LEAD(II) THIOCYANATE
Synonym(s):Lead sulfocyanide;Lead(II) rhodanide;Plumbous thiocyanate
- CAS NO.:592-87-0
- Empirical Formula: C2N2PbS2
- Molecular Weight: 323.36
- MDL number: MFCD00011155
- EINECS: 209-774-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 13:37:16
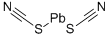
What is LEAD(II) THIOCYANATE?
Description
Lead thiocyanate is a white or light yellow,odorless, crystalline powder. Odorless. Molecularweight = 323.36; Specific gravity (H2O:1) = 3.82; Freezing/Melting point = 190℃(decomposes). Hazard Identification(based on NFPA-704 M Rating System): Health 3,Flammability 1, Reactivity 1. Slightly soluble in water;solubility = ,0.05%.
Chemical properties
White to yellow powder
Chemical properties
Leadthiocyanateisawhiteorlightyellow,odorless, crystalline powder. Odorless
The Uses of LEAD(II) THIOCYANATE
Reverse dyeing with aniline black; manufacture of safety matches and cartridges.
The Uses of LEAD(II) THIOCYANATE
Lead (II) thiocyanate can be used:
- To form a complex with Schiff-base lariat crown ether,?N,N′-bis(3-(salicylaldimino)benzyl)-4,13-diaza-18-crown-6.
- To investigate complexing and fluorescence properties of calixarene bearing two dansyl fluorophores grafted on a large pore mesoporous silica material.
- As a reagent in the 1,2-dithiocyanation of alkynes in the presence of (dichloroiodo)benzene.
- As a precursor to synthesize perovskite films for solar cell applications.
General Description
A white to yellow crystalline solid. Slightly soluble in water and denser than water. Primary hazard is threat to the environment. Immediate steps should be taken to limit spread to the environment. Used to make explosives, safety matches, and in dyeing.
Air & Water Reactions
Slightly soluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Nitric acid violently oxidized a thiocyanate solution [Bretherick 1979. p. 121]. Caution should be exercised in treating a thiocyanate with an oxidizing agent such as a peroxide or chlorate as such mixtures have been known to explode. May be thermally unstable. Special Hazards of Combustion Products: Irritating sulfur dioxide gas may form in fire [USCG, 1999].
Health Hazard
Early symptoms of lead intoxication via inhalation or ingestion are most commonly gastrointestinal disorders, colic, constipation, etc.; weakness, which may go on to paralysis, chiefly of the extensor muscles of the wrists and less often of the ankles, is noticeable in the most serious cases. Ingestion of a laarge amount causes local irritation of the alimentary tract; pain, leg cramps, muscle weakness, paresthesias, depression, coma, and death may follow in 1 or 2 days. Contact causes irritation of eyes and mild irritation of skin.
Fire Hazard
Special Hazards of Combustion Products: Irritating sulfur dioxide gas may form in fire.
Potential Exposure
An explosive, thermally unstable material. Used in making safety matches, primers for small arms cartridges; pyrotechnic devices; and in dyes.
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts theskin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediatelywith soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. Ifthis chemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure,begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR ifheart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medicalfacility. When this chemical has been swallowed, get medical attention. Give large quantities of water and inducevomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit.Note to physician: Administer saline cathartic and an enema.For relief of colic, administer antispasmodic (calciumgluconate, atropine, papaverine). Consider morphine sulfatefor severe pain.Whole blood lead levels, circulating plasma/erythrocytelead concentration ratio, urine ALA, and erythrocyte protoporphyrin fluorescent microscopy may all be useful in monitoring or assessing lead exposure. Chelating agents, such asedetate disodium calcium (Ca EDTA) and penicillamine(not penicillin), are generally useful in the therapy of acutelead intoxication.Antidotes and special procedures for lead: Persons with significant lead poisoning are sometimes treated with CaEDTA while hospitalized. This “chelating” drug causes arush of lead from the body organs into the blood and kidneys, and thus has its own hazards, and must be administered only by highly experienced medical personnel undercontrolled conditions and careful observation. Ca EDTA orsimilar drugs should never be used to prevent poisoningwhile exposure continues or without strict exposure control,as severe kidney damage can result.
storage
Color Code—Blue: Health Hazard/Poison: Storein a secure poison location. Prior to working with thischemical you should be trained on its proper handling andstorage. Store in tightly closed containers in a cool, wellventilated area away from hot water, heat, oxidizers, acids,acid fumes. Lead is regulated by an OSHA Standard1910.1025. All requirements of the standard must befollowed.
Shipping
UN2291 Lead compounds, soluble n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required
Incompatibilities
Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, and epoxides. Contact with acids or acid fumes caused decomposition with fumes of cyanide. Will decompose in hot water.
Properties of LEAD(II) THIOCYANATE
| Melting point: | 190 °C (dec.)(lit.) |
| Density | 3.82 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| solubility | cold water: soluble200 part(lit.) |
| form | white-yellow powder |
| Specific Gravity | 3.82 |
| color | white-yellow |
| Water Solubility | soluble ~200 parts cold, 50 parts boiling H2O [MER06]; g/L H2O: 0.0137 (18°) [KRU93] |
| Merck | 14,5426 |
| Solubility Product Constant (Ksp) | pKsp: 4.7 |
| BRN | 3687984 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 592-87-0(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Lead(II) thiocyanate (592-87-0) |
Safety information for LEAD(II) THIOCYANATE
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H373:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for LEAD(II) THIOCYANATE
LEAD(II) THIOCYANATE manufacturer
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid DIETHYL AMINOMALONATE HYDROCHLORIDE 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Lead thiocyanate, 98% CAS 592-87-0View Details
Lead thiocyanate, 98% CAS 592-87-0View Details
592-87-0 -
 LEAD THIOCYANATE Pure CAS 592-87-0View Details
LEAD THIOCYANATE Pure CAS 592-87-0View Details
592-87-0 -
 Lead(II) thiocyanate CAS 592-87-0View Details
Lead(II) thiocyanate CAS 592-87-0View Details
592-87-0 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 -
 733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8