 μM and 17.7 μM, respectively.
Mechanism of action
Magnolol (5,5’-diallyl-2,2’-dihydroxybiphenyl) is a polyphenolic binaphthalene compound and a structural isomer of honokiol. Both magnolol and honokiol are isolated from the stem bark of a traditional Chinese herbal medicine Magnolia officinalis, which has been used for management of nervous disturbance, abdominal distention or disorders, gastrointestinal food stagnancy, and coughing and dyspnea. Magnolol has showed a wide spectrum of beneficial activities, including anti-inflammation, antimicroorganism, antioxidation, antiangiogenesis, anticancer, neuroprotection, cardiovascular protection, and lipolysis activities.
Safety Profile
Moderately toxic by ingestion.When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke andirritating vapors.
in vitro
Magnolol is a bioactive lignin found in the bark of the Houpu magnolia (Magnolia officinalis) which shows antifungal properties. Magnolol preferentially increases (3)H-muscimol binding to hippocampus compared to cortex and cerebellum in vitro. Magnolol has a more potent enhancing effect on GABAA receptor alpha2 subunit. Magnolol shows significant inhibitory activities against Trichophyton mentagrophytes, Microsporium gypseum, Epidermophyton floccosum, Aspergillus niger, Cryptococcus neoformans, and Candida albicans with minimum inhibitory concentrations (MIC) in a range of 25-100 μg/ml.
in vivo
Magnolol (5-15 mg/kg, p.o.) significantly attenuates the phenotypic severity of dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced colitis in mice. Magnolol (10, 15 mg/kg, p.o.) attenuates histopathological changes and myeloperoxidase activity in the colon of DSS-treated mice, decreases DSS-induced high levels of proinflammatory cytokines TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6 in the colonic tissues. Magnolol (10 mg/kg, p.o.) also reverses abnormality of serum metabolome, and regulates tryptophan metabolic pathway in mice.
Properties of Magnolol
| Melting point: | 101.5-102° |
| Boiling point: | 180°C/1mmHg(lit.) |
| Density | 1.107±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| FEMA | 4559 | MAGNOLOL |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,2-8°C |
| solubility | ethanol: soluble1mg/mL |
| form | neat |
| pka | 9.49±0.43(Predicted) |
| form | Solid |
| color | White to Almost white |
| Odor | bitter |
| λmax | 292nm(EtOH)(lit.) |
| Merck | 14,5697 |
| JECFA Number | 2023 |
| Stability: | Light Sensitive |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 528-43-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Magnolol
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H318:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation H411:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. |
Computed Descriptors for Magnolol
New Products
4-Fluorophenylacetic acid 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate (6-METHYL-[1,3]DITHIOLO[4,5-b]QUINOXALIN-2-ONE INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Magnolol 98% CAS 528-43-8View Details
Magnolol 98% CAS 528-43-8View Details
528-43-8 -
 Magnolol CAS 528-43-8View Details
Magnolol CAS 528-43-8View Details
528-43-8 -
 Magnolol 98% (HPLC) CAS 528-43-8View Details
Magnolol 98% (HPLC) CAS 528-43-8View Details
528-43-8 -
 Magnolol CAS 528-43-8View Details
Magnolol CAS 528-43-8View Details
528-43-8 -
 Magnolol CAS 528-43-8View Details
Magnolol CAS 528-43-8View Details
528-43-8 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1