LATRUNCULIN A
Synonym(s):[1R-[1R*, 4Z, 8E, 10Z, 12S*, 15R*, 17R*(R*)]]-4-(17-Hydroxy-5,12-dimethyl-3-oxo-2,16-dioxabicyclo[13.3.1]nonadeca-4,8,10-trien-17-yl)-2-thiazolidinone;LAT-A;Latrunculin A, Latrunculia magnifica - CAS 76343-93-6 - Calbiochem
- CAS NO.:76343-93-6
- Empirical Formula: C22H31NO5S
- Molecular Weight: 421.55
- MDL number: MFCD27977552
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-10-28 23:16:16
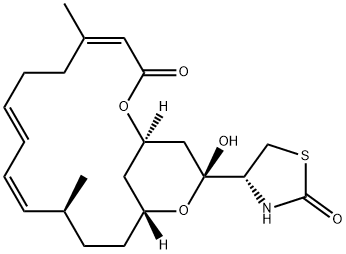
What is LATRUNCULIN A?
Description
Actin disruption is used to study cell functions in vitro (e.g., migration, endocytosis) and in vivo (e.g., tumor cell invasion). Latrunculin A is a bioactive 2-
The Uses of LATRUNCULIN A
Latrunculin A, Latrunculia magnifica is a stabilizer of monomeric G-actin and polymerization inhibitor.
The Uses of LATRUNCULIN A
Latrunculin A has been used as medium supplementation for A549 cells to determine the internalization mechanism of CAV9 in A549 human lung carcinoma cells.
What are the applications of Application
Latrunculin A, Latrunculia magnifica is a stabilizer of monomeric G-actin and polymerization inhibitor that disrupts microfilament organization in cultured cells.
Definition
ChEBI: A bicyclic macrolide natural product consisting of a 16-membered bicyclic lactone attached to the rare 2-thiazolidinone moiety. It is obtained from the Red Sea sponge Latrunculia magnifica and from the Fiji Islands sponge Cacospongia myc fijiensis. Latrunculin A inhibits actin polymerisation, microfilament organsation and microfilament-mediated processes.
General Description
Latrunculin A, a toxin extracted from the red sea sponge Latrunculia magnifica. It participates in vitro in the morphological alteration of the polymerization of pure actin. It forms a complex by binding with the nucleotide cleft of actin for actin filaments elongation.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Latrunculin A inhibits actin polymerization by a different mechanism than cytochalasins. Latrunculin A disrupts microfilament-mediated processes.
storage
-20°C
References
1) Coue et al. (1987), Inhibition of actin polymerization by latrunculin; FEBS Lett., 213 316 2) Spector et al. (1989), Latrunculins-novel marine macrolides that disrupt microfilament organization and affect cell growth; Cell Motil. Cytoskeleton, 13 127 3) Wang et al. (2005), Differential effects of latrunculin-A on myofibrils in cultures of skeletal muscle cells: Insights into mechanisms of myofibrillogenesis; Cell Motil. Cytoskeleton, 62 35 4) Reggiori et al. (2005), The actin cytoskeleton is required for selective types of autophagy, but not for non-specific autophagy, in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae; Mol. Biol. Cell, 16 5843 5) Asadi et al. (2016) A Genetic Screen for Fission Yeast Gene Deletion Mutants Exhibiting Hypersensitivity to Latrunculin A; G3 Genes Genomes Genetics, 6 3399 [Focus Citation]
Properties of LATRUNCULIN A
| alpha | D24 +152° (c = 1.2 in chloroform) |
| storage temp. | -20°C |
| solubility | DMSO: soluble |
| form | waxy solid |
| color | yellow |
| Stability: | Stable for 1 year from date of purchase as supplied. Solutions in DMSO or ethanol may be stored at -20° for up to 3 months. |
Safety information for LATRUNCULIN A
Computed Descriptors for LATRUNCULIN A
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate (S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3,4-Dibenzyloxybenzaldehyde 4-Hydrazinobenzoic acid 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 4-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 4-(3-chloropropyl)morpholine phenylhydrazine hydrochloride (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

![2-Fluoro-N-[2-(2-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl]benzamide](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/442633-00-3.gif)

You may like
-
 Latrunculin A, Latrunculia magnifica CAS 76343-93-6View Details
Latrunculin A, Latrunculia magnifica CAS 76343-93-6View Details
76343-93-6 -
 Latrunculin A, Latrunculia magnifica CASView Details
Latrunculin A, Latrunculia magnifica CASView Details -
 Latrunculin A CAS 76343-93-6View Details
Latrunculin A CAS 76343-93-6View Details
76343-93-6 -
 (9H-fluoren-9-yl)methyl (2,5-dioxopyrrolidin-1-yl) carbonate 82911-69-1 98.0%View Details
(9H-fluoren-9-yl)methyl (2,5-dioxopyrrolidin-1-yl) carbonate 82911-69-1 98.0%View Details
82911-69-1 -
 13057-17-5 95.0%View Details
13057-17-5 95.0%View Details
13057-17-5 -
 4-bromoaniline 106-40-1 99.0%View Details
4-bromoaniline 106-40-1 99.0%View Details
106-40-1 -
 5-bromo-2-chlorobenzoic acid 99.0%View Details
5-bromo-2-chlorobenzoic acid 99.0%View Details
21739-92-4 -
 15761-38-3 97.0%View Details
15761-38-3 97.0%View Details
15761-38-3