Hexachloro-1,3-butadiene
Synonym(s):Perchlorobutadiene
- CAS NO.:87-68-3
- Empirical Formula: C4Cl6
- Molecular Weight: 260.76
- MDL number: MFCD00000836
- EINECS: 201-765-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-10 11:56:18
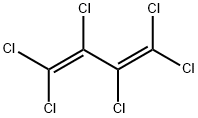
What is Hexachloro-1,3-butadiene?
Description
Hexachlorobutadiene was first synthesized in 1877 by chlorination of hexyl iodide. It is an industrial by-product of tetrachloroethylene, trichloroethylene, and perchloroethylene production.
Chemical properties
colourless liquid (typical odour recognition threshold:
Chemical properties
Hexachlorobutadiene is a clear, colorless liquid with a faint, turpentine-like odor.
Physical properties
Clear, yellowish-green liquid with a mild to pungent, turpentine-like odor. Odor threshold concentration is 6 ppb (quoted, Keith and Walters, 1992).
The Uses of Hexachloro-1,3-butadiene
Hexachloro-1,3-butadiene is used as an urinary biomarker as a tool for early screening of potential kidney toxicity. Hexachloro-1,3-butadiene (HCBD) causes kidney injury.
The Uses of Hexachloro-1,3-butadiene
Intermediate in the manufacture of rubber Compounds, chlorofluorocarbons, and lubricants. Hydraulic fluid, fluid for gyroscopes, heat transfer fluid, solvent, laboratory reagent. Soil fumigant for vineyards.
The Uses of Hexachloro-1,3-butadiene
Produced as an unwanted by-product during the production of tetrachloroethylene, trichloroethylene, carbon tetrachloride, and chlorine; formerly used as a pesticide in other countries
Definition
ChEBI: Hexachloro-1,3-butadiene is an organochlorine compound.
General Description
A colorless liquid with a mild odor. Insoluble in water and denser than water. Nonflammable. May be toxic by ingestion or inhalation. Used as a solvent and heat transfer fluid.
Air & Water Reactions
Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Hexachloro-1,3-butadiene rapidly decomposes rubber on contact. Can react vigorously with oxidizing materials. Reacts to form an explosive product with bromine perchlorate. . Gives highly toxic and irritating chloride fumes when burned.
Hazard
Toxic by ingestion and inhalation, a questionable carcinogen.
Health Hazard
Poisonous; may be fatal if inhaled, swallowed or absorbed through the skin. Inhalation causes repiratory difficulty and irritation of mucous membranes. Skin and eye irritant; may cause burns.
Potential Exposure
Hexachlorobutadiene is used as a sol vent; heat-transfer fluid; transformer fluid; hydraulic fluid; as a solvent for elastomers; as a wash liquor for removing higher hydrocarbons.
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek med-icalattention immediately. If this chemical contacts theskin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediatelywith soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. Ifthis chemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure,begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, includ-ing resuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR ifheart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medicalfacility. When this chemical has been swallowed, get medi-cal attention. Give large quantities of water and induce :vomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit.
Carcinogenicity
In rats given oral administration, it produced
benign and malignant tumors in the kidneys in both
sexes. The IARC then concluded that there is limited evidence
that HCBD is carcinogenic in rats.
Nakagawa et al. reported that HCBD is a potent nephrotoxicant
that selectively damaged the straight portion (pars
recta) of the proximal tubule in the rat. They also
reported administering 0.1% HCBD for 30 weeks to male
Wistar rats previously given 0.1% N-ethyl-N-hydroxyethylnitrosamine
(EHEN) in their drinking water for 2 weeks and
that the combined treatment resulted in a significantly higher
incidence of renal cell tumors than when EHEN was administered
alone.
Source
Hydraulic fluids and rubber (quoted, Verschueren, 1983). An impurity in aldrin.
Environmental Fate
Chemical/Physical. Hexachlorobutadiene will not hydrolyze to any reasonable extent (Kollig,
1993).
At influent concentrations of 1.0, 0.1, 0.01, and 0.001 mg/L, the GAC adsorption capacities
were 258, 91, 21, and 11 mg/g, respectively (Dobbs and Cohen, 1980).
Metabolic pathway
In the presence of glutathione (GSH), mouse liver microsomes and cytosol transform 14C-hexachloro- 1,3-butadiene (HCBD) to S- (pentachlorobutadienyl)glutathione (PCBG). PCBG formation in subcellular fractions from a mouse kidney is very limited. After an oral dose of HCBD to mice, PCBG in feces, and S-(pentachlorobutadienyl)-L- cysteine, N-acetyl-S-(pentachlorobutadienyl)-L- cysteine, and 1,1,2,3-tetrachlorobutenoic acid in the urine are identified as the metabolites.
Storage
Color Code- Blue: Health Hazard/Poison: Storein a secure poison location. Prior to working with thischemical you should be trained on its proper handling andstorage. Store in tightly closed containers in a cool, well-venti lated area away from oxidizers. Where possible, auto-matically pump liquid from drums or other storage contain-ers to process containers A regulated, marked area shouldbe established w here hex achlorobutadiene is handled, used,or stored. A regulated, marked area should be establi shedwhere this chemical is handled, used, or stored in compli-ance with OSHA Standard 1910. 1045.
Shipping
UN2279 Hexachlorobutadiene, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials.
Purification Methods
Wash the diene with four or five 1/10th volumes of MeOH (or until the yellow colour has been extracted), then stir it for 2hours with H2SO4, wash it with distilled water until neutral and filter it through a column of P2O5. Distil it under reduced pressure through a packed column. [Rytner & Bauer J Am Chem Soc 82 298 1960, Beilstein 1 IV 998.]
Toxicity evaluation
Hexachlorobutadiene specifically damages the pars recta portion of the proximal tubule with loss of the brush border. The mechanism involves nonoxidative formation of the glutathione conjugate in liver with subsequent transport to the kidney for mercapturic acid conjugate excretion. The resulting cysteine conjugates are substrates for cysteine-conjugate b-lyase, which removes ammonia and pyruvate from the cysteine conjugate to produce thionylacyl halides and thioketenes. These toxic thiol compounds can then bind covalently to proteins and DNA in proximal tubular cells to produce nephrotoxicity. S-(1,2,3,4,4- Pentachloro-1,3-butadienyl)-L-cysteine has been identified as the ultimate metabolite responsible for hexachlorobutadieneinduced nephrotoxicity. Mitochondrial dysfunction is reported to be the ultimate subcellular toxic lesion. Enterohepatic recirculation of hexachlorobutadiene–glutathione conjugates is believed to play a major role in this mechanism, since cannulation of the bile duct of rats prevents nephrotoxicity.
Incompatibilities
Strong reaction with oxidizers, aluminum powder. Attacks aluminum; some plastics, rubber and coatings
Waste Disposal
High temperature incineration with flue gas scrubbing. Consult with environmental regulatory agencies for guidance on acceptable disposal practices. Generators of waste containing this contaminant (≥100 kg/mo) must conform to EPA regulations governing storage, transportation, treatment, and waste disposal.
Properties of Hexachloro-1,3-butadiene
| Melting point: | -19 °C |
| Boiling point: | 210-220 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 1.68 |
| vapor pressure | 0.2 mm Hg ( 20 °C) |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | 210-220°C |
| storage temp. | +4°C
|
| solubility | Soluble in ethanol and ether (U.S. EPA, 1985) |
| form | neat |
| Odor | faint turpentine odor |
| Water Solubility | (mg/L): 4.78 at 25 °C (shake flask-LSC, Banerjee et al., 1980) 4 at 20–25 °C (Geyer et al., 1980) |
| Merck | 14,4678 |
| BRN | 1766570 |
| Henry's Law Constant | 3.55, 5.87, 6.90, 10.5, and 15.3 at 2.0, 6.0, 10.0, 18.0, and 25.0 °C, respectively (EPICS-SPME,
Dewulf et al., 1999) |
| Exposure limits | Potential occupational carcinogen. NIOSH REL: TWA 20 ppb (240 mg/m3);
ACGIH TLV: TWA 0.02 ppm (adopted). |
| Dielectric constant | 2.6(Ambient) |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with rubber, oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 87-68-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| IARC | 3 (Vol. 73) 1999 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Hexachlorobutadiene (87-68-3) |
Safety information for Hexachloro-1,3-butadiene
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H301:Acute toxicity,oral H310:Acute toxicity,dermal H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H351:Carcinogenicity H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Hexachloro-1,3-butadiene
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Hexachlorobutadiene CAS 87-68-3View Details
Hexachlorobutadiene CAS 87-68-3View Details
87-68-3 -
 Hexachloro-1,3-butadiene 97% CAS 87-68-3View Details
Hexachloro-1,3-butadiene 97% CAS 87-68-3View Details
87-68-3 -
 Hexachloro-1,3-butadiene CAS 87-68-3View Details
Hexachloro-1,3-butadiene CAS 87-68-3View Details
87-68-3 -
 3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 -
 4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
5305-40-8
