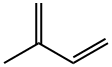
Isoprene
Synonym(s):2-Methyl-1,3-butadiene;Isoprene
- CAS NO.:78-79-5
- Empirical Formula: C5H8
- Molecular Weight: 68.12
- MDL number: MFCD00008600
- EINECS: 201-143-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-06-13 14:48:16
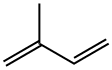
What is Isoprene?
Description
Isoprene is a naturally occurring clear colorless volatile liquid
(at room temperature) with a faint odor. Isoprene is an
important building block for lipids, steroids, terpenoids, and
a wide variety of natural products, including natural rubber.
Isoprene is found in abundance in nature and is produced and
emitted to the environment by plants and trees; it is also
emitted from food crops since isoprene serves as the basic
structural unit of numerous substances such as terpenes and
vitamins A and K. Hence, isoprene is found in ambient air at
low concentrations (e.g., the reported concentration of
isoprene in the ambient air of the United States ranges
between 1 and 21 ppb and is generally less than 10 ppb).
Because the biosynthesis of isoprene is associated with
photosynthesis, emission of isoprene from plants and trees is
negligible at night. Emission of isoprene from plants and trees
is also seasonal with the highest emission occurring in the
summer and the lowest emission occurring in the winter.
Once emitted to the atmosphere, isoprene is converted by free
radicals (e.g., nitric oxide, hydroxyl radicals, ozone) to various
species (e.g., aldehydes, hydroperoxides, organic nitrates,
epoxides) that mix with water droplets and help create aerosols
and haze.
Isoprene is produced endogenously in experimental
animals and humans. The rate of endogenous production of
isoprene in rats and mice is approximately 1.9 and
0.4 mmol kg-1 h-1, respectively, while in humans it is approximately
0.15 mmol kg-1 h-1 (approximately 2–4 μmol kg-1 per
day). The precursor to endogenous isoprene production in
humans is believed to be mevalonic acid, a precursor of
cholesterol synthesis. Isoprene is the major hydrocarbon found
in human breath, accounting for up to 70% of exhaled
hydrocarbons. The mean concentration of isoprene reported
in human breath is 118 ppb (range 0–474 ppb). The concentration
of isoprene in human blood is between 1 and
4.8 μg l-1. The rate of production of isoprene is higher in males
than females and in adults than in children.
Anthropogenic sources of isoprene include production of
ethylene by cracking naphtha, wood pulping, combustion of
wood and other biomass, tobacco smoke (smoking one cigarette
can increase the concentration of isoprene in exhaled air
by 70%), gasoline, and automobile exhaust.
Description
Isoprene (2-methyl-1,3-butadiene) is the monomer of natural rubber and a building block for many natural compounds. C. G. Williams first isolated it in 1860 by pyrolyzing rubber. Many methods have been developed for its commercial manufacture for the production of synthetic rubber and other polymers. About 500 megatons of isoprene is emitted into the atmosphere each year, mostly from natural sources—more than all organic compound emissions from anthropogenic sources.
Chemical properties
Isoprene (2-methyl-l,3-butadiene) is a colorless, volatile, flammable liquid with specific gravity 0.6758. It is highly reactive, usually occurs as its dimer, and unless inhibited undergoes explosive polymerization. Isoprene naturally occurs in the environment as emissions from vegetation. It may be released to the environment as emissions during wood pulping, biomass combustion, and rubber abrasion; through tobacco smoke, gasoline, turbine, and automobile exhaust. In tobacco smoke, isoprene has been determined to be the precursor of a number of polycyclic aromatics, as demonstrated by thermal condensations in the range of 450–700℃.
Chemical properties
Isoprene is a colourless liquid, b.p. 34°C.
Physical properties
Colorless, volatile, extremely flammable liquid with an petroleum-like odor. An odor threshold concentration of 48 ppbV was reported by Nagata and Takeuchi (1990).
The Uses of Isoprene
Isoprene occurs in nature and it is produced by many plants. Its polymers are the main component of natural rubber. The most important application of isoprene is to manufacture polymers and copolymers. Polyisoprene, a synthetic rubber made from isoprene, is used in a wide variety of rubber applications including medical equipment, baby bottle teats/nipples, toys, shoe soles, tires, elastic films, threads for golf balls or textiles, adhesives, paints, and coatings. Copolymer butyl rubber, made from isobutene with a small amount of isoprene, has excellent impermeability to gases and is used in inner tubes. Another copolymer styrene-isoprene rubber is used in pressure sensitive adhesives. Isoprene is also used as a chemical intermediate.
The Uses of Isoprene
The majority of isoprene produced commercially is used to make synthetic rubber (cis-polyisoprene), most of which is used to produce vehicle tires. The second- and third-largest uses are in the production of styrene-isoprene-styrene block polymers and butyl rubber (isobutene-isoprene copolymer) (IARC 1994).
The Uses of Isoprene
The primary use of isoprene is the manufacture of polyisoprene, or ‘synthetic’ natural rubber, which is subsequently used to make tires. Other major uses of isoprene include the production of styrenic thermoplastic elastomer block copolymers (styrene–isoprene–styrene) and butyl rubber (isobutene– isoprene copolymer). Isoprene is also used to manufacture other chemicals, intermediates, and derivatives, which are subsequently used to manufacture vitamins, pharmaceuticals, flavorings and fragrances, and epoxy hardeners.
Definition
ChEBI: A hemiterpene with the formula CH22C(CH3)CH2CH2; the monomer of natural rubber and a common structure motif to the isoprenoids, a large class of other naturally occurr ng compounds.
Production Methods
Rubber results from the polymerization of isoprene to form polyisoprene. The resultingstructure dictates the properties of the rubber. Natural rubber has a cis 1,4 structure.This means that the carbon atoms that form the chainattach to the same side ofthe chain at the 1 and 4 positions. The cisstructure gives rubber its elasticity. Polyisoprene alsoexists in a trans 1,3 configuration. In the trans configuration, the addition takes place onopposite sides of the carbon chain.
Natural rubber occurs in a colloidal milky suspension called latex, which is obtained fromnumerous plants. The most important of these is the para rubber tree, Hevea brasiliensis. Naturalrubber is harvested by cutting a v-shape incision into a plant and allowing latex to drain intoa container containing a preservative. About 50mL of latex is obtained on a daily basis. Latexis transported to collection stations where it is processed for shipment. Processing can includepreservation, coagulation, and concentrating before being sent to rubber factories.
Preparation
Isoprene is obtained from propylene by the followin,g route:

In the first step, propylene is dimerized to 2-methyl-l-pentene by passage over a catalyst of tri-n-propylaluminium at about 200??C and 20 MPa (200 atmospheres). This product is then isomerized to 2-methyl-2-pentene by heating at 150-300??C in the presence of a silica-alumina catalyst. The final step in the process is the pyrolysis of the olefin to isoprene at 650-800??C in the presence of a free radical initiator such as hydrogen bromide. The isomerization step is necessary because pyrolysis of 2-methyl-l-pentene gives much poorer yields of isoprene than pyrolysis of 2-methyl-2-pentene.
General Description
A clear colorless liquid with a petroleum-like odor. Density 5.7 lb / gal. Flash point -65°F. Boiling point 93°F. May polymerize exothermically if heated or contaminated. If polymerization takes place inside a closed container, the container may rupture violently. Less dense than water and insoluble in water. Vapors heavier than air.
Air & Water Reactions
Highly flammable. Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
ISOPRENE may react vigorously with strong oxidizing agents. May react exothemically with reducing agents to release hydrogen gas. May undergo exothermic addition polymerization in the presence of various catalysts (such as acids) or initiators. Undergoes autoxidation upon exposure to the air to form explosive peroxides. Mixing isoprene in equal molar portions with any of the following substances in a closed container caused the temperature and pressure to increase: chlorosulfonic acid, nitric acid (70%), oleum, sulfuric acid (90%) [NFPA 1991].
Hazard
Highly flammable, dangerous fire and explosion risk. Irritant. Possible carcinogen.
Health Hazard
Vapor produces no effects other than slight irritation of the eyes and upper respiratory tract. Liquid may irritate eyes; like gasoline.
Flammability and Explosibility
Extremely flammable
Carcinogenicity
Isoprene is reasonably anticipated to be a human carcinogen based on sufficient evidence of carcinogenicity from studies in experimental animals.
Environmental Fate
At 25 ℃, isoprene has a high vapor pressure of 733 hPa, a low water solubility of 642 mg l-1, and a Henry’s law constant of 7781 Pam3 mol-1. Isoprene’s log Kow is 2.42 while its log Koc is 1.83. Isoprene’s vapor density relative to air is 2.4. Because of its high vapor pressure at ambient temperature, isoprene will partition largely into the atmosphere, with negligible amounts partitioning to soil and water. Due to a short half-life in air (0.5 h by reaction with nitric oxide, 1.2–4 h by reaction with hydroxyl radicals, and 19 h by reaction with ozone), wet deposition of isoprene from air is not expected to play a significant role in its atmospheric fate. Although laboratory testing demonstrates that isoprene has the potential to biodegrade, microbial metabolism is unlikely to contribute significantly to the removal of isoprene from the environment due to rapid volatilization from terrestrial and aquatic media. Isoprene has a low bioaccumulation potential and is not expected to bioaccumulate.
Purification Methods
Reflux it with sodium then distil it from sodium or NaBH4 under nitrogen, and pass it through a column containing KOH, CaSO4 and silica gel. tert-Butylcatechol (0.02% w/w) is added, and the isoprene is stored in this way until redistilled before use. The inhibitor (tert-butylcatechol) in isoprene can be removed by several washings with dilute NaOH and water. The isoprene is then dried over CaH2, distilled under nitrogen at atmospheric pressure, and the fraction distilling at 32o is collected. Store it under nitrogen at -15o. [Beilstein 1 H 252, 1 IV 1001.]
Toxicity evaluation
The acute effects of isoprene are related to irritation, central nervous system depression, and asphyxia at high concentrations. The mutagenic and genotoxic effects of isoprene seen in in vivo and in vitro studies, as well as the carcinogenic effects of isoprene in experimental animals (principally mice), are believed to be due to the formation of isoprene diepoxide.
Properties of Isoprene
| Melting point: | 323-329 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 34 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 0.681 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| vapor density | 2.35 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 8.82 psi ( 20 °C) |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | −65 °F |
| storage temp. | Store at <= 20°C. |
| solubility | 0.7g/l |
| form | solid |
| pka | >14 (Schwarzenbach et al., 1993) |
| color | Clear colorless to very pale yellow |
| Odor | petroleum-like odor |
| Odor Threshold | 0.048ppm |
| explosive limit | 1-9.7%(V) |
| Water Solubility | 0.07 g/100 mL |
| FreezingPoint | -145.96℃ |
| λmax | 231nm(neat)(lit.) |
| Merck | 14,5201 |
| BRN | 969158 |
| Henry's Law Constant | (x 10-2 atm?m3/mol):
3.45 at 18 °C (dynamic stripping cell-MS, Karl et al., 2003) |
| Dielectric constant | 2.1(25℃) |
| Stability: | Stability Extremely flammable. Readily forms explosive mixtures with air. Note low flash point, low boiling point, high vapour pressure. Unstable - prone to spontaneous polymerization. May contain a polymerization inhibitor. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 78-79-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | 1,3-Butadiene, 2-methyl-(78-79-5) |
| IARC | 2B (Vol. 60, 71) 1999 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Isoprene (78-79-5) |
Safety information for Isoprene
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H224:Flammable liquids H341:Germ cell mutagenicity H350:Carcinogenicity H412:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P233:Keep container tightly closed. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. P403+P233:Store in a well-ventilated place. Keep container tightly closed. |
Computed Descriptors for Isoprene
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Isoprene, stabilized with ≈0.02% 4-tert-butylcatechol CAS 78-79-5View Details
Isoprene, stabilized with ≈0.02% 4-tert-butylcatechol CAS 78-79-5View Details
78-79-5 -
 Isoprene CAS 78-79-5View Details
Isoprene CAS 78-79-5View Details
78-79-5 -
 Isoprene (stabilized with TBC) CAS 78-79-5View Details
Isoprene (stabilized with TBC) CAS 78-79-5View Details
78-79-5 -
 Isoprene CAS 78-79-5View Details
Isoprene CAS 78-79-5View Details
78-79-5 -
 Isoprene CAS 78-79-5View Details
Isoprene CAS 78-79-5View Details
78-79-5 -
 2-Methyl-1,3-butadiene CAS 78-79-5View Details
2-Methyl-1,3-butadiene CAS 78-79-5View Details
78-79-5 -
 Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
110-86-1 -
 Thiourea 99% ARView Details
Thiourea 99% ARView Details
62-56-6
