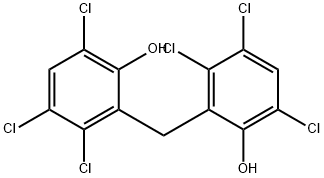
Hexachlorophene
Synonym(s):2,2′-Methylenebis(3,4,6-trichlorophenol);Hexachlorophene
- CAS NO.:70-30-4
- Empirical Formula: C13H6Cl6O2
- Molecular Weight: 406.9
- MDL number: MFCD00002171
- EINECS: 200-733-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:50:35
What is Hexachlorophene?
Absorption
Detectable blood levels of hexachlorophene following absorption through intact skin have been found in subjects who regularly scrubbed with hexachlorophene.
Toxicity
Oral, rat LD50: 66 mg/kg. Signs of overdose include anorexia, vomiting, abdominal cramps, diarrhea, dehydration, convulsions, hypotension, and shock, and in several reported instances, fatalities.
Description
Hexachlorophene (HCP) is a chlorinated bisphenol antiseptic and was introduced for use as an antibacterial component in drug and cosmetic products in 1941. It has bacteriostatic activity against gram-positive organisms (e.g., staphylococcus) but not against gram-negative organisms. HCP is readily absorbed orally and through the skin of humans, especially skin of premature infants or damaged skin. Hexachlorophene is a neurotoxicant, and symptomology may include lethargy, muscle weakness, irritability, cerebral edema, and paralysis leading to coma and death. The US Food and Drug Administration restricted the use of hexachlorophene preparation to ≤0.1% in 1972 and approved it for surgical scrubbing and handwashing. HCP is no longer used extensively in hospitals, rest homes, etc., because of its toxicity.
Chemical properties
Off-White Crystalline Solid
Chemical properties
Hexachlorophene is a crystalline solid com pound.
Originator
Gamophen,Ethicon,US,1950
The Uses of Hexachlorophene
Hexachlorophene is a topical antiseptic in germicidal soaps, creams, deodorants, cleansers, shampoos, after-shave creams, pHisoHex surgical cleanser and in veterinary medicine.
The Uses of Hexachlorophene
Used as an antiseptic
The Uses of Hexachlorophene
antiinfective (topical)
Background
A chlorinated bisphenol antiseptic with a bacteriostatic action against Gram-positive organisms, but much less effective against Gram-negative organisms. It is mainly used in soaps and creams and is an ingredient of various preparations used for skin disorders. (From Martindale, The Extra Pharmacopoeia, 30th ed, p797)
Indications
For use as a surgical scrub and a bacteriostatic skin cleanser. It may also be used to control an outbreak of gram-positive infection where other infection control procedures have been unsuccessful.
Definition
ChEBI: An organochlorine compound that is diphenylmethane in which each of the phenyl groups is substituted by chlorines at positions 2, 3, and 5, and by a hydroxy group at position 6. An antiseptic that is effective against Gram-positive organisms, it is used in soaps and creams for the treatment of various skin disorders. It is also used in agriculture as an acaricide and fungicide, but is not approved for such use within the European Union.
Indications
Hexachlorophene is a bacteriostatic antiseptic effective against gram-positive organisms,
specifically Staphylococcus. It has a cumulative and sustained effect. Although
it has a slow onset of action, with repeated use a film develops on the skin that
has long-acting properties. It is not effective against gram-negative organisms or
yeast. It is postulated to affect bacterial electron transport and membrane function.
With repeated use, it penetrates through the stratum corneum.
It is often used for
preoperative surgical scrubbing. One retrospective study showed that it may be
teratogenic if used excessively by pregnant women, although there have been no
subsequent, well-controlled studies that substantiate this. It should not be used in
infants, particularly those who are premature or have dermatoses. It is toxic to
tissues when applied to open wounds.
Preparation
Hexachlorophene is formed by reaction of 2,4,5-trichlorophenol with paraformaldehyde in fuming sulfuric acid (20% SO3) at 65–135 ℃. Hexachlorophene is a strong bacteriostat which also has a microbicidal effect at high concentrations. The use of Hexachlorophene as an antimicrobial agent in cosmetics, medicinal soaps, detergent solutions, and textiles has, however, been discontinued because of its toxicity.
Manufacturing Process
A mixture of 198 grams of 2,4,5-trichlorophenol and 18.8 grams of
paraformaldehyde was heated to 65°C and well stirred. 65 grams of oleum
20% was added dropwise and the addition was so regulated that the
temperature increased, without the application of external heat, until it
reached 135°C at the end of the acid addition, which took 10 to 15 minutes.
The contents of the reaction vessel were stirred for 2 minutes more and then
allowed to run into a solution of 100 grams of sodium hydroxide in 1,000 cc of
water.
The reaction flask was washed with a solution of 25 grams of sodium
hydroxide in 250 cc of water. The combined alkaline solutions were heated to
boiling for 5 minutes. A small amount (6 grams) of alkali-insoluble material remained and was filtered off. Sulfuric acid (62% H2SO4 content) was then
added at room temperature dropwise under stirring to the filtrate until a pH of
10.3 was reached. This required about 80 grams of the acid. The monosodium
salt of bis-(3,5,6-trichloro-2-hydroxyphenyl) methane precipitated out of
solution and was filtered and then washed with 200 cc of water. The salt was
then suspended in 2,000 cc of water and sulfuric acid (62% H2SO4 content)
was added under stirring until the contents were acid to Congo red paper. This
required about 30 grams of the acid.
The resulting bis-(3,5,6-trichloro-2-hydroxyphenyl) methane was filtered,
washed with water until acid-free and dried to constant weight at 100°C (170
grams, MP 154° to 158°C). Crystallization of the 170 grams of dried bis-
(3,5,6-trichloro-2-hydroxyphenyl)methane from 300 grams toluene yielded a
first crop amounting to 105 grams of substantially pure bis-(3,5,6-trichloro-2-
hydroxyphenyl) methane, having a MP of 161° to 163°C (from US Patent
2,435,593).
brand name
Dial (Dial); E-Z Scrub (Becton Dickinson Microbiology); Gamophen (Arabrook); Germa-Medica (Huntington); Hexa-Germ (Huntington); Hexascrub (Prof Dspls); Phiso-Scrub (Sanofi Aventis); Phisohex (Sanofi Aventis); Pre-Op (Davis & Geck); Septi-Soft (Calgon); Septisol (Vestal); Soy-Dome (Bayer); Turgex (Xttrium);99 armour formula;Acnestrol (broparestrol);Acnestrol 3;Akne pyodron kur;Aknefug;Aknelan;Anacal;Asecool;Aserbine cream;Bilvon vet;Bismodyne;Cinthol;Clenisep;Coopaphene;Cordocel-h;Cresophene;Delta pimafucort;Derivative;Derl;Derma 10;Derma leaf;Dermohex;Dermolle;Dexolan;Dial toilet soap;Distocid;Dk 2;Dovaso;Ecto pellicur;Ectofum;Emlab;Fisohen;Fisohexx;Fitty derm;Flenaphthol;Gamophen surgical soap;Germibon;Gill soap;Haemovin;Heksaden;Hepadist;Hexadespon;Hexal;Hexaphenyl(1&b);Hexocreme;Hex-o-san;Jabon antiseptico;Kalacid;Lf 530;Loftyzon;Mamex;Mantacido;Med liquide san t;Micogamma;Nestosyl;P 47;Paradentol;Permucal;Phaisohex;Phasca;Phiso scrub;Phisohex(winthrop);Phiso-med;Phisoscrub;Phlebodine;Phorac;Phosohex;Predekzem;Pretulon;Proct anex;Prodermopur;Sapo-chlor;Sapoderm;Sebbafon;Sebo-cds;Sergi-cen;Skrub kreme;Solu-heks;Steridermis washing cream;Ster-zac antibacterial shaving foam;Ster-zac antibacterial soap;Ster-zac dc skin cleanser;Ster-zac powder;Sumasept;Super sat;Surg salve;Surge vet;Toracsol;Torbetol lotion;Vanseb;Vetalderm;Vulnusol spray;Wesco hex;Wescohex;Westasept;Zalpon antibacterial washing cream.
Therapeutic Function
Topical antiinfective
World Health Organization (WHO)
Hexachlorophene, an antimicrobial agent, was introduced in 1948 in proprietary liquid preparations and powders and was subsequently used extensively as a topical antiseptic. By the early 1970s its use in infants had been conclusively demonstrated to cause encephalopathy as a result of transdermal absorption. More recently it has been suggested that the drug has a teratogenic potential. Many regulatory authorities have placed rigorous restrictions on the medicinal use of hexachlorophene, particularly in preparations intended for infants. However, its use still commonly remains permissible at low concentrations as a preservative in toiletries and cosmetics. (Reference: (WHODI) WHO Drug Information, 3, 6, 1978)
General Description
A white free-flowing odorless powder. Insoluble in water and denser than water. Contact may irritate skin, eyes and mucous membranes. May be toxic by ingestion. Used to make other chemicals.
Air & Water Reactions
Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Hexachlorophene is incompatible with strong oxidizers. Hexachlorophene forms salts with alkalis and alkaline earths.
Hazard
FDA prohibits use unless prescribed by a physician. Questionable carcinogen.
Health Hazard
Inhalation of dust is poisonous; irritating to mucous membranes. Eye and skin irritant. Poisonous if swallowed. Symptoms following ingestion include anorexia, nausea, vomiting, abdominal cramps, and diarrhea. Dehydration may be severe and may be associated with shock.
Pharmacokinetics
Hexachlorophene, a detergent cleanser, is an antibacterial sudsing emulsion for topical administration. It is a bacteriostatic cleansing agent. It cleanses the skin thoroughly and has bacteriostatic action against staphylococci and other gram-positive bacteria. Cumulative antibacterial action develops with repeated use. Cleansing with alcohol or soaps containing alcohol removes the antibacterial residue.
Potential Exposure
HCP has been used as an antibacterial agent in a wide variety of consumer products, including soaps and deodorants; as a disinfectant. It has also been used as an antifungal agent to treat various citrus fruits and vegetables.
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove any con-tact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek medi-cal attention immediately. If this chemical contacts the skin,remove contaminated clothing and wash immediately withsoap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. If this .chemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure, begin res-cue breathing (using universal precautions, including resusci-tation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR if heart actionhas stopped. Transfer promptly to a medical facility. Whenthis chemical has been swallowed, get medical attention.Give large quantities of water and induce vomiting. Do notmake an unconscious person vomit.
Environmental Fate
HCP adsorbs very strongly to soil and is not expected to leach to groundwater. It may undergo slow photodegradation on the surface of soils and water based on its absorption of light (290 nm). No information is available on its biodegradation in soil or surface water. HCP released in water adsorbs very strongly to sediments and may bioconcentrate in aquatic organisms. It has an estimated bioconcentration factor of 317 000. HCP is not expected to hydrolyze or to significantly evaporate from water. When released into the air, HCP is expected to be mainly in the particle-sorbed state due to its low vapor pressure and high estimated Koc. It is expected to be removed from the atmosphere primarily by dry deposition, but it is also degraded by reaction with photochemically produced hydroxyl radicals, with an estimated vapor phase half-life of 2.5 days.
Metabolism
Not Available
Storage
Color Code- Blue: Health Hazard/Poison: Storein a secure poison location. Prior to working with thischemical you should be trained on its proper handling andstorage. Store in tightly closed containers in a cool,well-ventilated area away from oxidizers.
Shipping
UN2875 Hexachlorophene, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials.
Purification Methods
It forms needles from MeOH, C2H4Cl2, or toluene. The diacetate has m 175-176o (EtOH). A disinfectant is also available in MeOH (5mg/L). [Beilstein 6 III 5407, 6 IV 6659.]
Toxicity evaluation
Following skin absorption, HCP enters the nervous system and results in intramyelinic edema, splitting the intraperiod line of myelin in both the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system. Experimental studies with erythrocyte membranes show that HCP binds tightly to cell membranes, resulting in osmotic swelling of erythrocyte membranes by altering their permeability to sodium and potassium. HCP uncouples oxidative phosphorylation.
Incompatibilities
Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explo sions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides.
Waste Disposal
Incineration, preferably after mixing with another combustible fuel. Care must be exercised to assure complete combustion to prevent the formation of phosgene. An acid scrubber is necessary to remove the halo acids produced. Consult with environmental regulatory agencies for guidance on acceptable disposal practices. Generators of waste con taining this contaminant (≥100 kg/mo) must conform to EPA regulations governing storage, transportation, treat ment, and waste disposal.
Properties of Hexachlorophene
| Melting point: | 163-165 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 519.9°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.6065 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.5550 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 11 °C |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | DMF: 30 mg/ml; DMSO: 30 mg/ml; Ethanol: 30 mg/ml; Ethanol:PBS (pH 7.2) (1:4): 0.2 mg/ml |
| form | crystalline |
| pka | pKa 4.89 ± 0.02(H2O,t = 25.0±0.1,I=0.1(NaCl)) (Uncertain) |
| color | off-white to tan |
| Water Solubility | 19mg/L(25 ºC) |
| λmax | 300nm(MeOH)(lit.) |
| Merck | 14,4680 |
| BRN | 2064407 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with alkalies, akaline earths, tweens, strong oxidizers. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 70-30-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| IARC | 3 (Vol. 20, Sup 7) 1987 |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | 2,2'-Methylenebis(3,4,6-trichlorophenol)(70-30-4) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Hexachlorophene (70-30-4) |
Safety information for Hexachlorophene
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. |
Computed Descriptors for Hexachlorophene
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Hexachlorophene CAS 70-30-4View Details
Hexachlorophene CAS 70-30-4View Details
70-30-4 -
 Hexachlorophene CAS 70-30-4View Details
Hexachlorophene CAS 70-30-4View Details
70-30-4 -
 Hexachlorophene 96% (HPLC) CAS 70-30-4View Details
Hexachlorophene 96% (HPLC) CAS 70-30-4View Details
70-30-4 -
 3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 -
 4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
5305-40-8
