Magnesium Bisglycinate
- CAS NO.:14783-68-7
- Empirical Formula: C4H8MgN2O4
- Molecular Weight: 172.42232
- MDL number: MFCD00274170
- EINECS: 238-852-2
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:49:29
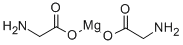
What is Magnesium Bisglycinate?
Description
Magnesium Bisglycinate is a great-tasting powder that can be mixed with water, juice, or with another powdered supplement.
Magnesium bisglycinate is an amino acid chelate that binds magnesium to glycine, aiming to reproduce the form in which magnesium is found naturally in food. Studies from the USA suggest good magnesium availability with this chelated form, which also doesn't appear to have any particular drawbacks.
The Uses of Magnesium Bisglycinate
Magnesium Glycinate Purified Powder can be used as a dietary ingredient and as a nutrient. Magnesium plays a vital role in regulating the neuromuscular activity of the heart, converts blood sugar to energy and is necessary for proper calcium and Vitamin C metabolism.
Magnesium 2-aminoacetate (Magnesium glycinate) is essential for DNA and RNA synthesis, cellular repair, and maintaining the antioxidant status of the cell.
Background
Magnesium glycinate is a magnesium salt of glycine that is available as dietary supplements as a source of magnesium. It is used in the treatment of magnesium deficiency.
Benefits
Health benefits of Magnesium Bisglycinate include:
relieve anxiety
promote bone health
manage blood sugar in people with diabetes and may lower the risk of developing type 2 diabetes
maintain regular heart rhythms
reduce symptoms of premenstrual syndrome (PMS)
amplify exercise performanceTrusted Source
reduce pain
Biological Functions
Magnesium glycinate (Magnesium bisglycinate), the magnesium salt of glycine, is a nutrient supplement. Magnesium glycinate has satisfactory physico-chemical properties and bioactivities. Metal glycinate chelates are formed by glycine and metal compounds through chemical reactions. Magnesium is an essential mineral that plays a critical role in the human body. Magnesium takes part in the process of energy metabolism and assists the maintenance of normal muscle function[1][2].
Calcium glycinate, magnesium glycinate and zinc glycinate are kinds of new-type and ideal nutrient supplements, which have satisfactory physico-chemical properties and bioactivities. They are important for prophylaxis and treat metal deficiency[1].
[1]. Kaewkarn Phuangsombut, et al. Nondestructive classification of mung bean seeds by single kernel near-infrared spectroscopy.
[2]. Zhang Y, et al. Can Magnesium Enhance Exercise Performance?. Nutrients. 2017;9(9):946. Published 2017 Aug 28.
Side Effects
Stomach upset and diarrhea may occur. A very serious allergic reaction to this drug is rare. However, get medical help right away if you notice any symptoms of a serious allergic reaction, including: rash, itching/swelling (especially of the face/tongue/throat), severe dizziness, trouble breathing.
Metabolism
Not Available
Advantages
Magnesium glycinate is formed by combining elemental magnesium with the amino acid glycine. This form of magnesium is highly bioavailable, meaning the magnesium is easily absorbed through the small intestine.
Properties of Magnesium Bisglycinate
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,Room Temperature |
| solubility | DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | Solid |
| color | White to Off-White |
| Water Solubility | Water: 2 mg/mL (11.60 mM) |
| InChI | InChI=1S/2C2H5NO2.Mg/c2*3-1-2(4)5;/h2*1,3H2,(H,4,5);/q;;+2/p-2 |
Safety information for Magnesium Bisglycinate
Computed Descriptors for Magnesium Bisglycinate
| InChIKey | AACACXATQSKRQG-UHFFFAOYSA-L |
| SMILES | C(=O)(CN)O[Mg]OC(=O)CN |
Magnesium Bisglycinate manufacturer
Nandana Bioscience (OPC) Private Limited
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Magnesium glycinate 97% CAS 14783-68-7View Details
Magnesium glycinate 97% CAS 14783-68-7View Details
14783-68-7 -
 Magnesium glycinate 98.00% CAS 14783-68-7View Details
Magnesium glycinate 98.00% CAS 14783-68-7View Details
14783-68-7 -
 Magnesium Bisglycinate (Mg 20%)View Details
Magnesium Bisglycinate (Mg 20%)View Details
14783-68-7 -
 Magnesium Glycinate 400 mg tablets Veggie Capsules, IPView Details
Magnesium Glycinate 400 mg tablets Veggie Capsules, IPView Details
14783-68-7 -
 Magnesium Bisglycinate, PrescriptionView Details
Magnesium Bisglycinate, PrescriptionView Details
14783-68-7 -
 Magnesium Glycinate 400mg CapsulesView Details
Magnesium Glycinate 400mg CapsulesView Details
14783-68-7 -
 Magnesium Glycinate 550mgView Details
Magnesium Glycinate 550mgView Details
14783-68-7 -
 14783-68-7 Magnessium Bis glycinate 98%View Details
14783-68-7 Magnessium Bis glycinate 98%View Details
14783-68-7
