Lactulose
Synonym(s):4-O-β-D -Galactopyranosyl-D -fructofuranose;4-O-β-D -Galactopyranosyl-D -fructose;Lactulose
- CAS NO.:4618-18-2
- Empirical Formula: C12H22O11
- Molecular Weight: 342.3
- MDL number: MFCD00151469
- EINECS: 225-027-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-22 14:18:24
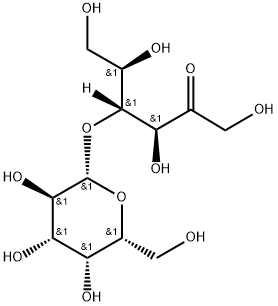
What is Lactulose?
Absorption
After administration by the oral route, less than 3% of the given dose of lactulose solution is absorbed by the small intestine. The remaining unabsorbed lactulose reaches the large intestine where it is metabolized - but even then, negligible quantities of unchanged lactulose or its metabolites are absorbed across the colon.
Toxicity
It has been documented that the oral LD50 of lactulose is 48.8 mL/kg in mice and more than 30 mL/ kg in rats.
It is expected that overdosage with lactulose would result in abdominal cramps and diarrhea, both of which should be treated with fluid and electrolyte replacement as required.
Considering the use of lactulose during pregnancy in humans has not been formally investigated, the agent should only be used during pregnancy only when clearly needed. Similarly, it is unknown whether lactulose is distributed into human breastmilk. Use of the medication in nursing women should subsequently be undertaken with caution.
Reproduction studies in rats, mice, and rabbits have not revealed any evidence of impaired fertility as a result of administering lactulose.
Data regarding the safety and efficacy of using lactulose in children for the treatment of chronic constipation or portal-systemic encephalopathy (PSE) is either very limited or yet to be established.
Information regarding the long-term mutagenic potential of lactulose solution in animals or humans and about the long-term carcinogenic potential in humans are not available.
Chemical properties
White Powder
Originator
Duphalac,Philips-Duphar,UK,1969
The Uses of Lactulose
Lactulose is is a synthetic, non-digestible sugar used in the treatment of chronic constipation; laxative.
The Uses of Lactulose
pharmaceutical excipient
The Uses of Lactulose
A keto analogue of lactose.
Indications
Lactulose is indicated for use as a laxative in the treatment of chronic constipation in adults and geriatric patients.
Additionally, lactulose is also employed as an adjunct to protein restriction and supportive therapy for the prevention and treatment of portal-systemic encephalopathy (PSE), including both the hepatic pre-coma and coma variations. In particular, lactulose solution has been effective at managing PSE resulting from surgical portacaval shunts or from chronic hepatic diseases like cirrhosis.
Moreover, there have also been studies demonstrating the capacity for lactulose to minimize the formation of gallstones and even some investigations regarding the experimental use of the agent in developing novel anticancer agents owing to its ability to bind galactin carbohydrates involved in various tumor progressions .
Background
Lactulose is a synthetic disaccharide derivative of lactose that is most commonly used as a laxative agent despite also being formally indicated to serve as an adjunct therapy in treating portal-systemic encephalopathy (PSE). Despite being first synthesized in 1929, investigations regarding its possible use as a laxative for the treatment of chronic constipation did not occur until the 1960s and its first clinical use for treating PSE was not until 1966.
Nevertheless, although lactulose received formal FDA approval in 1977 and has since become a readily available generic and brand-name non-prescription medication listed on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines as one of the most effective and safe medicines employed in a health system, data regarding its optimal place in therapy is often ambiguous.
Especially considering the use of lactulose as a laxative is typically only considered after lifestyle and dietary modifications fail and the fact that lactulose therapy cannot be ethically withheld from patients diagnosed with PSE in a placebo study, the substance may just be one of many options available for treating constipation and its efficacy in managing PSE may never be formally confirmed or refuted via clinical investigation.
What are the applications of Application
Lactulose is A keto analogue of lactose
Definition
ChEBI: A synthetic galactosylfructose disaccharide used in the treatment of constipation and hepatic encephalopathy.
Indications
Osmotic laxatives (e.g., lactulose, sorbitol) are poorly absorbed or nonabsorbable compounds that draw additional fluid into the GI tract. Lumen osmolality increases, and fluid movement occurs secondary to osmotic pressure. Lactulose is a synthetic disaccharide that is poorly absorbed from the GI tract, since no mammalian enzyme is capable of hydrolyzing it to its monosaccharide components. It therefore reaches the colon unchanged and is metabolized by colonic bacteria to lactic acid and to small quantities of formic and acetic acids.
Manufacturing Process
105 g of lactose monohydrate were dissolved in 500 ml of water. 48 g of NaAlO2 was dissolved in 100 ml of water and was then added to the lactose solution. The mixture was then diluted to one liter to provide a pH of 11.5. The reactant concentrations of 48 g of sodium aluminate and 105 g of lactose are equivalent to a mol ratio of two mols of aluminate to one mol of lactose. The mixture was then heated to 50°C and 100 ml aliquots were removed at periodic intervals to determine the level of conversion. The reaction was terminated after three hours by adding sufficient 30% HCl to lower the pH to 4.2. The pH was then raised to neutrality, i.e., 6.5 to 7.0, with ammonium hydroxide so as to completely precipitate insoluble aluminum hydroxide. The precipitate was then removed by vacuum filtration and the filtrate was analyzed for the presence of ketose sugar by chromatographic analysis. The chromatographic analysis of the filtrate confirmed that the main component of the filtrate was lactulose and not the monosaccharide ketose sugar, fructose.
brand name
Cephulac (Sanofi Aventis); Chronulac (Sanofi Aventis); Constulose (Acta- vis); Duphalac (Solvay Pharmaceuticals); Enulose (Actavis); Evalose (Teva); Generlac (Morton Grove); Heptalac (Teva); Laxilose (Technilab); Portalac (Solvay Pharma- ceuticals).
Therapeutic Function
Laxative
Pharmacokinetics
Lactulose formulations are most commonly administered via the oral route or the rectal route. Consequently, because the substance experiences minimal absorption by the gut it typically remains localized in the gastrointestinal tract environment and ultimately demonstrates almost all of its pharmacologic effects within the gut. In particular, as lactulose elicits its laxative effects in enhancing stool amounts and softening stool, such biochemical and physiologic activities can cause increased bowel sounds (borborygmi), a feeling of bloatedness, belching, frequent flatus, and diarrhea.
Clinical Use
Lactulose is used in the treatment of hepatic encephalopathy.
Side Effects
Since lactulose does contain galactose, it is contraindicated in patients who require a galactose-free diet. Metabolism of lactulose by intestinal bacteria may result in increased formation of intraluminal gas and abdominal distention.
Veterinary Drugs and Treatments
The primary use of lactulose in veterinary medicine is to reduce ammonia blood levels in the prevention and treatment of hepatic encephalopathy (portal-systemic encephalopathy; PSE) in small animals and pet birds. It is also used as a laxative in small animals.
Metabolism
Lactulose is essentially only metabolized in the colon by saccharolytic bacteria that are present there. In particular, the substance is broken down into lactic acid and small amounts of acetic and formic acid. Specific examples of bacteria that normally inhabit the large intestine that are capable of lactulose metabolism include Lactobacilli, Bacteroides, Escherichia coli, and Clostridia.
Purification Methods
Crystallise lactulose from MeOH or 50% MeOH. It mutarotates from [] D 20 -11.9o to –50.7o (c 1, H2O). [Montgomery & Hudson J Am Chem Soc 32 2101, 2104 1930, Beilstein 17 III/IV 3094, 17/7 V 214.] NMR in Me2SO at 24o shows 0% -pyranose, 27% -pyranose, 20% -furanose and 52% -furanose fforms [Angyal Adv Carbohydr Chem 42 15 1984].
Properties of Lactulose
| Melting point: | ~169 °C (dec.) |
| Boiling point: | 397.76°C (rough estimate) |
| alpha | -47 º (C=5, H2O, 12HR) |
| Density | 1,32g/cm |
| refractive index | 1,45-1,47 |
| storage temp. | Refrigerator |
| solubility | Freely soluble in water, sparingly soluble in methanol, practically insoluble in toluene. |
| form | Powder |
| pka | 11.67±0.20(Predicted) |
| color | White to almost white |
| optical activity | [α]20/D 48±2°, 24 hr, c = 1% in H2O |
| Water Solubility | 76.4 G/100 ML (30 ºC) |
| Merck | 5346 |
| BRN | 93773 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 4618-18-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | D-Fructose, 4-O-.beta.-D-galactopyranosyl- (4618-18-2) |
Safety information for Lactulose
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P271:Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. |
Computed Descriptors for Lactulose
| InChIKey | PFCRQPBOOFTZGQ-VZXVHDRGSA-N |
Lactulose manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran



![D-GALACTOSE 1-[2-(2-AZIDOETHOXY)ETHOXYETHYL]-2,3,4,6-TETRA-O-ACETATE](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/381716-33-2.gif)

You may like
-
 Lactulose, ≥98% CAS 4618-18-2View Details
Lactulose, ≥98% CAS 4618-18-2View Details
4618-18-2 -
 Lactulose 98% CAS 4618-18-2View Details
Lactulose 98% CAS 4618-18-2View Details
4618-18-2 -
 Lactulose CAS 4618-18-2View Details
Lactulose CAS 4618-18-2View Details
4618-18-2 -
 Lactulose CAS 4618-18-2View Details
Lactulose CAS 4618-18-2View Details
4618-18-2 -
 Lactulose CAS 4618-18-2View Details
Lactulose CAS 4618-18-2View Details
4618-18-2 -
 Lactulose CAS 4618-18-2View Details
Lactulose CAS 4618-18-2View Details
4618-18-2 -
 Lactulose CAS 4618-18-2View Details
Lactulose CAS 4618-18-2View Details
4618-18-2 -
 Lactulose CAS 4618-18-2View Details
Lactulose CAS 4618-18-2View Details
4618-18-2
