GALLIUM NITRATE
- CAS NO.:13494-90-1
- Empirical Formula: GaH4NO3
- Molecular Weight: 135.76
- MDL number: MFCD00011016
- EINECS: 236-815-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2023-11-09 17:14:14
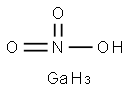
What is GALLIUM NITRATE?
Absorption
Gallium nitrate was infused at a daily dose of 200 mg/m2 for 5 (n=2) or 7 (n=10) consecutive days to 12 cancer patients. In most patients, mean steady-state plasma concentrations were reached after 18 to 24 hours of infusion. The average steady-state plasma levels of gallium observed among seven fully evaluable patients was between 1134 and 2399 ng/mL. In one patient who received daily infusion doses of 100, 150 and 200 mg/m2, the apparent steady-state levels of gallium did not increase proportionally with an increase in dose.
Toxicity
The oral, subcutaneous, and intravenous LD50 in mice are 4360 mg/kg, 600 mg/kg, and 55 mg/kg, respectively.
Rapid intravenous infusion of gallium nitrate or use of doses higher than recommended (200 mg/m2) may cause nausea and vomiting and a substantially increased risk of renal insufficiency. In the event of overdosage, further drug administration should be discontinued, serum calcium should be monitored, and the patient should receive vigorous intravenous hydration, with or without diuretics, for two to three days. During this time period, renal function and urinary output should be carefully monitored so that fluid intake and output are balanced.
Description
Gallium nitrate, initially developed as an anticancer agent, was introduced by Fujisawa as an orphan drug for the treatment of cancer-related hypercalcemia and bone metastases that do not respond to adequate hydration. The compound acts specifically on bone by inhibiting calcium resorption and also possibly by stimulating bone formation. Compared with calcitonin and etidronate, gallium nitrate is more potent and substantially longer acting. Other potential uses could be in the treatment of osteoporosis and Paget’s disease.
Chemical properties
white; crystal(s) powder(s) [MER06]
Chemical properties
The structural formula of gallium nitrate is Ga(NO3)3. Gallium nitrate is an anhydrate salt that is very soluble in water and soluble in 95% ethanol. It is stable in commonly used intravenous fluids for 14 days at room temperature and at 5 ℃, and physically compatible for injection with selected drug products, with the exception of diazepam injection.This chemical is an oxidizer, and is probably combustible
Originator
Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center (U.S.A.)
The Uses of GALLIUM NITRATE
Gallium is the second metal ion with clinical activity used in
cancer treatment. Gallium nitrate has demonstrated
antitumor activity in a variety of murine tumor models,
including Walker 256 carcinosarcoma, fibrosarcoma M-89,
leukemia K-1964, adenocarcinoma 755, mammary carcinoma
YMC, reticulum cell sarcoma A-RCS, lymphoma
P1798, and osteosarcoma 124F. It was, however,
ineffective in ascites, leukemias, plasma cell tumors, or
Ehrlich carcinoma. In phase II evaluation studies, gallium
nitrate has shown antitumor activity in patients with either
refractory lymphomas or small-cell lung carcinomas or
bladder cancer, with total objective response rates of 28%
and 11%, respectively. This drug has displayed its strongest
antineoplastic activity in the treatment of non-Hodgkin’s
lymphoma and bladder cancer.
In addition, according to two phase III comparative
trials,thanks to an inhibitory effect on calcium reabsorption
from bone, gallium nitrate is superior to alternative
therapies in the treatment of hypercalcemia associated with
malignancy and related disease states. Based on its clinical
efficacy, gallium nitrate (Ganite ) was approved by the Food
and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of cancerassociated
hypercalcemia.
Apart from its ability to control hypercalcemia, gallium
nitrate has been shown to inhibit bone turnover and
decrease osteolysis in patients with multiple myeloma
and in patients with bone metastases from a variety of
different cancers.
The Uses of GALLIUM NITRATE
Regulator (calcium).
The Uses of GALLIUM NITRATE
Gallium(III) nitrate solution, is used as the material for producing gallium salts and for scientific research and chemical reagent. It is also used as an intermediate.
Background
Gallium nitrate is a nitrate salt of Gallium cation, a heavy metal that has been used as a diagnostic agent. Gallium nitrate is reported to possess antiresorptive and hypocalcemic effects on bone. GANITE, a product of gallium nitrate previously used to treat cancer-related hypercalcemia, was discontinued from marketing in the US for reasons other than safety or effectiveness.
Apart from cancer-related hypercalcemia, gallium nitrate has been studied in arthritis, autoimmune disorders, and tumours.
Indications
Gallium nitrate does not currently have approved indications. It was previously used in the treatment of cancer-related hypercalcemia.
brand name
Ganite (Genta).
General Description
White crystals.
Air & Water Reactions
Deliquescent. Water soluble.
Reactivity Profile
Oxidizing agents, such as GALLIUM NITRATE, can react with reducing agents to generate heat and products that may be gaseous (causing pressurization of closed containers). The products may themselves be capable of further reactions (such as combustion in the air). The chemical reduction of materials in this group can be rapid or even explosive, but often requires initiation (heat, spark, catalyst, addition of a solvent). Explosive mixtures of inorganic oxidizing agents with reducing agents often persist unchanged for long periods if initiation is prevented. Such systems are typically mixtures of solids, but may involve any combination of physical states. Some inorganic oxidizing agents are salts of metals that are soluble in water; dissolution dilutes but does not nullify the oxidizing power of such materials. Organic compounds, in general, have some reducing power and can in principle react with compounds in this class. Actual reactivity varies greatly with the identity of the organic compound. Inorganic oxidizing agents can react violently with active metals, cyanides, esters, and thiocyanates.
Fire Hazard
Flash point data for GALLIUM NITRATE are not available, but GALLIUM NITRATE is probably combustible.
Pharmaceutical Applications
In clinical trials, gallium nitrate has proved to be highly active as an antitumour agent especially against non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma and bladder cancer. The cytotoxic activity of gallium nitrate has been demonstrated as single agent and as part of combination therapy, for example, together with fluorouracil. Gallium nitrate shows a relatively low toxicity and does not produce myelosuppression, which is a significant advantage over other traditional anticancer agents. Furthermore, it does not appear to show any cross-resistance with conventional chemotherapeutic agents.
These studies have also shown that gallium nitrate is able to decrease serum calcium levels in patients with tumour-induced hypercalcaemia. Subsequently, several studies have been carried out comparing traditional bisphosphonate drugs with gallium nitrate in their ability to decrease the calcium levels that are elevated as a result of cancer. Based on the clinical efficacy, gallium nitrate injections (GaniteTM) was granted approval by the FDA for the treatment of cancer-associated hypercalcaemia. Gallium nitrate is also believed to inhibit the bone turnover and therefore to decrease osteolysis, the active reabsorption of bone material, in patients with bone metastasis secondary to other cancers.
Pharmacokinetics
Gallium nitrate produces a hypocalcemic effect by inhibiting calcium resorption from bone, possibly blocking osteoclast activity and reducing increased bone turnover. Preclinical studies demonstrated that gallium dose-dependently accumulates in areas of high bone turnover, where it is incorporated into hydroxyapatite, making it less susceptible to dissolution and osteoclast-mediated resorption. No cytotoxic effects were observed on bone cells in drug-treated animals.
Gallium nitrate exhibits antitumour activity, which is reported to be unrelated to the physiological mechanism involved in its bone turnover effects. Anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressant effects have also been documented.
Carcinogenicity
Studies on the antitumor activity of gallium nitrate have shown that it is particularly active against solid tumors. It has demonstrated antitumor activity in a variety of murine tumor models, including Walker carcinosarcoma 256, fibrosarcoma M-89, leukemia K-1964, adenocarcinoma 755, mammary carcinoma YMC, reticulum cell sarcoma A-RCS, lymphoma P1798, and osteosarcoma 124F.
Metabolism
Gallium nitrate is not metabolized either by the liver or the kidney.
Properties of GALLIUM NITRATE
| Melting point: | 110°C (dec.) |
| solubility | soluble in H2O, ethanol, ethyl ether |
| form | Liquid |
| color | white crystals, crystalline powder |
| Water Solubility | It is soluble in water. |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 2 ppm; STEL 4 ppm OSHA: TWA 2 ppm(5 mg/m3) NIOSH: IDLH 25 ppm; TWA 2 ppm(5 mg/m3); STEL 4 ppm(10 mg/m3) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Gallium nitrate (13494-90-1) |
Safety information for GALLIUM NITRATE
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Over Circle Oxidizers GHS03  Corrosion Corrosives GHS05 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H272:Oxidising liquids;Oxidising solids H314:Skin corrosion/irritation H318:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P221:Take any precaution to avoid mixing with combustibles/… P303+P361+P353:IF ON SKIN (or hair): Remove/Take off Immediately all contaminated clothing. Rinse SKIN with water/shower. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P405:Store locked up. |
Computed Descriptors for GALLIUM NITRATE
New Products
4-AMINO-TETRAHYDRO-PYRAN-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID HCL 4-(Dimethylamino)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-carbonitrile 4-Aminotetrahydropyran-4-carbonitrile Hydrochloride (R)-3-Aminobutanenitrile Hydrochloride 3-((Dimethylamino)methyl)-5-methylhexan-2-one oxalate 1,4-Dioxa-8-azaspiro[4.5]decane 5-Bromo-2-nitropyridine Nimesulide BP Aceclofenac IP/BP/EP Diclofenac Sodium IP/BP/EP/USP Mefenamic Acid IP/BP/EP/USP Ornidazole IP Diclofenac Potassium THOMAIND PAPER PH 2.0 TO 4.5 1 BOX BUFFER CAPSULE PH 9.2 - 10 CAP SODIUM CHLORIDE 0.1N CVS ALLOXAN MONOHYDRATE 98% PLATINUM 0.5% ON 3 MM ALUMINA PELLETS (TYPE 73) LITHIUM AAS SOLUTION 2-Bromo-1-(bromomethyl)-3-chloro-5-nitrobenzene 2-Bromo-3-nitroaniline N-(3-Hydroxypropyl)-N-methylacetamide 3-Bromo-6-chloropyridazine 4-ethyl-3-nitrobenzoic acidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Gallium (III) nitrate solution CAS 13494-90-1View Details
Gallium (III) nitrate solution CAS 13494-90-1View Details
13494-90-1 -
 Gallium (III) nitrate solution CAS 13494-90-1View Details
Gallium (III) nitrate solution CAS 13494-90-1View Details
13494-90-1 -
 1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 -
 2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
1307449-08-6 -
 Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
25408-95-1 -
 2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
1805639-70-6 -
 1784294-80-9 98%View Details
1784294-80-9 98%View Details
1784294-80-9 -
 Lithium ClavulanateView Details
Lithium ClavulanateView Details
61177-44-4