hydrocortamate
- CAS NO.:76-47-1
- Empirical Formula: C27H41NO6
- Molecular Weight: 475.62
- MDL number: MFCD00864163
- EINECS: 200-963-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2023-05-04 17:34:42
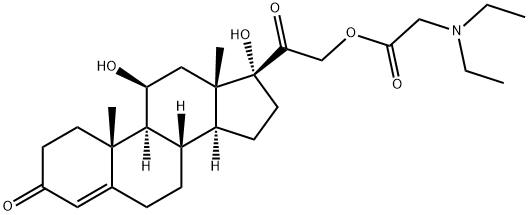
What is hydrocortamate?
Toxicity
Side effects include burning, itching, irritation, dryness, folliculitis, hypertrichosis, acneiform eruptions, hypopigmentation, perioral dermatitis, allergic contact dermatitis, maceration of the skin, secondary infection, skin atrophy, striae, miliaria.
Originator
Magnacort,Pfizer,US,1956
The Uses of hydrocortamate
Hydrocortamate is a synthetic glucocorticoid with anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive properties. It is used topically to treat inflammation due to corticosteroid-responsive dermatoses.
Indications
Used topically as an antiinflammatory in the treatment of steroid-responsive dermatoses
Background
Hydrocortamate is a synthetic glucocorticoid used for its anti-inflammatory or immunosuppressive properties to treat inflammation due to corticosteroid-responsive dermatoses. Glucocorticoids are a class of steroid hormones characterised by an ability to bind with the cortisol receptor and trigger a variety of important cardiovascular, metabolic, immunologic and homeostatic effects.
Definition
ChEBI: Hydrocortamate is a glycinyl ester, an 11beta-hydroxy steroid, a 17alpha-hydroxy steroid, a glucocorticoid, a 3-oxo-Delta(4) steroid and a tertiary alpha-hydroxy ketone. It has a role as an anti-inflammatory drug and an immunosuppressive agent. It is functionally related to a cortisone.
Manufacturing Process
1 g of hydrocortisone is introduced with stirring into 5 cc of anhydrous
pyridine. After heating to 45°C and then cooling again to 0°C to 5°C there is
slowly added dropwise a freshly prepared solution of 0.52 g (1 mol + 10%) of
chloracetic anhydride in 4 cc of absolute ether, The reaction temperature
should not exceed 10°C. During the whole time of reaction a stream of
nitrogen is passed through the reaction mixture in order to achieve an
exhaustive evaporation of the added ether. The batch is slowly allowed to
come to room temperature, an operation requiring 4 to 5 hours, and then 0.1
cc of water is added for decomposition of the excess of anhydride. The
reaction solution is introduced dropwise with stirrinq within 1 hour into 100 cc
of water as a result of which the 21-chloracetate of hydrocortisone is
deposited. After filtration with suction, washing is carried out with water, 5%
hydrochloric acid, water, 2% sodium bicarbonate solution and water again.
The substance is then dried in a vacuum desiccator. The white chloracetate
thus obtained melts at 213°C to 214°C with decomposition. It is free from
nitrogen and the yield amounts to 93.4% of the theoretical.
1 g of hydrocortisone-21-chloracetate is dissolved in 15 cc of anhydrous and
peroxide-free tetrahydrofuran. The solution produced is treated with a solution of 0.42 g of diethylamine in 15 cc of tetrahydrofuran. The reaction mixture is
allowed to stand for 24 hours at room temperature. The separated
diethylamine hydrochloride is filtered with suction and the filtrate evaporated
under vacuum in a nitrogen atmosphere at 40°C. The residue is triturated
with a little absolute ether and suction filtered. It is washed on the filter with
a little ether and then with hexane. The 21-diethylaminoacetate of
hydrocortisone melts at 150°C to 162°C. The base can be recrystallized from
ethyl acetate but its melting point remains practically unchanged at 162°C to
163°C. The yield amounts to 72.5% of the theoretical. For conversion of the
base into the hydrochloride it is suspended in ether and the suspension
treated with ethereal hydrochloric acid. The hydrochloride is filtered with
suction and recrystallized from ethanol; MP 222°C with decomposition.
With a starting quantity of 14g, the yield amounted to 85.4% of the
theoretical.
brand name
Magnacort (Pfizer).
Therapeutic Function
Corticosteroid
Pharmacokinetics
Hydrocortamate is a synthetic glucocorticoid used for its anti-inflammatory or immunosuppressive properties to treat inflammation due to corticosteroid-responsive dermatoses. Glucocorticoids are a class of steroid hormones characterised by an ability to bind with the cortisol receptor and trigger a variety of important cardiovascular, metabolic, immunologic and homeostatic effects. Glucocorticoids are distinguished from mineralocorticoids and sex steroids by having different receptors, target cells, and effects. Technically, the term corticosteroid refers to both glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, but is often used as a synonym for glucocorticoid. Glucocorticoids suppress cell-mediated immunity. They act by inhibiting genes that code for the cytokines IL-1, IL-2, IL-3, IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, IL-8 and TNF-alpha, the most important of which is the IL-2. Reduced cytokine production limits T cell proliferation. Glucocorticoids also suppress humoral immunity, causing B cells to express lower amounts of IL-2 and IL-2 receptors. This diminishes both B cell clonal expansion and antibody synthesis. The diminished amounts of IL-2 also leads to fewer T lymphocyte cells being activated.
Metabolism
Primarily hepatic via CYP3A4
Properties of hydrocortamate
| Melting point: | 162-163° |
| Boiling point: | 627.2±55.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.21±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| pka | 12.32±0.70(Predicted) |
Safety information for hydrocortamate
Computed Descriptors for hydrocortamate
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 42831-50-5 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 98%View Details
42831-50-5 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 98%View Details
42831-50-5 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1