Flecainide
- CAS NO.:54143-55-4
- Empirical Formula: C17H20F6N2O3
- Molecular Weight: 414.34
- MDL number: MFCD00864713
- EINECS: 685-650-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-24 14:33:46
What is Flecainide?
Absorption
Oral flecainide has a Tmax of 3-4h and a bioavialability of 90%. Taking flecainide with food or aluminum hydroxide antacids do not significantly affect the absorption of flecainide.
Toxicity
The oral LD50 in rats is 1346mg/kg and in mice is 170mg/kg. The subcutaneous LD50 in rats is 215mg/kg and in mice is 188mg/kg. The oral TDLO in women is 20mg/kg and in men is 40mg/kg/2W.
Patients experiencing an overdose may present with ECG abnormalities such as a lengthened PR interval, increased QRS duration, prolonged QT interval, increased amplitude of the T wave, reduced myocardial rate and contractility, hypotension, or death. Treat patients with symptomatic and supportive treatment which may involve administration of inotropic agents, assisted respiration, circulatory assistance, and acidification of the urine. Hemodialysis is not expected to be useful in the removal of flecainide from serum.
Description
From the chemical point, flecainide is an analog of procainamide, to which a 2.2.2-trifluoroethoxyl group was added at C2 and C3 of the benzene ring, and a diaminoethyl side chain is ended in the piperidine ring.
Chemical properties
White Crystalline Powder
Originator
Tambocor,Kettelhack Riker,W. Germany,1982
The Uses of Flecainide
Flecainide, as with other local anesthetics, is used for naturally occurring ventricular arrhythmia.
The Uses of Flecainide
Flecainide is an antiarrhythmic (class IC).
Indications
In New Zealand and America, flecainide is indicated to prevent supraventricular arrhythmias and ventricular arrhythmias. In the United States, it is also indicated to prevent paroxysmal atrial fibrillation and flutter.
What are the applications of Application
Flecainide is an antiarrhythmic RyR-2 inhibitor
Background
Flecainide is a Class I anti-arrhythmic agent like encainide and propafenone. Flecainide’s development began in 1966 and was first synthesized in 1972 as an attempt to generate new anesthetics. It is used to prevent supraventricular and ventricular arrhythmias, as well as paroxysmal atrial fibrillation and flutter.
Flecainide was granted FDA approval on 31 October 1985.
Definition
ChEBI: A monocarboxylic acid amide obtained by formal condensation of the carboxy group of 2,5-bis(2,2,2-trifluoroethoxy)benzoic acid with the primary amino group of piperidin-2-ylmethylamine. An antiarrhythmic agent used (in the form of its acetate salt) to prev nt and treat tachyarrhythmia (abnormal fast rhythm of the heart).
Manufacturing Process
Under a nitrogen atmosphere 2-aminomethylpiperidine (0.249 mol, 28.4 g) is treated dropwise over 25 minutes with 2,2,2-trifluoroethyl 2,5-bis(2,2,2- trifluoroethoxy)benzoate (0.0249 mol, 10.0 g). After 3 hours 50 ml of benzene is added to the thick mixture and stirred for about 40 hours at 45°C. The mixture is then concentrated under vacuum with heating to remove the volatile components. The residue solidifies after cooling, is steam distilled for further purification and is separated by filtration and extracted into dichloromethane. The dichloromethane solution is washed with saturated sodium chloride solution, and the organic layer is dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate. The magnesium sulfate is removed by filtration and 4 ml of 8.4 N hydrogen chloride in isopropanol is added to the dichloromethane solution with stirring.After 2 hours the mixture is cooled to about 0°C and the crude product is collected by filtration, washed with diethyl ether and dried in a vacuum oven. After treatment with decolorizing charcoal and recrystallization from an equivolume mixture of isopropanol and methanol, the product, 2,5-bis(2,2,2- trifluoroethoxy)-N-(2-piperidylmethyl)benzamide hydrochloride has a MP of 228°C to 229°C.
brand name
Tambocor (3M Pharmaceuticals).
Therapeutic Function
Antiarrhythmic
World Health Organization (WHO)
The membrane-stabilizing antiarrhythmic agent flecainide was introduced into medicine in 1982. The decision to delete the indications for patients with asymptomatic and less severe symptomatic ventricular arrhythmias was taken on the basis of the results of a trial (CAST study) that showed a two-fold increase in deaths in post-myocardiac patients taking flecainide compared with the placebo group.
Hazard
Human systemic effects.
Mechanism of action
Flecainide is effective if administered intravenously and orally; its effect is long-lasting. The drug combines the modes of action of class I a and I b drugs with those of class III.
Pharmacokinetics
Flecainide inhibits the action of sodium and potassium ion channels in the heart, raising the threshold for depolarization and correcting arrhythmias. Flecainide has a long duration of action, allowing for once daily dosing. The therapeutic index is narrow. Patients should not take this medication if there is already structural heart disease or left ventricular systolic dysfunction.
Clinical Use
Flecainide (Tambocor) is a fluorinated aromatic hydrocarbon
examined initially for its local anesthetic
action and subsequently found to have antiarrhythmic
effects. Flecainide inhibits the sodium channel, leading
to conduction slowing in all parts of the heart, but
most notably in the His-Purkinje system and ventricular
myocardium. It has relatively minor effects on repolarization.
Flecainide also inhibits abnormal automaticity.
Flecainide is effective in treating most types of atrial arrhythmias.
It is also used for life-threatening ventricular
arrhythmias. However, flecainide should be used with extreme
caution in any patient with structural heart disease.
Flecainide crosses the placenta, with fetal levels reaching
approximately 70% of maternal levels. In many centers,
it is the second-line drug after digoxin for therapy of fetal
arrhythmias. Because of the high incidence of proarrhythmia,
initiation of therapy or significant increases in
dosing should be performed only on inpatients.
Side Effects
Most adverse effects occur within a few days of initial
drug administration. The most frequently reported effects
are dizziness, light-headedness, faintness, unsteadiness,
visual disturbances, blurred vision (e.g., spots before
the eyes, difficulty in focusing), nausea, headache,
and dyspnea.
Worsening of heart failure and prolongation of the PR
and QRS intervals are likely to occur with flecainide, and
an increased risk of proarrhythmia has been reported.
Synthesis
Flecainide, N-(2-piperidylmethyl)-2,5-bis-(2,2,2-trifluoroethoxy)benzamide (18.1.14), is synthesized from 2,5-dihydroxybenzoic acid. Reacting this with trifluoroethylfluoromethylsulfonate gives 2.2.2-trifluoroethoxylation of all three hydroxyl groups, to produce 2,2,2-trifluoroethyl ester of 2,5-bis-(2,2,2-trifluoroethoxy)benzoic acid (18.1.12). Reacting this with 2-aminomethylpiridine gives the corresponding amide (18.1.13), which upon reduction of the pyridine ring with hydrogen gives flecainide (18.1.14).

Drug interactions
In patients whose condition has been stabilized by flecainide, the addition of cimetidine may reduce the rate of flecainide’s hepatic metabolism, increasing the potential for toxicity. Flecainide may increase digoxin concentrations on concurrent administration.
Metabolism
Flecainide is mainly metabolized to meta-O-dealkylated flecainide or the meta-O-dealkylated lactam of flecainide. Meta-O-dealkylated flecainide has 20% the activity of flecainide. Both of these metabolites are generally detected as glucuronide or sulfate conjugates. Flecainide’s metabolism involves the action of CYP2D6 and CYP1A2.
Precautions
Flecainide is contraindicated in patients with preexisting second- or third-degree heart block or with bundle branch block unless a pacemaker is present to maintain ventricular rhythm. It should not be used in patients with cardiogenic shock.
Properties of Flecainide
| Melting point: | 105-1070C |
| Boiling point: | 434.9±45.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.286±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| Flash point: | 9℃ |
| storage temp. | Keep in dark place,Inert atmosphere,Room temperature |
| solubility | Chloroform (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | Solid |
| pka | pKa 9.3 (Uncertain) |
| color | White to Off-White |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 54143-55-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Benzamide, n-(2-piperidinylmethyl)-2,5-bis(2,2,2-trifluoroethoxy)-(54143-55-4) |
Safety information for Flecainide
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H225:Flammable liquids H370:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P311:Call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. |
Computed Descriptors for Flecainide
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


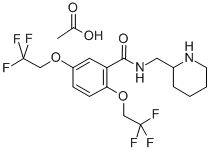
You may like
-
 (±)-Flecainide solution CAS 54143-55-4View Details
(±)-Flecainide solution CAS 54143-55-4View Details
54143-55-4 -
 Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
110-86-1 -
 Guanine , 99%View Details
Guanine , 99%View Details
73-40-5 -
 Piperazine Spot supply, best priceView Details
Piperazine Spot supply, best priceView Details
110-85-0 -
 Dibutyl PhthalateView Details
Dibutyl PhthalateView Details
84-74-2 -
 Imidazole Spot supply, competitive priceView Details
Imidazole Spot supply, competitive priceView Details
288-32-4 -
 Octadecyl 3-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)propionate 98% (GC)View Details
Octadecyl 3-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)propionate 98% (GC)View Details
2082-79-3 -
 Thiourea 99% ARView Details
Thiourea 99% ARView Details
62-56-6
