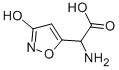
IBOTENIC ACID
Synonym(s):α-Amino-3-hydroxy-5-isoxazoleacetic acid;2-amino-2-(3-hydroxyisoxazol-5-yl) acetic acid, α-Amino-(3-hydroxy-5-isoxazolyl)acetic acid, Glutamate Receptor Agonist, Ibotenic acid;Ibotenic Acid - CAS 2552-55-8 - Calbiochem
- CAS NO.:2552-55-8
- Empirical Formula: C5H6N2O4
- Molecular Weight: 158.11
- MDL number: MFCD00069294
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 23:02:33
What is IBOTENIC ACID?
Description
Ibotenic acid (60573-88-8) is a conformationally restricted analog of glutamate which occurs naturally in Amanita mascaria and related mushrooms.? It is a non-specific glutamate receptor (both NMDA and mGluR) agonist.1 May be used to induce hippocampal lesioning in rat neurodegeneration models.2,3 Induces lesions in the subiculum in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease.4
Chemical properties
Crystalline solid; forms monohydrate; mp151°C (303.8°F) (anhydrous), 145°C (293°F)(monohydrate); soluble in water and alcohol.
The Uses of IBOTENIC ACID
Ibotenic acid is a neuroexcitatory amino acid originally isolated from Amanita species that functions as a NMDA and metabotropic glutamate receptor agonist. As a neurotoxin, ibotenic acid is often used to induce brain lesions in animals that model cognitive dysfunctions resulting from neurodegenerative diseases, traumatic brain injury, and stroke.
The Uses of IBOTENIC ACID
Neurobiological tool.
The Uses of IBOTENIC ACID
Ibotenic acid has been used to perform surgery in adult male zebra finches (Taeniopygia guttata) to study reversing reinforcement-induced vocal changes.
What are the applications of Application
Ibotenic acid is a conformationally restricted analog of glutamic acid and a a potent Glu agonist
Definition
A isoxazole which, together with muscimol, is largely responsible for the toxicities of a number of mushrooms including those of the genus Amanita. It is a potent excitatory amino acid.
Preparation
Isolated from the Japanese fly mushroom. The acid can be produced synthetically.
Hazard
Neurotoxic; causes motor depression, ataxia, changes in mood, perceptions and feelings.
Health Hazard
Ibotenic acid is a potent neurologic aminoacid. It exhibits neuroexcitatory activity andcauses sedative actions on spinal neurons.High doses can cause sleep, hallucinations,distorted perceptions, and nausea. In humansthe symptoms above may be manifested fromingestion of 6–8 mg of ibotenic acid.
LD50 value, oral (mice): 38 mg/kg
LD50 value, intraperitoneal (mice): 15 mg/kg.
Biological Activity
NMDA and metabotropic glutamate receptor agonist.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Non-selective agonist with preference for NMDA glutamate receptors; neurotoxin; neuroexcitatory amino acid originally isolated from Amanita species.
storage
-20°C (desiccate)
Purification Methods
It has been converted to the ammonium salt (m 121-123o dec) dissolved in H2O, passed through an Amberlite IR 120 resin (H+ form) and eluted with H2O. The acidic fractions are collected, evaporated to dryness and the residue recrystallises from H2O as the monohydrate (m 144-146o). The anhydrous acid is obtained by making a slurry with MeOH, decanting and evaporating to dryness, and repeating the process twice more to give the anhydrous acid (m 151-152o). Recrystallisation from H2O gives the monohydrate. [Nakamura Chem Pharm Bull Jpn 19 46 1971.] The ethyl ester forms needles when crystallised from a small volume of Et2O and has m 78-79o and IR (CHCl3) with max 35002300 (OH), 1742 (ester C=O), 1628, 1528cm-1, and UV with λmax (EtOH) at 206nm (ε 7,080). The hydrazide has m 174-175o (from MeOH) with IR (KBr) 1656 (C=O)cm-1.
References
1) Nakanishi (1992), Molecular diversity of glutamate receptors and implications for brain function; Science 258 597 2) Jarrard (1989), On the use of ibotenic acid to lesion selectively different components of the hippocampal formation; J. Neurosci. Methods 29 251 3) Isacson and Peschanski (1992), Is there capacity for anatomical and functional repair in the adult somatosensory thalamus?; Exp. Neurol. 115 173 4) George et al. (2014), Lesion of the subiculum reduces the spread of amyloid beta pathology to interconnected brain regions in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease; Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2 17
Properties of IBOTENIC ACID
| Melting point: | 141-147 °C |
| Density | 1.621±0.06 g/cm3 (20 ºC 760 Torr) |
| storage temp. | Keep in dark place,Inert atmosphere,Room temperature |
| solubility | H2O: soluble1mg/mL, clear, colorless (with sonication) |
| form | White solid |
| pka | 2.16±0.10(Predicted) |
| color | white |
| Odor | Practically odorless. Faint, meat-like, mild and sweet taste in aqueous dilutions. |
| Water Solubility | Soluble to 10 mM in water and to 100 mM in 1.1eq. NaOH |
| Stability: | Stable for 1 year from date of purchase as supplied. Solutions in distilled water may be stored at -20°C for up to 1 month. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 2552-55-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for IBOTENIC ACID
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H301:Acute toxicity,oral |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. P405:Store locked up. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for IBOTENIC ACID
| InChIKey | IRJCBFDCFXCWGO-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
IBOTENIC ACID manufacturer
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 2552-55-8 Ibotenic acid 95%View Details
2552-55-8 Ibotenic acid 95%View Details
2552-55-8 -
 2552-55-8 98%View Details
2552-55-8 98%View Details
2552-55-8 -
 Ibotenic Acid CAS 2552-55-8View Details
Ibotenic Acid CAS 2552-55-8View Details
2552-55-8 -
 Ibotenic acid CAS 2552-55-8View Details
Ibotenic acid CAS 2552-55-8View Details
2552-55-8 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1