ISOXABEN
- CAS NO.:82558-50-7
- Empirical Formula: C18H24N2O4
- Molecular Weight: 332.39
- MDL number: MFCD00072433
- EINECS: 407-190-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-27 09:38:02
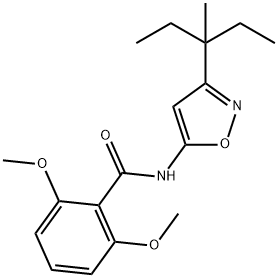
What is ISOXABEN?
The Uses of ISOXABEN
Isoxaben is used primarily for preemergence control of annual broadleaf weeds. Isoxaben is usually applied to soil either with light incorporation or before application of water (at least 0.5 in) within 3 weeks. As is the case with DCB, it is most effective on weed seedlings before emergence.
The Uses of ISOXABEN
Isoxaben is a herbicide residue in tea and other plants. A cellulose biosynthesis inhibitor in plants.
What are the applications of Application
Isoxaben is a benzamide family herbicide that inhibits cellulose biosynthesis
Definition
ChEBI: A benzamide obtained by formal condensation of the carboxy group of 2,6-dimethoxybenzoic acid and the amino group of 3-(3-methylpentan-3-yl)-1,2-oxazol-5-amine.
Pharmacology
Although isoxaben is readily absorbed through the
root system, foliar absorption and translocation is poor.
Reduced root absorption may be partly responsible for
the tolerance of some dicot species to isoxaben, although
differences in the site of action appears to be the major
contributing factor in tolerance (15).Up to 50% of absorbed
isoxaben is metabolized within 6 days following root application
(16). Differences in metabolism cannot explain
the selectivity of isoxaben between tolerant and susceptible
species (17,18). Metabolism of isoxaben involves
hydroxylation of the propyl side group and glucosylation.
2,6-dimethoxybenzamide is found as a minor metabolite
(19). Isoxaben prevents the germination and growth of
seedlings before emergence, by inhibiting cell division.
The primary mode of action of isoxaben is inhibition of
cellulose biosynthesis, although the exact mechanism is
unclear. Isoxaben has been shown to specifically inhibit
the incorporation of glucose into the acid-insoluble fraction
(presumed to be cellulose) of the cell walls of Arabidopsis
thaliana (20) and soybean cell suspension cultures (21).
This herbicide also disrupts cell plate formation in root
tips (22) and tobacco suspension cells (23). Isoxaben affects
a different site of action compared with DCB, as it inhibits
cytokinesis at an earlier stage in which callose is deposited
at the developing cell plate (23). There are no known cases
of resistance to this herbicide.
Metabolism
Isoxaben is adsorbed strongly to soil and therefore has very limited mobility. Volatilization and photodegradation of isoxaben is negligible when applied to soil. Isoxaben is mainly degraded by soil organisms and has an average half-life of 1 to 2 months in the field, providing an average of 5 to 6 months of weed control at normal rates of application (19).
Toxicity evaluation
Isoxaben is classified as a general use herbicide. Although
it is noncarcinogenic, it is classified as a Class C oncogen
based on increased incidence of benign liver tumors in
one experimental system tested (mice). It is relatively
nontoxic to mammals with an oral LD50 of >10 g/kg in
rats and mice (19).
Isoxaben is nonflammable and noncorrosive. It is stable
under normal conditions, but it is degraded by ultraviolet
light in aqueous solution and decomposes at 220 ?C (19).
Properties of ISOXABEN
| Melting point: | 175-179 °C |
| Boiling point: | 469.52°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.2149 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.5700 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | 0-6°C |
| pka | 11.44±0.70(Predicted) |
| form | neat |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Isoxaben (82558-50-7) |
Safety information for ISOXABEN
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H413:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P273:Avoid release to the environment. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for ISOXABEN
New Products
3-Iodophenylacetic acid 3-Pyridineacetonitrile, α-hydroxy- 2-Propanamine, 1-chloro-, hydrochloride (9CI) 3-(hexyloxy)-4-(pyridin-3-yl)-1,2,5-thiadiazole 2-Hexyn-1-ol Dibenzo-18-crown-6 Nickel(II) perchlorate hexahydrate, 98% 4-Bromophenylacetonitrile, 95% 3-Bromo-4-fluoroaniline, 97% Sodium tetraborate decahydrate, 98% Palladium(II) acetate, trimer, Pd 99% 4-Bromo-2-chlorotoluene, 97% N N Dimethylformamide Dimethyl Acetal (Dmf Dma) 2,3-Dichloro Benzoyl Cyanide [Side Chain] Bis(2-Chloroethyl) Amine Hydrochloride L-Glutamic Acid Diethyl Ester Hydrochloride 5-(Difluoromethoxy)-2-Mercaptobenzimidazole 1-Ethyl-3-(3-Dimethylaminopropyl)-Carbodiimide Hydrochloride [EDC Hcl] 1,4-Napthoquinone Bromoiodomethane Sodium Bicarbonate Methylene Dichloride (MDC) Ethyl Acetate Indole-3-Carbinol (I3C)Related products of tetrahydrofuran
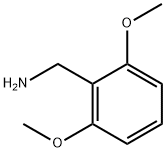
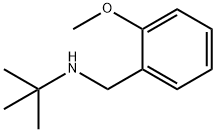
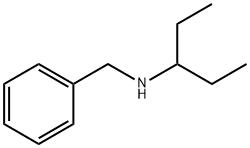
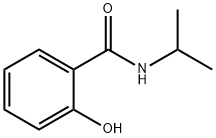

You may like
-
 Isoxaben CAS 82558-50-7View Details
Isoxaben CAS 82558-50-7View Details
82558-50-7 -
 Isoxaben CAS 82558-50-7View Details
Isoxaben CAS 82558-50-7View Details
82558-50-7 -
 17604-74-9 3-Pyridineacetonitrile, α-hydroxy- 98+View Details
17604-74-9 3-Pyridineacetonitrile, α-hydroxy- 98+View Details
17604-74-9 -
 131987-69-4 98+View Details
131987-69-4 98+View Details
131987-69-4 -
 Cyclohexane, (2-propynyloxy)- 67967-07-1 98+View Details
Cyclohexane, (2-propynyloxy)- 67967-07-1 98+View Details
67967-07-1 -
 2-Propanamine, 1-chloro-, hydrochloride (9CI) 98+View Details
2-Propanamine, 1-chloro-, hydrochloride (9CI) 98+View Details
5968-21-8 -
 3-Iodophenylacetic acid 1878-69-9 98+View Details
3-Iodophenylacetic acid 1878-69-9 98+View Details
1878-69-9 -
 132945-75-6 (S)-1-Boc-3-methanesulfonyloxy-pyrrolidine 98+View Details
132945-75-6 (S)-1-Boc-3-methanesulfonyloxy-pyrrolidine 98+View Details
132945-75-6
