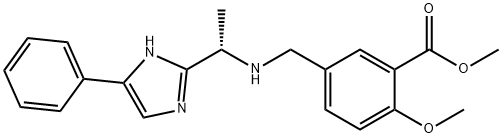
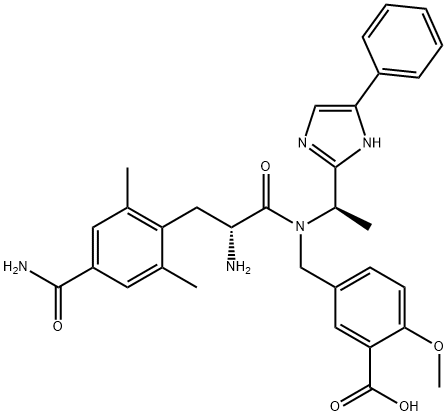
Eluxadoline
- CAS NO.:864821-90-9
- Empirical Formula: C32H35N5O5
- Molecular Weight: 569.65
- MDL number: MFCD28386164
- EINECS: 1592732-453-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-21 10:54:39

What is Eluxadoline?
Absorption
The oral absorption of eluxadoline is poor - estimated to be 1.02%, this could be attributed to poor in vitro GI permeability, and its zwitterionic nature leading to a negatively charged molecule across the GI pH range.
Toxicity
The most common adverse reactions (>5%) are constipation, nausea and abdominal pain.
Description
Eluxadoline, originally developed by Janssen and currently marketed by Allergan (formerly Actavis), was approved in May 2015 by the FDA for the treatment of diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome (IBS-D). Eluxadoline, an orally dosed agent, employs a unique mechanism for IBS-D treatment, as it functions simultaneously as a μ- and κ-opioid receptor agonist and a δ- opioid receptor antagonist, leading to a first-in-class therapy for treatment of IBS-D. Specifically, in animal studies, eluxadoline was found to interact with opioid receptors in the gut, inhibiting neurogenically mediated secretion and reducing intestinal contractility. Additionally, the treatment led to a decrease in stress-induced acceleration of upper GI transit without causing rebound constipation, earning its mark as a first-line therapeutic treatment for IBS-D. In two phase III clinical trials of over 2400 patients with IBS-D, patients taking eluxadoline showed a greater improvement toward the end point (≥30% improvement from their baseline IBS-D score on at least 50% of days treated with eluxadoline) compared to patients treated with placebo.
The Uses of Eluxadoline
Eluxadoline is an orally-active drug used to reduce symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome such as diarrhea and abdominal pain.
Indications
For the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome with diarrhea (IBS-D).
Background
Eluxadoline is a mixed mu-opioid receptor agonist, kappa-opioid receptor agonist, and a-delta opioid receptor antagonist indicated for use in diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome (IBS-D). The mu-, kappa-, and delta-opioid receptors mediate endogenous and exogenous opioid response in the central nervous system and peripherally in the gastrointestinal system. Agonism of peripheral mu-opioid receptors results in reduced colonic motility, while antagonism of central delta-opioid receptors results in improved analgesia, making eluxadoline usable for the symptoms of both pain and diarrhea characteristic of IBS-D.
Marketed under the tradename Viberzi (FDA), eluxadoline is an antimotility agent that decreases bowel contractions, inhibits colonic transit, and reduces ?uid/ion secretion resulting in improved symptoms of abdominal pain and reductions in the Bristol Stool Scale.
Definition
ChEBI: An amino acid amide obtained by the formal condensation of the carboxy group of 4-carbamoyl-2,6-dimethyl-L-phenylalanine with the secondary amino group of 2-methoxy-5-({[(1S)-1-(4-phenylimidazol-2-yl)ethyl]amino}methyl)ben oic acid. It has mixed opioid receptor activity and is used for treatment of irritable bowel syndrome with diarrhoea.
Clinical Use
Mixed mu-opioid receptor agonist, kappa-opioid receptor
agonist, and a-delta opioid receptor antagonist:
Treatment of irritable bowel syndrome with
diarrhoea
Synthesis
The synthesis of eluxadoline begins with preparation of
advanced coupling component 85, which could be completed
via a four-step route from commercially available N-Bocprotected
aminoester 83 . Triflate formation using N-phenyltrifluoromethanesulfinimide in DCM under
basic conditions led to nearly quantitative yield of the desired
triflate, which was subjected to a carbonylation reaction to yield
aryl acid 84 in 94% yield. Employing NH4Cl as a source of
ammonia, amidation of 84 took place in the presence of
PyBOP/HOBt and DIPEA in DMF. Finally, acid 85 was
revealed upon methyl ester saponification with aqueous LiOH
in THF. This sequence provided 85 without purification.
With coupling component 85 in hand and initiated from a HOBt and EDC?¤HCl-mediated coupling of commercial
N-Cbz-L-alanine (86) with commercial 2-amino acetophenone
hydrochloride (87) to provide intermediate 88 in 83%
yield. Addition of NH4OAc and AcOH to a suspension
of 88 in refluxing xylenes furnished the desired imidazole in
excellent yield (95%). Submission of this N-Cbz-imidazole to
hydrogenation conditions (H2, Pd/C, MeOH) enabled
liberation of the free amine to access 89 in quantitative yield
following filtration and concentration. From intermediate 89,
reductive amination with commercially available aryl aldehyde
90 under standard conditions (NaBH4, MeOH) followed by
subsequent coupling of the corresponding crude amine with acid 85 using HOBt/EDC?¤HCl enabled formation of the
carbon framework of eluxadoline (91). Saponification of the
ester within 91 with LiOH in MeOH/THF yielded the
corresponding acid in quantitative yield. Immediate subjection
of this intermediate to acidic conditions (HCl in EtOAc/THF)
led to N-Boc cleavage and isolation of eluxadoline (XII) as the
bis-HCl salt in 71% yield, requiring no further purification.
It should be noted that since this initial report, additional
details for the isolation of eluxadoline in high purity in various
crystal forms and as a zwitterion have been reported,66 although
most reported routes described isolation of this drug in its HCl
salt form.

Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs Antibacterials: concentration possibly increased by rifampicin - avoid. Antivirals: concentration possibly increased by atazanavir, lopinavir, ritonavir, saquinavir and tipranavir - avoid. Ciclosporin: concentration of eluxadoline increased - avoid. Lipid-lowering agents: concentration possibly increased by gemfibrozil - avoid.
Metabolism
The metabolism of eluxadoline is currently unclear, however evidence suggests limited glucoronidation forms an acyl glucuronide metabolite that is then excreted into urine.
Metabolism
Eluxadoline is mainly excreted in the faeces, either as unabsorbed active substance or via the biliary system with the kidney playing a minimal role in elimination.
Properties of Eluxadoline
| Melting point: | >180°C (dec.) |
| Boiling point: | 834.2±65.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.284±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | Refrigerator |
| solubility | DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 4.01±0.10(Predicted) |
| color | White to Off-White |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 864821-90-9 |
Safety information for Eluxadoline
Computed Descriptors for Eluxadoline
Abamectin manufacturer
Honour Lab Limited
New Products
4-AMINO-TETRAHYDRO-PYRAN-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID HCL 4-(Dimethylamino)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-carbonitrile 4-Aminotetrahydropyran-4-carbonitrile Hydrochloride (R)-3-Aminobutanenitrile Hydrochloride 3-((Dimethylamino)methyl)-5-methylhexan-2-one oxalate 1,4-Dioxa-8-azaspiro[4.5]decane 5-Bromo-2-nitropyridine Nimesulide BP Aceclofenac IP/BP/EP Mefenamic Acid IP/BP/EP/USP Diclofenac Sodium IP/BP/EP/USP Ornidazole IP Diclofenac Potassium THOMAIND PAPER PH 2.0 TO 4.5 1 BOX BUFFER CAPSULE PH 9.2 - 10 CAP SODIUM CHLORIDE 0.1N CVS ALLOXAN MONOHYDRATE 98% PLATINUM 0.5% ON 3 MM ALUMINA PELLETS (TYPE 73) LITHIUM AAS SOLUTION 2-Bromo-1-(bromomethyl)-3-chloro-5-nitrobenzene 2-Bromo-3-nitroaniline N-(3-Hydroxypropyl)-N-methylacetamide 3-Bromo-6-chloropyridazine 4-ethyl-3-nitrobenzoic acidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran



You may like
-
 864821-90-9 Eluxadoline 98%View Details
864821-90-9 Eluxadoline 98%View Details
864821-90-9 -
 864821-90-9 98%View Details
864821-90-9 98%View Details
864821-90-9 -
 EluxadolineView Details
EluxadolineView Details
864821-90-9 -
 1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 -
 2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
1307449-08-6 -
 Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
25408-95-1 -
 2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
1805639-70-6 -
 Lithium ClavulanateView Details
Lithium ClavulanateView Details
61177-44-4