Halothane
Synonym(s):2-Bromo-2-chloro-1,1,1-trifluoroethane;Halothane
- CAS NO.:151-67-7
- Empirical Formula: C2HBrClF3
- Molecular Weight: 197.38
- MDL number: MFCD00009602
- EINECS: 205-796-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-27 09:38:02
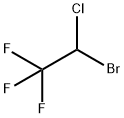
What is Halothane?
Toxicity
Toxic effects of halothane include malignant hyperthermia and hepatitis.
Description
Halothane was introduced into medical practice in the United States in 1956 as a
nonflammable, nonexplosive, halogenated volatile anesthetic that usually is mixed with air or
oxygen. The presence of the carbon–halogen bonds contributes to its nonflammability. This clear
liquid with a sweet odor was developed based on predictions that its halogenated structure would
provide chemical stability, an intermediate blood solubility, and significant anesthetic potency.
Halothane is the only useful volatile anesthetic possessing a bromine atom, which has been
suggested to contribute to its potency. Similarly, the addition of fluorine atoms, of which halothane
has three, is thought to contribute to the increased potency, volatility, and increased chemical
stability of the hydrocarbon skeleton.
Halothane produces rapid onset and recovery from anesthesia with high potency when used alone
or in combination with nitrous oxide. Most metals, with the exception of chromium, nickel, and
titanium, are easily tarnished by halothane. Although halothane is relatively stable, it is subject to
spontaneous oxidative decomposition to hydrochloric acid, hydrobromic acid, and phosgene. For
this reason, it is available in dark, amber glass containers with thymol added as a preservative to
minimize decomposition. Halothane may permeate into the rubber components of the anesthetic
delivery devices, which might account for some slowing of the induction onset and recovery.
Approximately 20% of an administered dose is metabolized, which accounts, in part, for the
increased hepatotoxicity observed with this agent.
Chemical properties
Clear, colourless, mobile, heavy, non-flammable liquid
Chemical properties
Halothane is a highly volatile, nonflammable, colorless liquid. Sweet odor.
Originator
Fluothane,Ayerst,US,1958
The Uses of Halothane
Halothane is used as a clinical anesthetic.
The Uses of Halothane
2-Bromo-2-chloro-1,1,1-trifluoroethane, or halothane, has been used in a study that combined molecular simulations with free energy simulations to study solvation of halothane in polarizable water and methanol. Halothane has also been used in a study to investigate the interaction of anesthetics with the Rho GTPase regulator Rho GDP dissociation inhibitor.
The Uses of Halothane
depigmentor, antioxidant
Background
A nonflammable, halogenated, hydrocarbon anesthetic that provides relatively rapid induction with little or no excitement. Analgesia may not be adequate. nitrous oxide is often given concomitantly. Because halothane may not produce sufficient muscle relaxation, supplemental neuromuscular blocking agents may be required. (From AMA Drug Evaluations Annual, 1994, p178)
Indications
For the induction and maintenance of general anesthesia
What are the applications of Application
2-Bromo-2-chloro-1,1,1-trifluoroethane is an inhalation anesthetic
Indications
Because of its potent and rapid effect, halothane (MAC0.77) is used in special vaporizers mixed with oxygen and water. The high lipid – blood partition coefficient leads to considerable accumulation in tissue and fat. Halothane reduces the peripheral vascular resistance, increases the possibility of arrythmias, and has a negative effect on liver function. On repeated use it is hepatotoxic.
Definition
ChEBI: A haloalkane comprising ethane having three flouro substituents at the 1-position as well as bromo- and chloro substituents at the 2-position.
Definition
A colorless nonflammable liquid halocarbon used as a general anesthetic. The systematic name is 1-chloro-1-bromo-2,2,2-trifluoroethane.
Manufacturing Process
According to US Patent 2,849,502, the apparatus used consisted of a 2" x 24"
silica tube packed with silica chips and enclosed in a vertical electric furnace.
1,1,1-trifluoro-2-chloroethane as vapor and bromine as liquid were introduced
into a narrow tube passing down the inside of the reaction tube. The mixed
reactants then passed up through the reaction tube which was maintained at
a temperature of about 465°C. The reaction products were passed through a
water-cooled condenser which condensed out most of the desired 1,1,1-
trifluoro-2-bromo-2-chloroethane along with any high boiling by-products and
unchanged bromine.
This condensate was washed with dilute caustic soda solution and dried over
calcium chloride. The exit gases from this condenser were scrubbed with
water and dilute caustic soda solution, dried and passed to a condenser cooled
with a mixture of solid carbon dioxide and trichloroethylene which caused the
unchanged 1,1,1-trifluoro-2-chloroethane to condense. This second
condensate was then combined with the first and the mixture was fractionally
distilled.
During a run of 2 hours 620 grams of 1,1,1-trifluoro-2-chloroethane and 630
grams of bromine were fed to the reactor and the product was worked up as
described above. On fractional distillation there was obtained a first cut up to
50°C consisting of unchanged 1,1,1-trifluoro-2-chloroethane, then a middle
cut between 50° and 52°C consisting of substantially pure 1,1,1-trifluoro-2-
bromo-chloroethaneand a higher boiling residue that contained a further
quantity of the desired product together with some 1,1,1-trifluoro-2,2-
dibromo-2-chloroethane. On redistillation of the middle fraction pure 1,1,1-
trifluoro-2-bromo-2-chloroethane was obtained with BP 50° to 50.5°C.
brand name
Fluothane (Wyeth).
Therapeutic Function
Inhalation anesthetic
Biological Functions
Halothane (Fluothane) depresses respiratory function,
leading to decreased tidal volume and an increased rate
of ventilation. Since the increased rate does not adequately
compensate for the decrease in tidal volume,
minute ventilation will be reduced; plasma PaCO2 rises,
and hypoxic drive is depressed.With surgical anesthesia,
spontaneous ventilation is inadequate, and the patient’s
ventilation must be controlled.
Halothane administration can result in a marked reduction
in arterial blood pressure that is due primarily
to direct myocardial depression, which reduces cardiac
output. The fall in pressure is not opposed by reflex
sympathetic activation, however, since halothane also
blunts baroreceptor and carotid reflexes. Systemic vascular
resistance is unchanged, although blood flow to
various tissues is redistributed. Halothane also sensitizes
the heart to the arrhythmogenic effect of catecholamines.
Thus, maintenance of the patient’s blood
pressure with epinephrine must be done cautiously.
General Description
Clear colorless highly volatile liquid with a sweet chloroform-like odor . Density 1.875 g / cm3. Boiling point 122.4°F (50.2°C). Noncombustible.
General Description
Halothane is a nonflammable, nonpungent, volatile, liquid,halogenated (F, Cl, and Br) ethane (bp=50°C), introducedin 1956. Halothane may increase heart rate, cause cardiacarrhythmias, increase cerebral blood flow, and increase intracranialpressure.It can undergo spontaneous oxidationwhen exposed to ultraviolet light to yield HCl, HBr, Cl ,Br- , and phosgene (COCl2). To prevent oxidation it ispackaged in amber bottles with a low concentration of thymol(0.01%) as a stabilizer. The drug has a high potency(MAC=0.75%), a blood:gas partition coefficient of 2.4,and high adipose solubility. Halothane undergoes both reductiveand oxidative processes with up to 20% of the doseundergoing metabolism .The trifluoroacetylchloride metabolite is electrophilic and can form covalentbonds with proteins leading to immune responses andhalothane hepatitis upon subsequent halothane exposure.Halothane hepatitis is rare with 1 case reported for every6,000 to 35,000 patients exposed.
Air & Water Reactions
Slightly water soluble.
Reactivity Profile
2-BROMO-2-CHLORO-1,1,1-TRIFLUOROETHANE is sensitive to exposure to light. Incompatible with oxidizing materials. Tarnishes or corrodes most metals, with the exception of chromium, nickel and titanium. When moisture is present, 2-BROMO-2-CHLORO-1,1,1-TRIFLUOROETHANE attacks aluminum, brass and lead, but not copper. Contact causes rubber and some plastics to deteriorate rapidly.
Health Hazard
Health hazard may arise from exposure tohigh concentrations of vapors. The target sites are the central nervous system, car diovascular system, and liver. The toxiceffects include depression of the central ner vous system, nausea, vomiting, increasedbody temperature, excitability, arrhythmias,vasodilatation, hepatitis, and liver necrosis.An anesthetic effect in humans is noted atan exposure level of 10,000 ppm. Repeatedexposure to halothane at anesthetic concen trations may result in hepatic lesions andnecrosis. Contact of liquid with the eyes mayresult in severe irritation. The lethal con centration in humans for a 3-hour exposureperiod is in the range of 7000 ppm.
LC50 value, inhalation (mice): 22,000 ppm/10 min
LD50 value, oral (guinea pigs): 6000 mg/kg
No mutagenic effect was observed. Carcino genicity in animals has not been reported.
Fire Hazard
Literature sources indicate that 2-BROMO-2-CHLORO-1,1,1-TRIFLUOROETHANE is nonflammable.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Inhalation anesthetic. In an effect believed to be independent of anesthesia, halothane inhibits synthesis of 5-hydroxytryptamine in brain tissue, probably at the tryptophan hydroxylase step.
Pharmacokinetics
Halothane is a general inhalation anesthetic used for induction and maintenance of general anesthesia. It reduces the blood pressure and frequently decreases the pulse rate and depresses respiration. It induces muscle relaxation and reduces pains sensitivity by altering tissue excitability. It does so by decreasing the extent of gap junction mediated cell-cell coupling and altering the activity of the channels that underlie the action potential.
Clinical Use
The use of inhaled anesthetics and halothane in particularcan produce malignant hyperthermia (MH) in geneticallysusceptible individuals. This results in an increase inbody temperature, tachycardia, tachypnea, acidosis, andrhabdomylolysis. MH is a result of the excessive release ofcalcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR). Patientswith an inherited mutation in the ryanodine receptor(RYR1), which is located in the SR, are at an increased riskof developing MH when exposed to an inhaled anesthetictriggering agent. Treatment entails discontinuing the anestheticagent, rapid cooling, intravenous dantrolene sodium,and supportive measures. MH has been reported to occurwith all anesthetics agents and with succinylcholine, a depolarizingneuromuscular blocker. The combination ofhalothane and succinylcholine appears to trigger a great extentof the MH episodes. Patients with a family history ofMH can be genetically screened for MH susceptibility viathe caffeine–halothane contracture test. This test is invasiverequiring a piece of skeletal muscle to conduct and it isexpensive costing approximately $5,000 (cost in 2008).Noninvasive molecular genetic screening is currently beingdeveloped.
Synthesis
Halothane is manufactured by chlorination of
CF3CH2Br or bromination of CF3CH2Cl in the
gas phase at 250 – 475 ?C or by the rearrangement
.
Potential Exposure
Halothane is used as an inhalation anesthetic. It has been estimated that halothane accounts for two-thirds of all anesthetics.
Veterinary Drugs and Treatments
Halothane remains a useful general anesthetic in veterinary medicine due to its relative safety, potency, controllability, non-flammability, and comparatively low cost. However, its use has been largely supplanted by newer agents such as isoflurane and sevoflurane that have less cardiodepressant effects.
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek med-ical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts theskin, remove contaminated clothingand wash immediatelywith soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately.If this chemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure,begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, includ-ing resuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR ifheart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medicalfacility. When this chemical has been swallowed, get medi-cal attention. Give large quantities of water and induce :vomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit.
Metabolism
Halothane is metabolized in the liver, primarily by CYP2E1, and to a lesser extent by CYP3A4 and CYP2A6.
Storage
Color Code- Green: General storage may be used.Prior to working with this chemical you should be trainedon its proper handling and storage. Store in tightly closedcontainers in a dark, cool, well-ventilated area, away fromdirect sunlight, oxidizers.
Shipping
UN3082 Environmentally hazardous substances, liquid, n.o.s., Hazard class: 9; Labels: 9-Miscellaneous haz ardous material, Technical Name Required.
Incompatibilities
May attack rubber and some plastics; sensitive to light. Light causes decomposition. May be stabilized with 0.01% thymol. Halothane is incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanga nates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); con tact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides. Tarnishes or corrodes most metals, with the exception of copper, chromium, nickel, and titanium. Attacks aluminum, brass and lead in the presence of moisture. Attacks rubber and causes some plastics to deteriorate rapidly.
Waste Disposal
The compound is mixed with a combustiblesolvent and burned in a chemical incineratorequipped with an afterburner and scrubber.
Properties of Halothane
| Melting point: | -115.75°C |
| Boiling point: | 50.2 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 1.872 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| vapor pressure | 4.5 psi ( 20 °C) |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | 49-50°C |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Slightly soluble in water, miscible with anhydrous ethanol and with trichloroethylene. |
| form | Colorless liquid |
| color | Colorless to light yellow |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in water (8 mg/ml). |
| Sensitive | Light Sensitive |
| Merck | 14,4603 |
| BRN | 1736947 |
| Exposure limits | TLV-TWA 50 ppm (~400 mg/m3) (ACGIH). |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 151-67-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Halothane (151-67-7) |
Safety information for Halothane
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H318:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation H360:Reproductive toxicity |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Halothane
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
110-86-1 -
 Guanine , 99%View Details
Guanine , 99%View Details
73-40-5 -
 Piperazine Spot supply, best priceView Details
Piperazine Spot supply, best priceView Details
110-85-0 -
 Potassium Hydroxide 90%View Details
Potassium Hydroxide 90%View Details
1310-58-3 -
 Dibutyl PhthalateView Details
Dibutyl PhthalateView Details
84-74-2 -
 Imidazole Spot supply, competitive priceView Details
Imidazole Spot supply, competitive priceView Details
288-32-4 -
 Octadecyl 3-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)propionate 98% (GC)View Details
Octadecyl 3-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)propionate 98% (GC)View Details
2082-79-3 -
 Thiourea 99% ARView Details
Thiourea 99% ARView Details
62-56-6
