Lead(II) carbonate basic
Synonym(s):Lead(II) carbonate
- CAS NO.:1319-46-6
- Empirical Formula: 2CO3.2Pb.H2O2Pb
- Molecular Weight: 775.63
- MDL number: MFCD00078155
- EINECS: 215-290-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-07-04 15:31:25
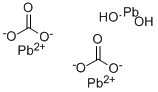
What is Lead(II) carbonate basic?
Description
Lead carbonate—white lead—is found as the mineral cerussite, which is mined and processed to produce lead and lead compounds. White lead has also been used as a pigment since antiquity; however, it has been phased out in many countries because of its toxicity. Although other white pigments exist (zinc oxide, titanium dioxide), many artists continue to use flake white, which is made with lead carbonate, because of its superior properties, such as fast drying and better durability.
Chemical properties
dense white powder
Chemical properties
Basic lead carbonate forms white hexagonal crystals; it decomposes when heated to 400 °C. It is insoluble in water and alcohol, slightly soluble in carbonated water, and soluble in nitric acid.
The Uses of Lead(II) carbonate basic
Lead(II) carbonate basic can be used as pigment in oil paints and water colors; in cements; for making putty and lead carbonate paper; in the processing of parchment.
The Uses of Lead(II) carbonate basic
Lead(II) carbonate is used in ceramic glaze and exterior paint.
Definition
Acid-soluble, heavy, white powder or crystalline substance, insoluble in water and alco- hol.
Preparation
Many commercial processes have been developed for manufacturing basic lead carbonate. These include: Thomson-Stewart process, Carter process, and Dutch process. The method of preparation involves treating lead with acetic acid vapors in the presence of carbon dioxide at 60°C. In the Thomson-Stewart process, finely divided lead monoxide or lead metal is mixed with water to give aqueous slurry, which is then mixed with acetic acid in the presence of air and carbon dioxide. All these processes are slow, taking weeks to obtain products of desired composition.
Basic lead carbonate also is precipitated by dissolving lead monoxide in lead(II) acetate solution, and treating the solution with carbon dioxide. It also is produced by electrolysis of sodium nitrate or sodium acetate using lead anode and then precipitating out the product by adding sodium carbonate.
.
Production Methods
Basic Lead Carbonate is produced by several methods, in which soluble lead acetate is treated with carbon dioxide. For example, in the Thompson-Stewart process, an aqueous slurry of finely divided lead metal or monoxide, or a mixture of both, is treated with acetic acid in the presence of air and carbon dioxide. High quality, very fine particle-size basic lead carbonate is produced, ranging in carbonate content from 62 to 65% (vs 68.9% PbCO3, theoretical).
Flammability and Explosibility
Non flammable
Properties of Lead(II) carbonate basic
| Melting point: | 400 °C (dec.)(lit.) |
| Density | 6,14 g/cm3 |
| solubility | insoluble in H2O, ethanol; soluble in acid solutions |
| form | Powder |
| color | White to off-white |
| Specific Gravity | 6.14 |
| Water Solubility | Insoluble |
| Solubility Product Constant (Ksp) | pKsp: 13.13 |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 0.05 mg/m3 NIOSH: IDLH 100 mg/m3; TWA 0.050 mg/m3 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, strong acids. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 1319-46-6(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Basic lead carbonate (1319-46-6) |
Safety information for Lead(II) carbonate basic
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H373:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Lead(II) carbonate basic
Lead(II) carbonate basic manufacturer
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

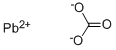
You may like
-
 LEAD CARBONATE 98%View Details
LEAD CARBONATE 98%View Details -
 Lead Carbonate 98%View Details
Lead Carbonate 98%View Details -
 Lead carbonate, basic 98%View Details
Lead carbonate, basic 98%View Details -
 Lead(II) Carbonate, Basic CAS 1319-46-6View Details
Lead(II) Carbonate, Basic CAS 1319-46-6View Details
1319-46-6 -
 Lead(II) carbonate, Basic CAS 1319-46-6View Details
Lead(II) carbonate, Basic CAS 1319-46-6View Details
1319-46-6 -
 Lead(II) carbonate, Basic CAS 1319-46-6View Details
Lead(II) carbonate, Basic CAS 1319-46-6View Details
1319-46-6 -
 Lead carbonate, basic CAS 1319-46-6View Details
Lead carbonate, basic CAS 1319-46-6View Details
1319-46-6 -
 Lead Carbonate Basic PureView Details
Lead Carbonate Basic PureView Details
1319-46-6
