Isoprothiolane
Synonym(s):Diisopropyl 2-(1,3-dithiolan-2-ylidene)malonate
- CAS NO.:50512-35-1
- Empirical Formula: C12H18O4S2
- Molecular Weight: 290.4
- MDL number: MFCD00210314
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 20:33:22
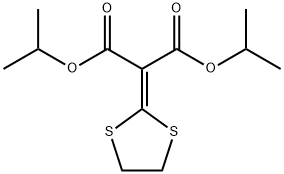
What is Isoprothiolane?
The Uses of Isoprothiolane
Isoprothiolane is a dithiolane pesticide. Isoprothiolane is commonly used in agriculture as a fungicide to control planthoppers and blast disease in rice plants.
The Uses of Isoprothiolane
Isoprothiolane is a fungicide that is used to control rice blast (Pyriculuriu aryzae), rice stem rot and Fusarium leaf spot on rice. It also reduces the plant-hopper population on rice.
Definition
ChEBI: Isoprothiolane is a malonate ester that is diisopropyl malonate in which the two methylene hydrogens at position 2 are replaced by a 1,3-dithiolan-2-ylidene group. An insecticide and fungicide used to control a range of diseases including Pyricularia oryzae, Helminthosporium sigmoideum and Fusarium nivale. It has a role as an insecticide, an environmental contaminant, a phospholipid biosynthesis inhibitor and an antifungal agrochemical. It is a malonate ester, a member of dithiolanes and an isopropyl ester. It is functionally related to a malonic acid. It derives from a hydride of a 1,3-dithiolane.
Hazard
Moderately toxic by ingestion.
Metabolic pathway
Isoprothiolane is easily oxidized by rat liver 9000 g supernatant to produce its racemic sulfoxide in this process, NADPH is an effective cofactor but NADH is not. The liver microsomes, however, preferentially form its (?+)-isomer in an enantiomeric excess of 38-43%. The sulfoxidation of isoprothiolane by rice plants proceeds too slowly to determine the metabolites. Both isoprothiolane (+?)- and (-)- sulfoxides undergo rapid racemization by rat cytosol (105 000 g supernatant) or rice plants, accompanied with reduction to isoprothiolane.
Degradation
Half-lives of isoprothiolane in river water were greater than 50 days (Hayakawa et. al., 1992). The compound is decomposed slowly in deionised water under UV light or sunlight. In rice paddy water, photodegradation was greatly accelerated by the presence of natural organic constituents (Chou and Eto, 1980; Eto et al., 1979). Isoprothiolane was placed on a silica gel TLC plate and irradiated at 10 cm distance with a 10 W lamp emitting mainly at 254 nm. Isoprothiolane photodegraded rapidly (half-life about 3 hours). Five products were detected. Proposed pathways of photodegradation are shown in Scheme 1 and involved cleavage of the dithiolane ring, ester hydrolysis, decarboxylation and the formation of dimeric heterocyclic compounds. The identities of oxalic acid (2), dithiolanylidenemalonic acid (3), dithiolanylideneacetic acid (4), 2,4- bis[bis(isopropoxycarbonyl)methylene]-1,3-dithietane (5), 3,5-bis[bis(isopropoxycarbonyl) methylene]-1,2,4-trithiolane (6) and elemental sulfur were confirmed. Isoprothiolane degraded more rapidly on sand than on a glass plate (Chou and Eto, 1980).
Properties of Isoprothiolane
| Melting point: | 54°C |
| Boiling point: | 402.48°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.3402 (rough estimate) |
| vapor pressure | 1.9 Pa (25 °C) |
| refractive index | 1.4950 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | Keep in dark place,Sealed in dry,2-8°C |
| solubility | Chloroform (Slightly), Ethyl Acetate (Slightly) |
| form | Solid |
| form | neat |
| Water Solubility | 54 mg l-1 (25 °C) |
| color | Light yellow to yellow |
| BRN | 2128528 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 50512-35-1(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Propanedioic acid, 1,3-dithiolan-2-ylidene-, bis(1-methylethyl) ester(50512-35-1) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Propanedioic acid, 1,3-dithiolan-2-ylidene-, bis(1-methylethyl) ester (50512-35-1) |
Safety information for Isoprothiolane
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral |
Computed Descriptors for Isoprothiolane
Abamectin manufacturer
Crop Life Science Limited
New Products
4-(Dimethylamino)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-carbonitrile 4-AMINO-TETRAHYDRO-PYRAN-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-Aminotetrahydropyran-4-carbonitrile Hydrochloride (R)-3-Aminobutanenitrile Hydrochloride 4-AMINO-TETRAHYDRO-PYRAN-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID HCL 3-((Dimethylamino)methyl)-5-methylhexan-2-one oxalate 5-Bromo-2-nitropyridine Nimesulide BP Aceclofenac IP/BP/EP Diclofenac Sodium IP/BP/EP/USP Mefenamic Acid IP/BP/EP/USP Ornidazole IP Diclofenac Potassium SODIUM AAS SOLUTION ZINC AAS SOLUTION BUFFER SOLUTION PH 10.0(BORATE) GOOCH CRUCIBLE SINTERED AQUANIL 5 BERYLLIUM AAS SOLUTION Methylcobalamin (vitamin B12) SODIUM METHYL PARABEN SODIUM VALPROATE AMOXICILLIN (AMOXYCILLIN) TRIHYDRATE ACICLOVIRRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 50512-35-1 Isoprothiolane 99%View Details
50512-35-1 Isoprothiolane 99%View Details
50512-35-1 -
 Diisopropyl 2-(1,3-dithiolan-2-ylidene)malonate 95% (GC) CAS 50512-35-1View Details
Diisopropyl 2-(1,3-dithiolan-2-ylidene)malonate 95% (GC) CAS 50512-35-1View Details
50512-35-1 -
 Isoprothiolane CAS 50512-35-1View Details
Isoprothiolane CAS 50512-35-1View Details
50512-35-1 -
 1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 -
 2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
1307449-08-6 -
 Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
25408-95-1 -
 2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
1805639-70-6 -
 Lithium ClavulanateView Details
Lithium ClavulanateView Details
61177-44-4