FORMANILIDE
Synonym(s):N-Phenylformamide
- CAS NO.:103-70-8
- Empirical Formula: C7H7NO
- Molecular Weight: 121.14
- MDL number: MFCD00003276
- EINECS: 203-136-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-27 09:38:02
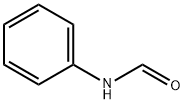
What is FORMANILIDE?
Chemical properties
white or light yellow crystals or powder
The Uses of FORMANILIDE
Formanilide was used to study the zero electron kinetic energy(ZEKE) spectra of cis- and trans-formanilide. It was used to investigate the gas-phase structures of the two isomers of the trans-formanilide-water complex by two-colour (1+1′) resonance enhanced multiphoton ionisation (REMPI) and ZEKE spectroscopy.
Definition
ChEBI: A member of the class of formamides that is formamide in which one of the amino hydrogens is replaced by a phenyl group.
Synthesis Reference(s)
Synthetic Communications, 13, p. 635, 1983 DOI: 10.1080/00397918308060342
Tetrahedron Letters, 26, p. 3703, 1985 DOI: 10.1016/S0040-4039(00)89228-X
General Description
White crystalline solid.
Air & Water Reactions
FORMANILIDE may be sensitive to prolonged exposure to air. . Soluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
FORMANILIDE is an amide. Amides/imides react with azo and diazo compounds to generate toxic gases. Flammable gases are formed by the reaction of organic amides/imides with strong reducing agents. Amides are very weak bases (weaker than water). Imides are less basic yet and in fact react with strong bases to form salts. That is, they can react as acids. Mixing amides with dehydrating agents such as P2O5 or SOCl2 generates the corresponding nitrile. The combustion of these compounds generates mixed oxides of nitrogen (NOx).
Health Hazard
SYMPTOMS: Exposure to FORMANILIDE may cause cyanosis, headache, dizziness, confusion, decreased blood pressure, convulsions and coma.
Fire Hazard
FORMANILIDE is probably combustible.
Purification Methods
Crystallise formanilide from Et2O (m 45.3o), Et2O/pet ether (m 46o), pet ether (m 47.6o), ligroin/xylene, or distil it preferably under reduced pressure. [Beilstein 12 H 230, 12 II 135, 12 III 453.]
Properties of FORMANILIDE
| Melting point: | 46-48 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 166 °C14 mm Hg(lit.) |
| Density | 1.144 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| refractive index | 1.5908 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | >230 °F |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,2-8°C |
| solubility | water: soluble25.4g/L at 20°C |
| form | Crystals |
| pka | 15.00±0.70(Predicted) |
| Specific Gravity | 1.144 |
| color | White to pale grayish-beige |
| Merck | 14,4238 |
| BRN | 906934 |
| Stability: | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 103-70-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Formanilide (103-70-8) |
Safety information for FORMANILIDE
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for FORMANILIDE
FORMANILIDE manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran



You may like
-
 103-70-8 FORMANILIDE N-Phenylformamide 98%View Details
103-70-8 FORMANILIDE N-Phenylformamide 98%View Details
103-70-8 -
 103-70-8 99%View Details
103-70-8 99%View Details
103-70-8 -
 Formanilide 95% CAS 103-70-8View Details
Formanilide 95% CAS 103-70-8View Details
103-70-8 -
 Formanilide CAS 103-70-8View Details
Formanilide CAS 103-70-8View Details
103-70-8 -
 Formanilide CAS 103-70-8View Details
Formanilide CAS 103-70-8View Details
103-70-8 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4
