glucomannan
- CAS NO.:11078-31-2
- Empirical Formula: (C35H49O29)n
- Molecular Weight: 1000000
- MDL number: MFCD00131256
- EINECS: 234-394-2
- Update Date: 2024-11-14 14:09:35
What is glucomannan?
Description
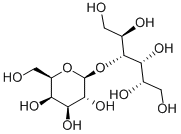
Glucomannan is a linear polysaccharide comprising 1,4-β-linked D-glucosyl and D-mannosyl residues, where the glucose:mannose (Glc:Man) ratio varies considerably. Konjac (Amorphophallus konjac) glucomannan has a Glc:Man ratio of approx. 2:3, Aloe vera glucomannan a ratio of 1:2, and salep (Orchis mureo) glucomannan has a ratio of approximately 1:4. All of the polysaccharides are acetylated, which imparts water solubility. Glucomannans are major cell-wall reserve carbohydrates in tubers of several plant genera. At certain stages in the development of the plants, the glucomannan is degraded and serves as an energy source. The only industrially exploited glucomannan is konjac. Like carob galactomannan, this polysaccharide interacts with agar, carrageenan and xanthan to form solutions of increased viscosity or gels. This interaction is exploited in the pet-food industry in canned dog food. Recently, glucomannan has also been used in jelly sweets. In this application, the glucomannan has been found to be dangerous, leading to choking deaths of some consumers. This has led to a ban of these types of sweets in Europe and America, and a need for an accurate analytical procedure for glucomannan analysis.
Chemical properties
Raw glucomannan is a soluble, fermentable, and highly viscous dietary fiber from the elephant yam or konjac plant, native to Asia. Konjac glucomannan (KGM) is water soluble and a viscous dietary fiber due to its high water absorbing capacity. The chemical structure of glucomannan consists in an 8:5 mannose:glucose ratio, linked by b-glycosidic bonds, making raw glucomannan the highest molecular weight and viscosity of any other known dietary fibers.
Occurrence
Glucomannan is purifi ed from konjac fl our by chemical processing.
The Uses of glucomannan
Glucomannan is useful as a bulk laxative.
Biological Functions
Weight Management:Glucomannan is a soluble fiber with a high molecular weight and viscosity compared to other fibers, providing enhanced support for weight management. Significant mean weight loss was observed in one 8-week double blind trial, an effect that may be due to the effect of konjac glucomannan on satiety. A later study demonstrated that addition of a resistance and endurance exercise training program to a glucomannan-rich diet provides enhanced support for healthy body composition, lipid metabolism and triglycerides.
Cardiovascular Health: In several controlled trials, konjac glucomannan supported healthy lipid metabolism and triglyceride levels, possibly by promoting healthy bile acid secretion. Additionally, it supports healthy glucose utilization and vascular function to support overall cardiovascular health.
GI Health: As a dietary fiber, konjac glucomannan supports GI regularity. Research indicates that it also promotes healthy microflora balance, enhancing the growth of lactobacillus and bifidobacteria for a healthy gastrointestinal tract.
Side Effects
Gastric discomfort, loose stools, flatulence, and diarrhea are the most commonly reported side effects.
Mode of action
Glucomannan improved blood lipid levels by enhancing fecal excretion of neutral sterol; and bile acids bind biliary salts, taking the blood lipids with them.
Lipid-lowering action may include an inhibition of cholesterol absorption in the jejunum (19) and bile acid absorption in the ileum (33) mediated by viscosity or less postprandial stimulation of 3-hydroxy3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase.
Raw glucomannan is thought to prolong gastric emptying time, which increases satiety, reduces body weight, decreases the ingestion of foods that increase cholesterol and glucose concentrations, reduces the postprandial rise in plasma glucose, suppresses hepatic cholesterol synthesis, and increases the fecal elimination of cholesterol-containing bile acids. There is no evidence that nonviscous versions more commonly marketed in the U.S. provide any health effects.
Precautions
In tablet form, there have been reports of esophageal and gastrointestinal obstruction, as well as choking to the point of causing obstruction. Advise patients to use glucomannan in powdered or capsule form (nonviscous, no health effects).
Glucomannan displays no evidence of psychotropic activity, but now has considerable choking hazard.
Safety information for glucomannan
glucomannan manufacturer
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 11138-66-5 99%View Details
11138-66-5 99%View Details
11138-66-5 -
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1