Honokiol
Synonym(s):5,3ʹ-Diallyl-2,4ʹ-dihydroxydiphenyl, VEGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor XIX, VEGFR2 Kinase Inhibitor XV;5,3′-Diallyl-2,4′-dihydroxybiphenyl;Honokiol - CAS 35354-74-6 - Calbiochem;NSC 293100
- CAS NO.:35354-74-6
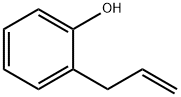
- Empirical Formula: C18H18O2
- Molecular Weight: 266.33
- MDL number: MFCD00016674
- EINECS: 609-119-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 23:02:33
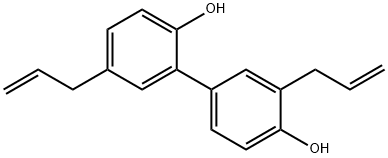
What is Honokiol?
Description
Magnolol is derived from the root bark and branch bark of magnolia or Magnolia officinalis. Magnolia officinalis was first written in the《ben jing》, it prefers cool and humid climate and well-drained acid soil. Cortex magnoliae officinalis (hou po) is mainly produced in Sichuan (Wan quan, Shizhu, Guanxian), Hubei (Shien,Yichang, Lichuan), Zhejiang (Longquan, Anhui), and other places. It is also distributed in Fujian, Jiangxi, Hunan, Guangxi, Yunnan, Guizhou, Shanxi, Gansu, and other places. Cortex magnoliae officinalis from Sichuan and Hubei is called “chuan pu,” with better quality, while in Zhejiang, it is called “warm park,” with a larger output.
Physical properties
Appearance: white fine powder. Solubility: practically insoluble in water; very soluble in benzene, ethyl ether, chloroform, and acetone. Melting point: magnolol is 102 °C. Honokiol is 87.5 °C.
History
In 1930, magnolol was first isolated from the bark of Cortex magnoliae officinalis
in China by Japanese Sugii, and it was also isolated from Cortex magnoliae officinalis
in Japan. In 1973, magnolol and its isomers honokiol were isolated from Cortex magnoliae officinalis in China and Japan by Japanese Fujita.
The drug research and development of magnolol and honokiol remain in pharmacological activity and preclinical research. Kyung Hee University from Korea declared a preclinical study in 2003, in which allergy, anxiety, angina, and heart failure are indications for honokiol.
The Uses of Honokiol
Honokiol is a small-molecule polyphenol isolated from the genus Magnolia. Recent studies show that Honokiol displays antiangiogenic, antiinflammatory, and antitumor properties in preclinical models, w ithout appreciable toxicity. Honokiol has been shown to inhibit the bone metastatic growth of human prostate cancer cells.
The Uses of Honokiol
Honokiol has been used:
- to study its effects on plasmid hSirt3102-399 deacetylation activity
- as an antioxidant to study its cytoprotective role in human ovarian cancer cells (SKOV-3) and Chinese hamster ovary cells (CHOK1)
- to explore its effects on oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction via a sirt3-dependent manner
- for intracerebroventricular (ICV) cannulation
What are the applications of Application
Honokiol is a biphenyl neolignan from Magnolia extract that inhibits phosphorylation of Akt, p44/42 MAPK, and src
Indications
These compounds are recorded in the British Pharmacopoeia (2017) and European Pharmacopoeia (8.7th ed.). They are mainly used as antibacterial and antifungal agents.
Definition
ChEBI: Honokiol is a member of biphenyls.
General Description
Honokiol exhibits analgesic, antithrombotic, antispasmodic, antidepressant, antimicrobial and neuroprotective effects. It regulates gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) A receptors. Honokiol is associated with an increased risk of bleeding. It prevents platelet aggregation, protects myocardium from ischemic damage and inhibits ventricular arrhythmia.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Honokiol is a natural biphenyl neolignan from magnolia extract. It is antiangiogenic, antitumor, and anxiolytic.
Pharmacology
Magnolol and honokiol have the pharmacological effects of prolonging central muscle relaxation, inhibition of the central nervous, anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, antimicrobial, antiulcer, antioxidant, antitumor, hormone regulation, and antidiabetes .
storage
+4°C
Properties of Honokiol
| Melting point: | 86℃ |
| Boiling point: | 400.1±40.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.107±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | DMSO: 36 mg/mL |
| form | powder |
| pka | 9.89±0.48(Predicted) |
| color | White to Off-White |
| Merck | 14,4742 |
| Stability: | Light Sensitive |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 35354-74-6(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Honokiol
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H318:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H411:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P391:Collect spillage. Hazardous to the aquatic environment P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for Honokiol
| InChIKey | FVYXIJYOAGAUQK-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate (S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 4-Hydrazinobenzoic acid 3,4-Dibenzyloxybenzaldehyde Electrolytic Iron Powder 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 4-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 3-(Hydroxymethyl)benzoate N-Boc-2-chloroethylamine 1-Bromo-2-methoxy-3-nitrobenzene N-Methyl-3-cyclopenten-1-amine 2-Bromo-3-hydroxybenzaldehyde 1H-indazole-5-carboxamideRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Honokiol CAS 35354-74-6View Details
Honokiol CAS 35354-74-6View Details
35354-74-6 -
![Honokiol [Optimized for Cell Culture] CAS 35354-74-6](https://img.chemicalbook.in//Content/image/CP5.jpg) Honokiol [Optimized for Cell Culture] CAS 35354-74-6View Details
Honokiol [Optimized for Cell Culture] CAS 35354-74-6View Details
35354-74-6 -
 Honokiol 98% (GC) CAS 35354-74-6View Details
Honokiol 98% (GC) CAS 35354-74-6View Details
35354-74-6 -
 Honokiol 98% CAS 35354-74-6View Details
Honokiol 98% CAS 35354-74-6View Details
35354-74-6 -
 Honokiol CAS 35354-74-6View Details
Honokiol CAS 35354-74-6View Details
35354-74-6 -
 Honokiol CAS 35354-74-6View Details
Honokiol CAS 35354-74-6View Details
35354-74-6 -
 Honokiol CAS 35354-74-6View Details
Honokiol CAS 35354-74-6View Details
35354-74-6 -
 2490430-37-8 98%View Details
2490430-37-8 98%View Details
2490430-37-8