INSECTICIDE
- CAS NO.:174060-41-4
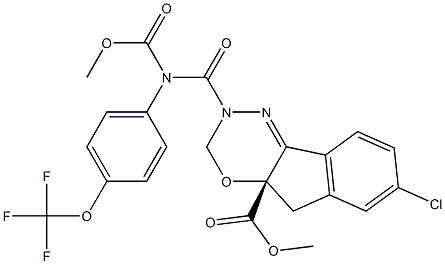
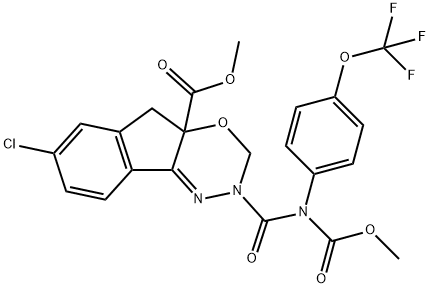
- Empirical Formula: C22H17ClF3N3O7
- Molecular Weight: 527.8344896
- EINECS: 605-683-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2023-05-04 17:34:34
What is INSECTICIDE?
Definition
ChEBI: Indoxacarb is an organochlorine insecticide and a methyl ester. It has a role as a voltage-gated sodium channel blocker.
Agricultural Uses
Insecticide is a substance which is toxic to insects and hence used to control them. Insecticides are used where insects cause economic damage or endanger the health of man and his domestic animals.
The broad types of insecticides are: (i) Inorganic insecticides: arsenic, lead and copper compounds and their mixtures, the use of which has diminished sharply in recent years because of the development of more effective types that are less toxic to man. (ii) Natural organic compounds: rotenone and pyrethrins (which are relatively harmless to man), nicotine, copper MphtheMte and petroleum derivatives. (iii) Synthetic organic compounds: (a) chlorinated hydrocarbons, such as DDT, dieldrin, endrin, lindane, chlordane and p- dichlorbenzene, (b) organic esters of phosphorus, and (c) imidazole and its derivatives which act on the principle of metabolic inhibition. Besides direct application, these can be fed to growing plants, with the result that the plants can no longer serve as nutrient for the specific insect.
There are three main types of insecticides based on their mechanism of action. They are (a) stomach insecticides which are ingested by the insects with their food, (b) contact insecticides which penetrate the cuticle, and (c) fumigant insecticides which are inhaled. Stomach insecticides are used to control chewing insects like caterpillars and sucking insects like aphids. They may be applied to the plant (in anticipation) where they remain active for a considerable time. Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) are added to some insecticides to increase their effectiveness and persistence.
Insecticides must be used with considerable caution on food plants or animal forage. For example, arsenic compounds are absorbed by the plant and transported to all its parts. Contact insecticides (like nicotine, demes and pyrethrum), and some synthetic compounds such as DDT and other chlorinated hydrocarbons, organophosphates (Malathion) and carbamates are quickly broken down, and have lasting presence on the plants
Highly persistent insecticides may be concentrated in food chains and exert harmful effects on other animals such as birds and fish.
Safety information for INSECTICIDE
New Products
4-Aminotetrahydropyran-4-carbonitrile Hydrochloride (R)-3-Aminobutanenitrile Hydrochloride 4-AMINO-TETRAHYDRO-PYRAN-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID HCL 4-(Dimethylamino)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-carbonitrile 3-((Dimethylamino)methyl)-5-methylhexan-2-one oxalate 1,4-Dioxa-8-azaspiro[4.5]decane 5-Bromo-2-nitropyridine Nimesulide BP Aceclofenac IP/BP/EP Diclofenac Sodium IP/BP/EP/USP Mefenamic Acid IP/BP/EP/USP Ornidazole IP Diclofenac Potassium SODIUM AAS SOLUTION ZINC AAS SOLUTION BUFFER SOLUTION PH 10.0(BORATE) GOOCH CRUCIBLE SINTERED AQUANIL 5 BERYLLIUM AAS SOLUTION 2-Bromo-1-(bromomethyl)-3-chloro-5-nitrobenzene 2-Bromo-3-nitroaniline N-(3-Hydroxypropyl)-N-methylacetamide 3-Bromo-6-chloropyridazine 4-ethyl-3-nitrobenzoic acidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
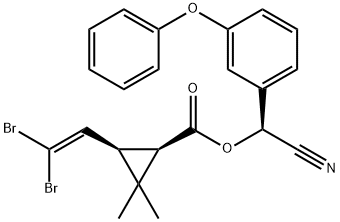
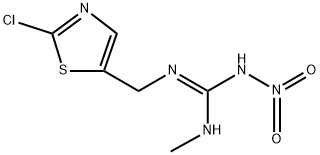
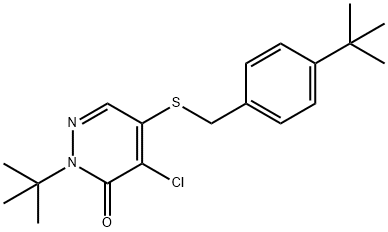
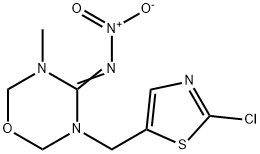
You may like
-
 1-Methyl-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyridazine-3-carbonitrile 98%View Details
1-Methyl-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyridazine-3-carbonitrile 98%View Details
99903-60-3 -
 88491-46-7 98%View Details
88491-46-7 98%View Details
88491-46-7 -
 1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 -
 2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
1307449-08-6 -
 Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
25408-95-1 -
 2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
1805639-70-6 -
 1784294-80-9 98%View Details
1784294-80-9 98%View Details
1784294-80-9 -
 Lithium ClavulanateView Details
Lithium ClavulanateView Details
61177-44-4