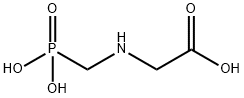
Glyphosate
Synonym(s):N-(Phosphonomethyl)glycine;Glyphosate
- CAS NO.:1071-83-6
- Empirical Formula: C3H8NO5P
- Molecular Weight: 169.07
- MDL number: MFCD00055350
- EINECS: 213-997-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-23 21:30:31
What is Glyphosate?
Description
Glyphosate (N-(phosphonomethyl)glycine; 1071-83-6) is the active ingredient in several commercial herbicides for nonselective weed control. Glyphosate herbicides are among the world’s most widely used herbicides. Roundup?, containing the active ingredient glyphosate, was developed and introduced by Monsanto Company in 1974. Other formulations include WeatherMax, UltraMAX, Buccaneer, Razor Pro, Rodeo, and AquaMaster?. Some crops such as soybeans and cotton have been genetically engineered to be resistant to glyphosate (Roundup Ready), allowing farmers to use glyphosate as a postemergence herbicide. The United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) considers glyphosate to be relatively low in toxicity compared to organochlorine and organophosphate pesticides.
Description
Glyphosate, or?N-(phosphonomethyl)glycine, was originally developed as a corrosion inhibitor, but it has been the world’s most widely used herbicide for almost 40 years. Monsanto patented it in the early 1970s and began to sell it under the trade name Roundup. More recently, the company developed glyphosate-resistant transgenic crop seeds. But competition has hurt Roundup, and?Monsanto has announced cutbacks?associated with this business unit.
Chemical properties
Glyphosate is a broad-spectrum, non-selective systemic herbicide. It is a colorless crystal at room temperature and is soluble in acetone, ethanol, xylene, and water. Glyphosate is used for the control of annual and perennial plants, including grasses, sedges, broadleaved weeds, and woody plants. It can be used on non-cropland as well as on many varieties of crops. Glyphosate itself is an acid, but it is commonly used in salt form, most commonly isopropylamine salt. It may also be available in acidic or trimethylsulfonium salt forms. It is generally distributed as water-soluble concentrates and powders. Glyphosate is a GUP.
Chemical properties
Glyphosate, an organophosphate/carboxylic acid (substituted), is a colorless crystalline powder. Often used as a liquid in a carrier solvent which may change physical and toxicological properties.
The Uses of Glyphosate
Glyphosate is the active ingredient in several commercial herbicides. It is a broad-spectrum systemic herbicide for various types of weeds, grasses (Poaceae), and woody plants.
The Uses of Glyphosate
Nonselective, postemergence, broad spectrum herbicide used to control annual and perennial grasses, sedges, broad-leaved and emerged aquatic weeds. This herbicide is also used to control insects on fruit trees.
What are the applications of Application
Glyphosate is an herbicide
Definition
ChEBI: Glyphosate is a phosphonic acid resulting from the formal oxidative coupling of the methyl group of methylphosphonic acid with the amino group of glycine. It is one of the most commonly used herbicides worldwide, and the only one to target the enzyme 5-enolpyruvyl-3-shikimate phosphate synthase (EPSPS). It has a role as an agrochemical, an EC 2.5.1.19 (3-phosphoshikimate 1-carboxyvinyltransferase) inhibitor and a herbicide. It is a phosphonic acid and a glycine derivative. It is a conjugate acid of a glyphosate(2-) and a glyphosate(1-).
General Description
Odorless white powder. Decomposition begins at approximately 419°F (darkens). pH (1% solution in water) 2.5.
Reactivity Profile
Glyphosate may react with galvanized steel or unlined steel (except stainless steel) containers to produce hydrogen gas which may form a highly combustible or explosive gas mixture. Glyphosate can react with caustic (basic) materials to liberate heat. Glyphosate is corrosive to iron.
Health Hazard
Glyphosate is practically non-toxic if ingested, with a reported acute oral LD50 of 5600 mg/kg in the rat. The toxicities of the technical acid (glyphosate) and the formulated product (Roundup) are nearly the same. Laboratory animals, such as rats, dogs, mice, and rabbits, exposed to glyphosate for 2 years did not indicate any kind of adverse health effects.
Fire Hazard
Flash point data for Glyphosate are not available; however, Glyphosate is probably combustible.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Glyphosate?(N-[phosphonomethyl] glycine) is the herbicide form of the isopropylamine salt of glyphosate.
Pharmacology
Glyphosate is the only known inhibitor of the biosynthesis
of aromatic acids that has been commercialized as a
successful herbicide (1). Glyphosate acts as a competitive
inhibitor of phosphoenolpyruvate, the natural substrate of
the enzyme 5-enolpyruvyl-shikimate-3-phosphate (EPSP)
synthase, and causes amassive accumulation of shikimate
in treated plant tissue (1).
Glyphosate is a nonselective herbicide, and it has
been characterized as a low-risk herbicide for the
evolution of herbicide resistance. A few weed species
are somewhat tolerant to glyphosate, probably due
to uptake or translocation mechanisms, but no plant
species has sufficient resistance to glyphosate to allow its use directly on the crop as a selective herbicide.
The complicated procedure used to genetically engineer
the commercialized glyphosate-tolerant crops (31) would
suggest that the evolution of glyphosate-resistant weeds
will be a very slow process and that the level of resistance
from field selection will be relatively low.
Safety Profile
Poison by intraperitoneal route. Moderately toxic by ingestion. Human systemic effects: arrhythmias, blood pressure lowering, body temperature increase, change in heart rate, convulsions, darrhea, fibrosing alveolitis, fibrosis, hypermoultty, respiratory depression, respiratory stimulation. Used as an herbicide. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of NOx and POx.
Potential Exposure
A potential danger to those involved in the manufacture, formulation, and application of this nonselective and nonresidual pre-emergence organophos phate herbicide. Has wide residential use in the United States for the control of weeds.
Environmental Fate
Soil. Degrades microbially in soil releasing phosphoric acid, N-nitrosoglyphosate (Newton et al., 1984), ammonia (Cremlyn, 1991), N,N-dimethylphosphinic acid, N-methylphosphinic acid, aminoacetic acid (glycine), N-methylaminoacetic acid (sarcosine), hydroxymethylphosphonic acid (Duke et al., 1991), aminomethylphosphonic acid (Normura and Hilton, 1977; Rueppel et al., 1977; Hoagland, 1980; Duke et al., 1991; Muir, 1991) and carbon dioxide (Sprankle et al., 1975; Cremlyn, 1991). N-Nitrosoglyphosate also formed from the nitrosation of glyphosate in soil solutions containing nitrite ions (Young and Kahn, 1978).
The reported half-life of glyphosate in soil is <60 days (Hartley and Kidd, 1987). In the laboratory, experimentally determined dissipation rates of glyphosate in a Lintonia sandy loam, Drummer silty clay, Norfolk sandy loam and Raye silty loam were 0.028
Plant. In a forest brush field ecosystem, the half-life of glyphosate in foliage and litter ranged from 10.4 to 26.6 days, respectively (Newton et al., 1984).
Photolytic. When an aqueous solution of glyphosate (1 ppm) was exposed to outdoor sunlight for 9 weeks (from August 12 through October 15, 1983), aminomethylphosphonic acid and ammonia formed as major and minor photoproducts, respectively (Lund-H?ie and Friestad, 1986). More than 90% degradation was observed after only 4 weeks of exposure. Photodegradation was also observed when an aqueous solution was exposedindoors to UV light (λ = 254 nm). The reported half-lives of this reaction at starting concentrations of 1.0 and 2,000 ppm were 4 days and 3–4 weeks, respectively. When aqueous solutions were exposed indoors to sodium light (λ = 550–650 nm) and mercury light (λ = 400–600 nm), no photo-degradation occurred (Lund-H?ie and Friestad, 1986).
Chemical/Physical. Under laboratory conditions, the half-life of glyphosate in natural waters was 7–10 weeks (Muir, 1991). A 1% aqueous solution has a pH of 2.5 (Keith and Walters, 1992). This suggests glyphosate will react with alkalies and amin
Metabolic pathway
The photolytic degradation of glyphosate results in the formation of glycine, (aminomethyl)phosphonic acid (AMPA), and NH3. Glyphosate undergoes nitrogen ? carbon cleavage on reaction with m- chloroperoxybenzoic acid, leading ultimately to many of the same products formed on their metabolism and environmental degradation. It is suggested that insoluble complexes of glyphosate with iron(III), copper(II), calcium, and magnesium ions are formed at near-neutral pH, a mechanism of which is the inactivation of glyphosate in contaminated groundwater.268 The bacterium degrades high levels of glyphosate, primarily by converting to AMPA. Appreciable uptake of glyphosate is observed with seedlings and leaves and to a lesser extent with culture cells in the form of non-metabolized glyphosate, with AMPA as the only detectable metabolite.
Metabolism
In soils, glyphosate is rapidly mineralized within 1 to 2 weeks, and degradation occurs under aerobic and anaerobic conditions (79). The C?P bond is relatively resistant to chemical degradation, but several bacteria, e.g., Arthrobacter (80), Pseudomonas (81), various members of the Rhizobiaceae family (82), and certain fungi (83), have been shown to metabolize glyphosate.
Shipping
UN3077 Environmentally hazardous substances, solid, n.o.s., Hazard class: 9; Labels: 9-Miscellaneous haz ardous material, Technical Name Required.
Toxicity evaluation
Glyphosate’s herbicidal action works by disrupting 5-enolpyruvylshikimate- 3-phosphate (EPSP) synthase, a plant enzyme involved in the production of the amino acids such as phenylalanine, tyrosine, and tryptophan. EPSP synthase is not present in humans or animals and is the reason why glyphosate has relatively low mammalian toxicity. Additional mechanisms of action such as uncoupling of oxidative phosphorylation have been proposed. Glyphosate-based formulations have been shown to disrupt aromatase activity and mRNA levels and interact with the active site of the purified enzyme in human placental cells. As a result, some researchers consider formulations like Roundup? to be a potential endocrine disruptor. Adjuvants present in many commercial preparations may facilitate the observed effect. In contrast to organophosphate insecticides, glyphosate is not an inhibitor of acetylcholinesterase.
Incompatibilities
Organophosphates are susceptible to for mation of highly toxic and flammable phosphine gas in the presence of strong reducing agents such as hydrides. Partial oxidation by oxidizing agents may result in the release of toxic phosphorus oxides. Compounds of the carboxyl group react with all bases, both inorganic and organic (i.e., amines) releasing substantial heat, water, and a salt that may be harmful. Incompatible with arsenic compounds (releases hydrogen cyanide gas), diazo compounds, dithio carbamates, isocyanates, mercaptans, nitrides, sulfides (releasing heat, toxic, and possibly flammable gases), thio sulfates, and dithionites (releasing hydrogen sulfate and oxides of sulfur). Solutions are corrosive to iron, unlined steel, and galvanized steel, forming a highly combustible or explosive gas mixture. Do not store glyphosate in contain ers made from these materials.
Properties of Glyphosate
| Melting point: | 230 °C (dec.) (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 465.8±55.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.74 |
| Flash point: | 230°C |
| storage temp. | APPROX 4°C
|
| solubility | DMSO: slightly soluble; PBS (pH 7.2): slightly soluble |
| pka | 1.22±0.10(Predicted) |
| form | solid |
| color | White to off-white |
| Odor | odorless |
| Water Solubility | 1.2 g/100 mL |
| Decomposition | 230 ºC |
| Merck | 13,4525 |
| BRN | 2045054 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with metals, strong oxidizing agents, strong bases. May be light sensitive. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 1071-83-6(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| IARC | 2A (Vol. 112) 2017 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Glyphosate (1071-83-6) |
Safety information for Glyphosate
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H312:Acute toxicity,dermal H318:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H411:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P391:Collect spillage. Hazardous to the aquatic environment P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Glyphosate
| InChIKey | XDDAORKBJWWYJS-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Glyphosate manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Glyphosate >98% (HPLC) CAS 1071-83-6View Details
Glyphosate >98% (HPLC) CAS 1071-83-6View Details
1071-83-6 -
 Glyphosate 40% aqueous solution 95% CAS 1071-83-6View Details
Glyphosate 40% aqueous solution 95% CAS 1071-83-6View Details
1071-83-6 -
 Glyphosate 71% Sg, Packet, 100gmView Details
Glyphosate 71% Sg, Packet, 100gmView Details
1071-83-6 -
 Granules Glyphosate 71 Sg, 25 kgView Details
Granules Glyphosate 71 Sg, 25 kgView Details
1071-83-6 -
 Glyphosate 71 Sg, Hdpe BagsView Details
Glyphosate 71 Sg, Hdpe BagsView Details
1071-83-6 -
 Glyphosate 54%SL, 1 LitersView Details
Glyphosate 54%SL, 1 LitersView Details
1071-83-6 -
 Liquid Entire Kill Glyphosate 41% SLView Details
Liquid Entire Kill Glyphosate 41% SLView Details
1071-83-6 -
 Systemic Knock Down(Glyphosate 41%SL), Packaging Type: BottleView Details
Systemic Knock Down(Glyphosate 41%SL), Packaging Type: BottleView Details
1071-83-6
