Famotidine
Synonym(s):{3-[((2-((Aminoiminomethyl)amino)-4-thiazolyl)methyl)thio]-N′-(aminosulfonyl)propaneimidamide};N′-(Aminosulfonyl)-3-([2-(diaminomethyleneamino)-4-thiazolyl]methylthio)propanamidine;Famotidine
- CAS NO.:76824-35-6
- Empirical Formula: C8H15N7O2S3
- Molecular Weight: 337.45
- MDL number: MFCD00079297
- EINECS: 616-396-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-22 18:23:36

What is Famotidine?
Absorption
Following oral administration, the absorption of famotidine is dose-dependent and incomplete. The oral bioavailability ranges from 40-50%, and the Cmax is reached in 1-4 hours post-dosing. While the bioavailability can be slightly increased with the intake of food and decreased by antacids, there is no clinical significance.
Toxicity
The oral LD50 is 4049 mg/kg in rats and 4686 mg/kg in mice. The subcutaneous LD50 is 800 mg/kg in rats and mice. The lowest published toxic dose (TDLo) in man following oral administration is 4 mg/kg/7D.
Symptoms of overdose resemble the adverse events seen with the use of recommended doses, and they should be responded with supportive and symptomatic treatment. Any unabsorbed drug should be removed from the gastrointestinal tract, and the patient should be monitored accordingly. The use of hemodialysis to eliminate the drug from the systemic circulation is effective, but the experience of using hemodialysis in response to famotidine overdose is limited in clinical settings.
Description
Many of us suffer from gastric reflux, which manifests itself as a burning sensation known variously as heartburn, acid indigestion, and cardialgia. The preeminent treatment for this condition is famotidine, a drug developed in Japan and marketed since 1981 in the United States and elsewhere under the trade name Pepcid. The patents on famotidine expired in 2001, after which generic versions came onto the market.
Famotidine is a histamine H2 antagonist. It prevents histamine in the parietal cells of the stomach from secreting the acid that triggers heartburn.
Description
Famotidine is a competitive histamine H2-receptor antagonist, and the main pharmacodynamic effect of famotidine is to cause the inhibition of gastric secretion. Famotidine on decomposition releases toxic products such as carbon oxides (CO, CO2), nitrogen oxides (NO, NO2), and sulphur oxides (SO2, SO3). Famotidine is a medication that is available both in prescription and over-the-counter forms. It is used to treat conditions related to the oesophagus, stomach, and intestines. Some specific famotidine is used for the treatment of duodenal ulcers, gastric ulcers (stomach ulcers), gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), and pathological hypersecretory conditions that occur when stomach acid is secreted/ produced in very large quantities, an abnormal health condition called ‘Zollinger-Ellison syndrome’.
Chemical properties
White Powder
Originator
Yamauouchi (Japan)
The Uses of Famotidine
Contact dermatitis from famotidine, a H2 -receptor agonist, was described in a nurse. In industry, three cases were reported due to intermediates of synthesis, 2- diamino-ethylene-amino-thiazolyl-methylenethiourea-dichloride and 4-chloromethyl-2-guanidinothiazolenitrochloride.
The Uses of Famotidine
Use as an H2-antagonist. An anti-ulcer agent
The Uses of Famotidine
Histamine H2-receptor antagonist. Antiulcerative.
The Uses of Famotidine
antiinflammatory
The Uses of Famotidine
For the treatment of peptic ulcer disease (PUD) and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
Indications
Famotidine is indicated in pediatric and adult patients (with the bodyweight of 40 kg and above) for the management of active duodenal ulcer (DU), active gastric ulcer, symptomatic non-erosive gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), and erosive esophagitis due to GERD, diagnosed by biopsy.
It is also indicated in adult patients for the treatment of pathological hypersecretory conditions (e.g., Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome, multiple endocrine neoplasias) and reduction of the risk of DU recurrence.
Background
Famotidine is a competitive histamine-2 (H2) receptor antagonist that works to inhibit gastric acid secretion. It is commonly used in gastrointestinal conditions related to acid secretion, such as gastric ulcers and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), in adults and children. Compared to other H2 receptor antagonists, famotidine displays high selectivity towards this receptor; in a study consisting of healthy volunteers and patients with acid hypersecretory disease, famotidine was about 20 to 50 times more potent at inhibiting gastric acid secretion than cimetidine and eight times more potent than ranitidine on a weight basis. Famotidine is used in various over-the-counter and off-label uses. While oral formulations of famotidine are more commonly used, the intravenous solution of the drug is available for use in hospital settings.
Manufacturing Process
60.0 kg of dichloroacetone is dissolved in 550 ml of acetone. After cooling the
solution to -5°C, 55.8 kg of amidinothiourea is added to the solution under
cooling portionwise at one hour intervals in a 10 kg amount of
amidinothiourea. The mixture is stirred continuously for 5 days below 0°C.
The 111.6 kg resultant precipitates of N"-[4-(chloromethyl)-4,5-dihydro-4-
hydroxy-2-thiazolyl]-guanidine hydrochloride are collected, and washed with
50 L of acetone. In 500 ml of water are dissolved 111.6 kg of N"-[4-
(chloromethyl)-4,5-dihydro-4-hydroxy-2-thiazolyl]-guanidine hydrochloride
and 32.9 kg of thiourea. The solution is stirred for one hour at 50°C. N'-[4-
[[(Aminoiminomethyl)thio]methyl]-2-thiazolyl]-guanidine dihydrochloride is
formed in the reaction mixture, and this reaction mixture containing this
compound is directly used for the next process without isolation of the formed
compound.
The reaction mixture obtained is cooled below 10°C, and to the solution are
added 45.6 kg of beta-chloropropionitrile and 200 L of isopropanol. A solution
of 69.1 kg of sodium hydroxide in 280 L of water is added dropwise to the
solution under nitrogen stream followed by stirring for 2 hours at 0°C. The
crystals precipitated are collected by filtration, and washed with cold water
and dried to provide 91.7 kg of the N"-[4-[[(2-cyanoethyl)thio]methyl]-2-
thiazolyl]-guanidine, melting point 125-126.5°C.
In 60 L of anhydrous dimethylformamide is dissolved 34.3 kg of the N"-[4-
[[(2-cyanoethyl)thio]methyl]-2-thiazolyl]-guanidine. After adding 60 L of
anhydrous methanol to the solution, 61.9 kg of hydrogen chloride gas is
passed through the solution below 5°C. After stirring the reaction mixture for
2 days at 0°C, the reaction mixture is poured into a mixture of 350 L of water,
250 kg of potassium carbonate, 30 L of ethyl acetate and ice while stirring
below 5°C for 2 hours. The resultant precipitates are collected by filtration.
After stirring a mixture of the precipitates and 400 L of water for 0.5 hour at
0°, the resultant precipitates are collected by filtration, washed with 40 L of
water and 10 L of cooled acetone respectively, and dried at reduced pressure to provide 30.6 kg of the methyl 3-[[[2-[(diaminomethylene)amino]-4-
thiazolyl]methyl]thio]propionimidate showing a melting point of 125.7°C.
In 340 L of methanol is dissolved 88.4 kg of sulfamide under heating, and the
solution is cooled to 30°C. To the solution, 114.2 kg of the methyl 3-[[[2-
[(diaminomethylene)amino]-4-thiazolyl]methyl]thio]propionimidate are added
portionwise three times while stirring at 20-30°C. (The second addition is
added 8 hours after the first addition, and the third addition is added 24 hours
after the first addition). After stirring the reaction mixture for a further 2
days, the crystals formed are collected by filtration, washed with 200 L of
cooled methanol, and air-dried at room temperature to provide 87.5 kg of the
3-[[[2-[(diaminomethylene)amino]-4-thiazolyl]methyl]thio]-Nsulfamoylpropionamidine
(generic name: famotidine) showing a melting point
of 157.6°C. Some of the obtained product is recrystallized from
dimethylformamide-water, and is dissolved in an equivalent molar amount of
aqueous acetic acid (%). To the solution is added an equivalent molar amount
of a dilute sodium hydroxide solution in water to separate crystals showing a
melting point of 163-164°C.
brand name
Fluxid (Schwarz Pharma); Pepcid (Merck);Amifatidine;Famodil;Pepsidac;GASTER.
Therapeutic Function
Antiulcer
General Description
Famotidine is a histamine H2-receptor antagonist, which promotes the healing of erosive esophagitis, gastric and duodenal ulcers since it inhibits the gastric acid secretion in humans.
Pharmaceutical secondary standards for application in quality control, provide pharma laboratories and manufacturers with a convenient and cost-effective alternative to the preparation of in-house working standards.
Contact allergens
Contact dermatitis in a nurse from famotidine, an H2-receptor agonist, was described. In industry, three cases were reported due to intermediates of the synthesis of 2-diamino-ethylene-amino-thiazolyl-methylenethio urea-dichloride, and 4-chloromethyl-2-guanidinothiaz ole-nitrochloride.
Biochem/physiol Actions
H2 histamine receptor antagonist; anti-ulcer agent
Pharmacokinetics
Famotidine decreases the production of gastric acid, suppresses acid concentration and pepsin content, and decreases the volume of gastric secretion. Famotidine inhibits both basal and nocturnal gastric acid secretion, as well as acid secretion stimulated by food, caffeine, insulin, and pentagastrin.
Famotidine has a dose-dependent therapeutic action, with the highest dose having the most extended duration of action and the highest inhibitory effect on gastric acid secretion. Following oral administration, the onset of action is within one hour, and the peak effect is reached within 1-3 hours. The duration of effect is about 10-12 hours.
Clinical Use
Famotidine is a histamine H2-antagonist more potent than cimetidine and ranitidine. Administered once or twice daily, it is useful in the treatment of gastric, duodenal and anastomotic ulcers, upper gastrointestinal tract hemorrhage, reflux esophagitis and Zollinger-Ellison syndrome. Like ranitidine, it is lacking in antiandrogenic effects.
Synthesis
Famotidine, 3-[[[2-[(aminomethyl)amino]-4-thiazolyl] methyl]thio]- N-(aminosulfonyl)propanimidamide (16.2.13), is synthesized from S-(2-aminothiazol-4-ylmethyl) isothiourea (16.2.9), which is synthesized by reacting 1,3-dichloroacetone with two molecules of thiourea, during which a thiazol ring is formed and the chlorine atom is substituted, giving an intermediate 2-amino-5-chlormethylthiazol. Reacting this with 2-chlorpropionitrile gives S-(2-aminothiazol-4-yl-methyl)-2-cyanoethane (16.2.10), which in turn is reacted with benzoylizthiocyanate. The resulting benzoylthiourea derivative (16.2.11) first undergoes S-methylation by methyliodide and further cleaved by ammonia into 3-[[[2- (aminomethyl)amino]-4-thiazolyl]-methyl]thio]ethylcyanide (16.2.12). Successive methanolysis of the nitrile group and subsequent reaction of the resulting iminoether with sulfonamide gives famotidine (16.2.13).

Veterinary Drugs and Treatments
In veterinary medicine, famotidine may be useful for the treatment
and/or prophylaxis
of gastric, abomasal and duodenal ulcers,
uremic gastritis, stress-related or drug-induced erosive gastritis,
esophagitis, duodenal gastric reflux, and esophageal reflux.
Famotidine has fewer drug interactions and activity may persist
longer than cimetidine.
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs Antifungals: absorption of itraconazole and ketoconazole reduced; concentration of posaconazole possibly reduced - avoid with suspension. Antivirals: concentration of atazanavir reduced - adjust doses of both drugs; concentration of raltegravir possibly increased - avoid; avoid for 12 hours before and 4 hours after rilpivirine. Ciclosporin: possibly increased ciclosporin levels. Cytotoxics: possibly reduced dasatinib concentration - avoid if possible; avoid with erlotinib; possibly reduced absorption of pazopanib - give at least 2 hours before or 10 hours after famotidine; possibly reduced absorption of lapatinib. Ulipristal: contraceptive effect possibly reduced - avoid with high dose ulipristal.
Metabolism
Famotidine undergoes minimal first-pass metabolism. About 25-30% of the drug is eliminated through hepatic metabolism. The only metabolite identified in humans is the S-oxide.
Metabolism
Metabolism of famotidine occurs in the liver, with formation of an inactive metabolite, the sulfoxide. Following oral administration, the mean urinary excretion of famotidine is 65-70% of the absorbed dose, 25-30% as unchanged compound. Renal clearance is 250-450 mL/min, indicating some tubular excretion. A small amount may be excreted as the sulfoxide.
Storage
Store at -20°C
Properties of Famotidine
| Melting point: | 163-164°C |
| Boiling point: | 562.7±60.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.5111 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.7400 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Very slightly soluble in water, freely soluble in glacial acetic acid, very slightly soluble in anhydrous ethanol, practically insoluble in ethyl acetate. It dissolves in dilute mineral acids |
| form | neat |
| pka | pKa 6.76(H2O t=23.0) (Uncertain) |
| appearance | white to pale yellow crystals or powder |
| form | Solid |
| color | White to Off-White |
| Water Solubility | 1.1 mg/mL |
| Stability: | Light Sensitive |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C8H15N7O2S3/c9-6(15-20(12,16)17)1-2-18-3-5-4-19-8(13-5)14-7(10)11/h4H,1-3H2,(H2,9,15)(H2,12,16,17)(H4,10,11,13,14) |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 76824-35-6(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Propanimidamide, 3-[[[2-[(aminoiminomethyl)amino]-4-thiazolyl]methyl]thio]-N-(aminosulfonyl)- (76824-35-6) |
Safety information for Famotidine
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H303:Acute toxicity,oral |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P403:Store in a well-ventilated place. |
Computed Descriptors for Famotidine
| InChIKey | XUFQPHANEAPEMJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | C(NS(N)(=O)=O)(=N)CCSCC1=CSC(NC(N)=N)=N1 |
Famotidine manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
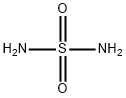
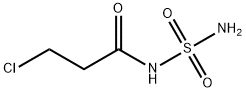
![[3-[[[2-(DiaMinoMethyleneaMino)-4-thiazolyl]Methyl]thio]propionyl]sulfaMide Hydrochloride
(FaMotidine IMpurity)](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/76824-17-4.gif)
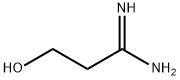
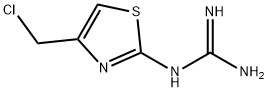
![3-[2-(Diaminomethyleneamino)-1,3-thiazol-4-ylmethylsulphinyl]-N-sulphamoyl
propanamide](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS2/GIF/1020719-36-1.gif)
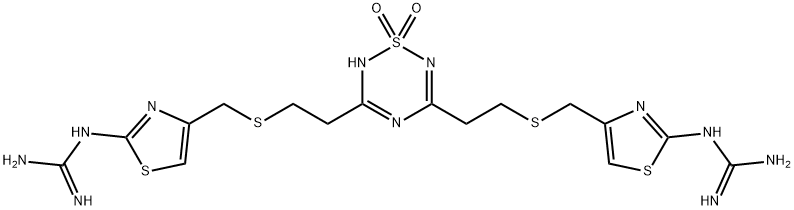
![Bis[(2-guanidino-4-thiazolyl)methyl]disulfide](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS2/GIF/129083-44-9.gif)
You may like
-
 Famotidine 76824-35-6 98%View Details
Famotidine 76824-35-6 98%View Details
76824-35-6 -
 Famotidine 99%View Details
Famotidine 99%View Details -
 Famotidine 98%View Details
Famotidine 98%View Details
76824-35-6 -
 FAMOTIDINE 76824-35-6 95-99%View Details
FAMOTIDINE 76824-35-6 95-99%View Details
76824-35-6 -
 Famotidine 98% CAS 76824-35-6View Details
Famotidine 98% CAS 76824-35-6View Details
76824-35-6 -
 Famotidine Api Powder, USPView Details
Famotidine Api Powder, USPView Details
76824-35-6 -
 Famotidine Powder API, BPView Details
Famotidine Powder API, BPView Details
76824-35-6 -
 Famotidine API MANUFACTURER INDIAView Details
Famotidine API MANUFACTURER INDIAView Details
76824-35-6
