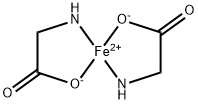
Copper glycinate
- CAS NO.:13479-54-4
- Empirical Formula: C4H8CuN2O4
- Molecular Weight: 211.66
- MDL number: MFCD00065114
- EINECS: 236-783-2
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:07:02
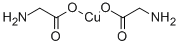
What is Copper glycinate?
Chemical properties
Blue, triboluminescent crystals. Slightly soluble in water and alcohol; insoluble in hydrocarbons, ethers, and ketones.
The Uses of Copper glycinate
Catalyst for rapid biochemical assimilation of iron, electroplating baths, photometric analysis, feed additive.
Benefits
Copper glycinate has the following benefits:
Helps activate enzymes important to energy metabolism
Assists in the formation of hemoglobin and red blood cells
Supports protein metabolism and phospholipid synthesis
Available in copper citrate with enhanced bioavailability and copper glycinate forms
Made with high-quality vegan ingredients backed by verifiable science
General Description
Occurs as monohydrate and as dihydrate. The monohydrate is long deep-blue needles. The dihydrate is light blue powdery crystals.
Air & Water Reactions
Water soluble.
Reactivity Profile
Salts, basic, such as Copper glycinate, are generally soluble in water. The resulting solutions contain moderate concentrations of hydroxide ions and have pH's greater than 7.0. They react as bases to neutralize acids. These neutralizations generate heat, but less or far less than is generated by neutralization of the bases in reactivity group 10 (Bases) and the neutralization of amines. They usually do not react as either oxidizing agents or reducing agents but such behavior is not impossible.
Health Hazard
INHALATION: Inhalation of dust may cause nasal congestion. EYES: Conjunctivitis and edema of eyelids. SKIN: Irritation. INGESTION: Vomiting caused by local irritant and astringent action of ionic copper on stomach and bowel.
Flammability and Explosibility
Not classified
Side Effects
Too much copper can cause nausea, vomiting, stomach pain, headache, dizziness, weakness, diarrhea, and a metallic taste in the mouth. Copper toxicity is rare but can cause heart problems, jaundice, coma, even death. DO NOT use copper supplements if you have diarrhea.
Properties of Copper glycinate
| Melting point: | chars 213℃ [MER06] |
| Boiling point: | decomposes with evolution of gas at 228℃ [MER06] |
| Density | 762[at 20℃] |
| vapor pressure | 0Pa at 25℃ |
| storage temp. | under inert gas (nitrogen or Argon) at 2–8 °C |
| Water Solubility | soluble H2O, slightly soluble alcohol [MER06] |
| InChI | InChI=1S/2C2H5NO2.Cu/c2*3-1-2(4)5;/h2*1,3H2,(H,4,5);/q;;+2/p-2 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 13479-54-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Copper, bis(glycinato-.kappa.N,.kappa.O)- (13479-54-4) |
Safety information for Copper glycinate
Computed Descriptors for Copper glycinate
| InChIKey | VVYPIVJZLVJPGU-UHFFFAOYSA-L |
| SMILES | C(CN)(=O)O[Cu]OC(CN)=O |
Copper glycinate manufacturer
ShanPar Industries Pvt Ltd
West Bengal Chemical Industries Ltd.
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid DIETHYL AMINOMALONATE HYDROCHLORIDE 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 13479-54-4 Copper Glycinate 99%View Details
13479-54-4 Copper Glycinate 99%View Details
13479-54-4 -
 13479-54-4 98%View Details
13479-54-4 98%View Details
13479-54-4 -
 Copper Glycinate 98%View Details
Copper Glycinate 98%View Details
13479-54-4 -
 13479-54-4 99%View Details
13479-54-4 99%View Details
13479-54-4 -
 Copper glycinate 98% CAS 13479-54-4View Details
Copper glycinate 98% CAS 13479-54-4View Details
13479-54-4 -
 Bis (2-Aminoacetoxy) Copper 98.00% CAS 13479-54-4View Details
Bis (2-Aminoacetoxy) Copper 98.00% CAS 13479-54-4View Details
13479-54-4 -
 GLYCINE, CUPRIC SALT CAS 1091630-81-7View Details
GLYCINE, CUPRIC SALT CAS 1091630-81-7View Details
1091630-81-7 -
 733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8