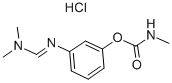
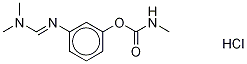
FORMETANATE HYDROCHLORIDE
- CAS NO.:23422-53-9
- Empirical Formula: C11H16ClN3O2
- Molecular Weight: 257.72
- MDL number: MFCD00055560
- EINECS: 245-656-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:15:30
What is FORMETANATE HYDROCHLORIDE?
Description
Formetanate hydrochloride is a white oryellowish, crystalline solid or powder with a faint odor.Molecular weight=257.75; Freezing/Melting point 5200 C-202 C (decomposes). Hazard Identification (basedon NFPA-704 M Rating System): Health 3, Flammability 1,Reactivity 0. Highly soluble in water.
Chemical properties
Formetanate hydrochloride is a white or yellowish, crystalline solid or powder with a faint odor.
The Uses of FORMETANATE HYDROCHLORIDE
Formetanate is an insecticide and acaricide with contact and stomach action. It is used to control spider mites and some insects (Diptera, Hemiptera and Thysanoptera) on ornamentals, fruit, vegetables and alfalfa.
General Description
White powder with a faint odor. Used as a plant insecticide, acaricide, and miticide.
Air & Water Reactions
Hydrolyzed at pH less than 4 [EPA, 1998].
Reactivity Profile
FORMETANATE HYDROCHLORIDE is a carbamate ester. Carbamates are chemically similar to, but more reactive than amides. Like amides they form polymers such as polyurethane resins. Carbamates are incompatible with strong acids and bases, and especially incompatible with strong reducing agents such as hydrides. Flammable gaseous hydrogen is produced by the combination of active metals or nitrides with carbamates. Strongly oxidizing acids, peroxides, and hydroperoxides are incompatible with carbamates.
Health Hazard
Extremely toxic to humans. Not absorbed through contact with skin. Inhalation or ingestion may cause poisoning. Inhibits cholinesterase activity so effects are in relation to action on nervous system and can result in death.
Fire Hazard
FORMETANATE HYDROCHLORIDE may burn but does not ignite readily. Container may explode in heat of fire. Hydrolyzed at pH less than 4
Agricultural Uses
Insecticide, Acaricide: Registered for use in the U.S. Not listed for use in EU countries. An insecticide used for thrips and true bug control on fruit crops.
Trade name
CARZOL®; CARZOL® SP; DICARZOL®; ENT 27566®; EP-332®; MORTON® EP332; NOR-AM® EP 332; SCHERING® 36056; SN 36056®
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion and intraperitoneal routes. Mddly toxic by skin contact. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of NOx and HCl.
Potential Exposure
A potential danger to those involved in the manufacture, formulation, and application of this plant insecticide, acaricide and miticide.
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts theskin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediatelywith soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. Ifthis chemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure,begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR ifheart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medicalfacility. When this chemical has been swallowed, get medical attention. Give large quantities of water and inducevomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit.
Metabolic pathway
Formetanate is hydrolysed rapidly in field and laboratory soils under aerobic and anaerobic conditions. It is metabolised by similar pathways in plants and animals. It is hydrolytically deaminated to produce a formyl derivative and subsequently hydrolysed at the carbamate ester to give a phenolic product. The phenol is deformylated to 3-aminophenol and acetylated to 3-acetamidophenol. Formetanate and most phase 1 metabolites are found conjugated. Its metabolism has been reviewed by Cool and Jankowski (1985), Fukuto (1972) and Kuhr and Dorough (1976).
storage
Color Code—Blue: Health Hazard/Poison: Storein a secure poison location. Prior to working with thischemical you should be trained on its proper handling and storage. Store in tightly closed containers in a cool, wellventilated area.
Shipping
UN2757 Carbamate pesticides, solid, toxic, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials. UN2811 Toxic solids, organic, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required.
Degradation
Formetanate is hydrolysed rapidly under basic conditions. DT50 values at pH 5, 7 and 9 (22 °C) are reported to be 65 days, 23 hours and 2 hours, respectively (PM). The photolysis of formetanate hydrochloride in solutions of distilled water at pH 3.1 and 7.1 or natural river water was studied. Samples were irradiated for 4 days by a high pressure Hg lamp immersed in the solutions. Light of wavelength <286 nm was filtered out. Analysis of solutions was by TLC, IR and MS. The carbamate moiety was more stable than the formamidine. Photolysis gave four products, viz. the formaminophenol (2), the 3-aminophenyl carbamate (3), the formamino compound (4) and 3-hydroxyphenyl methylcarbamate (5), a product of oxidative deamination of formetanate. Yields increased in the order given. The proposed pathways of photolysis of formetanate are given in Scheme 1 (Su and Zabick, 1972). Soil surface photolysis occurs with a DT50 value of 16 hours (PM).
Incompatibilities
Carbamates are incompatible with strong acids and bases, and especially incompatible with strong reducing agents such as hydrideds and active metals. Contact with active metals or nitrides form flammable gas eous hydrogen. Incompatible with strongly oxidizing acids, peroxides, and hydroperoxides.
Waste Disposal
In accordance with 40CFR 165 recommendations for the disposal of pesticides and pesticide containers. Must be disposed properly by follow ing package label directions or by contacting your local or federal environmental control agency, or by contacting your regional EPA office. Consult with environmental regulatory agencies for guidance on acceptable disposal practices. Generators of waste containing this contaminant (≥kg/mo) must conform with EPA regulations gov erning storage, transportation, treatment, and waste disposal.
Properties of FORMETANATE HYDROCHLORIDE
| Melting point: | 201℃ (decomposition) |
| Density | 1.3616 (rough estimate) |
| vapor pressure | 1.6 x 10-6 Pa (25 °C) |
| refractive index | 1.5270 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | 0-6°C |
| solubility | DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly), Water (Slightly) |
| pka | 8.0 (base) |
| form | neat |
| Water Solubility | 822,000 mg l-1 (25 °C) |
| Stability: | Hygroscopic |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Formetanate hydrochloride (23422-53-9) |
Safety information for FORMETANATE HYDROCHLORIDE
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H317:Sensitisation, Skin H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. |
Computed Descriptors for FORMETANATE HYDROCHLORIDE
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran



You may like
-
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 42831-50-5 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 98%View Details
42831-50-5 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 98%View Details
42831-50-5 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1