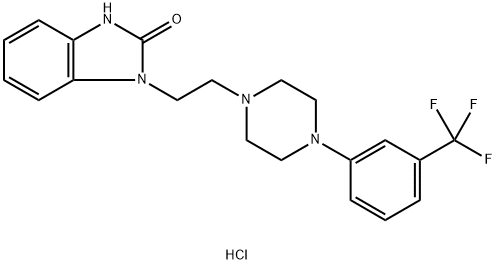
Flibanserin
Synonym(s):1,3-Dihydro-1-[2-[4-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-1-piperazinyl]ethyl]-2H-benzimidazol-2-one;BIMT 17;BIMT 17BS
- CAS NO.:167933-07-5
- Empirical Formula: C20H21F3N4O
- Molecular Weight: 390.4
- MDL number: MFCD00918402
- EINECS: 643-002-2
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 17:20:15
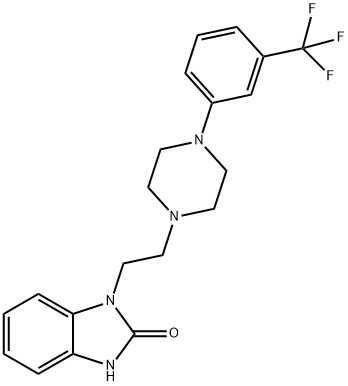
What is Flibanserin?
Absorption
Flibanserin has an absolute oral availability of 33%.
Description
Flibanserin is a drug originally developed by Boehringer-Ingelheim and later Sprout Pharmaceuticals, which was approved in 2015 by the FDA for the treatment of premenopausal women with hypoactive sexual desire disorder (HSDD). The drug, which was originally developed for the treatment of depression by Boehringer- Ingelheim, is a full agonist of the 5-HT1A receptor, an antagonist of the 5-HT2A receptor, and a partial agonist of the dopamine-4 (D4) receptor, which triggers increased dopamine and norepinephrine levels along with decreased serotonin levels. In three randomized trials involving 2400 premenopausal women, the drug was found to increase the number of satisfying sexual events by 0.5-1.0 events per month and increased sexual desire on average by 10-12% over placebo. Side effects include decreased blood pressure and loss of consciousness, especially in subjects who consumed alcohol.
The Uses of Flibanserin
Antidepressant (5-HT1a agonist and 5-HT2 antagonist).
Background
Flibanserin is the first drug to be approved for hypoactive sexual desire disorder (HSDD) in premenopausal women by the FDA in August 2015. It was originally developed as an antidepressant medication by Boehringer Ingelheim, but showed lack of efficacy in trials and was further developed as a hypoactive sexual disorder drug by Sprout Pharmaceuticals. Flibanserin's mechanism of action is attributed to its high affinity for 5-HTA1 and 5-HTA2 receptors, displaying agonist activity on 5-HTA1 and antagonist on 5-HTA2, resulting in lowering of serotonin in the brain as well as an effect on increasing norepinephrine and dopamine neurotransmitters.
Indications
For the treatment of hypoactive sexual desire disorder (HSDD) in premenopausal women.
Definition
ChEBI: Flibanserin is an N-alkylpiperazine that is 1-[2-(1,3-dihydro-2-oxobenzimidazol-1-yl)ethyl]piperazine in which the remaining amino proton is replaced by a 3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl group. A multifunctional serotonin agonist and antagonist which is used for the treatment of pre-menopausal women with hypoactive sexual desire disorder. It has a role as a serotonergic agonist, a serotonergic antagonist and an antidepressant. It is a member of benzimidazoles, a N-arylpiperazine, a N-alkylpiperazine and an organofluorine compound.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Flibanserin is a 5-HT1A receptor agonist and 5-HT2A receptor antagonist. Flibanserin has high affinity for human 5-HT1A receptors (Ki = 1 nm) and lower affinity for 5-HT2A (Ki = 49 nm) and D4 (Ki = 4–24 nm) receptors, and negligible affinity for a variety of other neurotransmitter receptors and ion channels. Flibanserin was investigated as a novel, non-hormonal treatment for pre-menopausal women with Hypoactive Sexual Desire Disorder (HSDD). Flibanserin. Recently, Flibanserin was found to reduce L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia in a model of Parkinson′s Disease.
Synthesis
The large-scale synthesis of flibanserin (X) mostly follows a patent from Symed Laboratories Limited which demonstrated hundred-gram-scale preparation of the drug as described in Scheme. Starting from commercially available 1-(prop-1- en-2-yl)-1,3-dihydro-2H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-one (74), installation of an ethylene side chain was accomplished under conventional alkylation conditions with 1,2-dibromoethane and base, and this event was immediately followed by a second alkylation reaction involving piperazine to secure piperazinyl benzimidazolone 75. Interestingly, the enamine double bond within 74 was apparently reduced to the corresponding isopropyl group under these conditions. Although the authors do not comment about this reduction directly, similar examples of olefin reduction under non-hydrogenative alkylation conditions have been reported in the literature separately by both Pai and Ryu. Removal of the isopropyl group was facilitated by means of aqueous sodium hydroxide to afford 76, which underwent N-arylation under Buchwald conditions with 1-bromo-3-(trifluoromethyl)benzene 77 to furnish flibanserin (X) in 63% yield.

in vitro
previous study found that flibanserin was a 5-ht(1a) agonist, a very weak partial agonist on dopamine d(4) receptors, and a 5-ht(2a) antagonist. flibanserin could reduce neuronal firing rate and flibanserin-induced reduction in firing rate was likely mediated via stimulation of postsynaptic 5-ht(1a) receptors. moreover, flibanserin could quickly desensitize somatic 5-ht autoreceptors and enhance tonic activation of postsynaptic 5-ht(1a) receptors. in addition, flibanserin was able to reduce synthesis and extracellular levels of 5-ht in the cortex [1].
in vivo
previous animal study showd that flibanserin had antidepressant-like activity in most animal models sensitive to antidepressants, and such activity seemed different from that exerted by other antidepressants. in addition, flibanserin did not show consistent effects in animal models of anxiety and seemed to exert potential antipsychotic effects [1].
Metabolism
Metabolism is primarily via CYP3A4, slightly CYP2C19. Minimal involvement of CYP1A2, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9 or CYP2D6. At least 35 metabolites of flibanserin are produced, 2 of which reach plasma concentrations as high as parent drug, however they are pharmacologically inactive.
References
[1] borsini f, evans k, jason k, rohde f, alexander b, pollentier s. pharmacology of flibanserin. cns drug rev. 2002 summer;8(2):117-42.
[2] katz m et al. efficacy of flibanserin in women with hypoactive sexual desire disorder: results from the begonia trial. j sex med. 2013 jul;10(7):1807-15.
Properties of Flibanserin
| Density | 1.292±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | DMSO: soluble10mg/mL, clear |
| form | powder |
| pka | 12.12±0.30(Predicted) |
| color | white to beige |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C20H21F3N4O/c21-20(22,23)15-4-3-5-16(14-15)26-11-8-25(9-12-26)10-13-27-18-7-2-1-6-17(18)24-19(27)28/h1-7,14H,8-13H2,(H,24,28) |
Safety information for Flibanserin
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H301:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Flibanserin
| InChIKey | PPRRDFIXUUSXRA-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | C1(=O)N(CCN2CCN(C3=CC=CC(C(F)(F)F)=C3)CC2)C2=CC=CC=C2N1 |
Flibanserin manufacturer
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 167933-07-5 Flibanserin 98%View Details
167933-07-5 Flibanserin 98%View Details
167933-07-5 -
 167933-07-5 98%View Details
167933-07-5 98%View Details
167933-07-5 -
 Flibanserin 99%View Details
Flibanserin 99%View Details
167933-07-5 -
 Flibanserin 98%View Details
Flibanserin 98%View Details
167933-07-5 -
 Flibanserin CAS 167933-07-5View Details
Flibanserin CAS 167933-07-5View Details
167933-07-5 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1