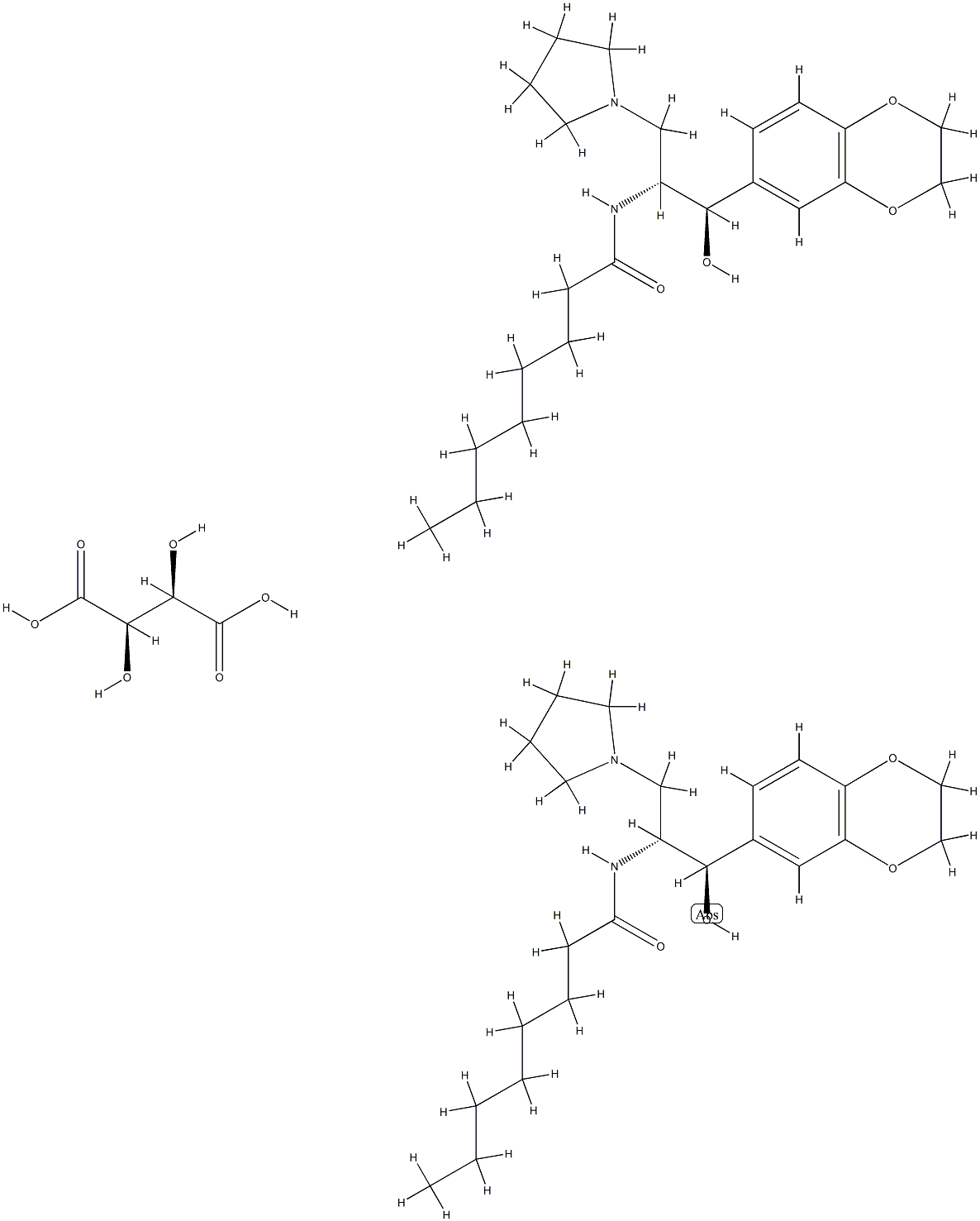
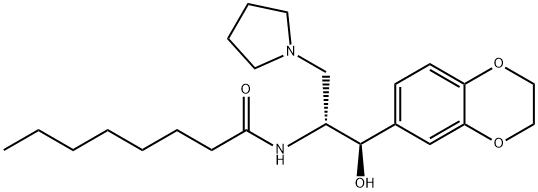
Eliglustat
- CAS NO.:491833-29-5
- Empirical Formula: C23H36N2O4
- Molecular Weight: 404.54
- MDL number: MFCD19443735
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2023-05-18 11:31:07
What is Eliglustat?
Absorption
Eliglustat administered in multiple doses of 84 mg twice daily had a Cmax of 12.1 to 25.0 ng/mL in CYP2D6 extensive metabolizers (EMs), 44.6 ng/mL in CYP2D6 intermediate metabolizers (IMs), and 113 to 137 ng/mL in CYP2D6 poor metabolizers (PMs). The median Tmax was 1.5-2 hr in CYP2D6 EMs, 2 hr in CYP2D6 IMs, and 3 hr in CYP2D6 PMs. The AUCtau was 76.3-143 ng?hr/mL in CYP2D6 EMs, 306 ng?hr/mL in CYP2D6 IMs, and 922-1057 ng?hr/mL in CYP2D6 PMs. In CYP2D6 EMs, the pharmacokinetics of eliglustat is time-dependent, and for doses that range between 42 and 294 mg, exposure increases in a more than dose-proportional fashion. In CYP2D6 PMs, eliglustat pharmacokinetics is linear and time-independent. In a steady state, the systemic exposure of 84 mg eliglustat twice daily is 7- to 9-fold higher in CYP2D6 PMs compared to EMs.
Following the oral administration of a single 84 mg dose of eliglustat, bioavailability in CYP2D6 EMs was lower than 5%. The low oral bioavailability of eliglustat suggests the role of transporters and/or an extensive first-pass metabolism. Eliglustat can be taken with or without food. In CYP2D6 EMs, severe renal impairment did not have an effect on eliglustat pharmacokinetics. The effect of renal impairment on eliglustat pharmacokinetics was not evaluated in CYP2D6 IMs, CYP2D6 PMs or CYP2D6 EMs with end-stage renal failure. Compared to CYP2D6 EMs with normal hepatic function, Cmax and AUC were 1.2-fold higher in CYP2D6 EMs with mild hepatic impairment, while Cmax and AUC were 2.8- and 5.2-fold higher, respectively, in CYP2D6 EMs with moderate hepatic impairment. The effect of mild and moderate hepatic impairment in CYP2D6 IMs and PMs, and the effect of severe hepatic impairment were not evaluated.
Toxicity
Eliglustat overdose may manifest as dizziness marked by disequilibrium, hypotension, bradycardia, nausea, and vomiting. These symptoms were detected in a healthy subject taking 21-times the dose recommended to type 1 Gaucher disease patients.
Eliglustat has no known antidote. In case of acute overdose, the patient should be carefully observed and given symptomatic and supportive treatment.
Due to the large volume of distribution of eliglustat, hemodialysis is not likely to be beneficial.
Acute dose toxicity studies were performed in rats and dogs. In rats, the maximum tolerated dose was 200 mg/kg, and in non-fasted dogs, the maximum tolerated dose was 25 mg/kg. Some of the adverse effects detected in these toxicity studies manifested on the GI tract, hematology parameters related to hemoglobin and coagulation process, reproductive organs, thymus and other lymphoid organs. Adverse effects in the kidney and liver were only detected in rats.
Carcinogenic studies were performed in both Sprague-Dawley rats and CD-1 mice. In doses up to 50 mg/kg/day in female Sprague-Dawley rats and 75 mg/kg/day in male Sprague-Dawley rats and CD-1 mice, eliglustat did not induce neoplasms. Eliglustat was negative in the following mutagenesis tests: Ames test, chromosome aberration test in human peripheral blood lymphocytes, mouse lymphoma gene mutation assay and in vivo oral mouse micronucleus test.
The Uses of Eliglustat
Eliglustat is a specific and potent inhibitor of glucosylceramide synthase.
Background
Eliglustat is a glucosylceramide synthase inhibitor used for the long-term treatment of type 1 Gaucher disease. Gaucher disease is a rare genetic disorder characterized by the deficiency of acid β-glucosidase, an enzyme that converts glucosylceramide into glucose and ceramide. In patients with Gaucher disease, the accumulation of glucosylceramide leads to the formation of Gaucher cells that infiltrate the liver, spleen, bone marrow and other organs. This leads to complications such as anemia and thrombocytopenia. By inhibiting glucosylceramide synthase, eliglustat reduces the accumulation of glucosylceramide.
Eliglustat is mainly metabolized by CYP2D6. Patients selected for eliglustat treatment undergo an FDA-cleared genotyping test to establish if they are CYP2D6 extensive metabolizers (EMs), intermediate metabolizers (IMs), or poor metabolizers (PMs). The results of this test dictate eliglustat dosing recommendations for each type of patient. There are no dosing recommendations for CYP2D6 ultra-rapid or indeterminate metabolizers. Eliglustat was approved by the FDA in August 2014 as an oral substrate reduction therapy for the first-line treatment of type 1 Gaucher disease. Enzyme replacement continues to be the standard of care for the treatment of type 1 Gaucher disease (imiglucerase, velaglucerase alfa, taliglucerase alfa); however, oral substrate reduction therapies with favourable safety profiles, such as eliglustat, represent a treatment alternative.
Indications
Eliglustat is a glucosylceramide synthase inhibitor indicated for the long-term treatment of type 1 Gaucher disease in adult patients who are CYP2D6 extensive metabolizers (EMs), intermediate metabolizers (IMs), or poor metabolizers (PMs) as detected by an FDA-cleared test. CYP2D6 ultra-rapid metabolizers may not achieve adequate eliglustat concentrations to achieve a therapeutic effect. A specific dosage cannot be recommended for CYP2D6 indeterminate metabolizers.
Definition
ChEBI: A carboxamide obtained by formal condensation of the carboxy group of octanoic acid with the primary amino group of (1R,2R)-2-amino-1-(2,3-dihydro-1,4-benzodioxin-6-yl)-3-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)propan-1-ol. A ceramide glucosyltr nsferase inhibitor used (as its tartrate salt) for treatment of Gaucher's disease.
Pharmacokinetics
Eliglustat is a specific inhibitor of glucosylceramide synthase (IC50 =10 ng/mL). In vitro studies suggest that eliglustat has minimal or no off-target activity against other glycosidases, such as α-glucosidase I and II, and lysosomal and non-lysosomal glucosylceramidases.
At 8 times the recommended dose (800 mg) and a ??mean peak concentration of 237 ng/mL, eliglustat did not have a clinically significant effect on QTc prolongation. However, modelling of PK/PD data predicts that at a plasma concentration of 500 ng/mL, PR, QRS and QTcF intervals increase 22, 7, and 13 msec, respectively. Since high plasma concentrations of eliglustat may increase the risk of cardiac arrhythmias, there are warnings and precautions for patients taking CYP2D6 or CYP3A4 inhibitors, those with specific CYP2D6 metabolizer status and different degrees of hepatic impairment. Depending on each case, the use of this drug is contraindicated, to be avoided, or requires dosage adjustment.
Patients with preexisting cardiac disease (congestive heart failure, recent acute myocardial infarction, bradycardia, heart block, ventricular arrhythmia), long QT syndrome, or those taking Class IA or Class II antiarrhythmic drugs are advised to avoid eliglustat.
Metabolism
Eliglustat is mostly metabolized by CYP2D6, and to a lower extent, by CYP3A4. In patients that are CYP2D6 poor metabolizers (PMs), eliglustat is mainly metabolized by CYP3A4. The primary metabolic pathways of eliglustat involve the sequential oxidation of the octanoyl moiety and the 2,3-dihydro-1,4-benzodioxane moiety. The combination of these two pathways results in the production of several oxidative metabolites.
After evaluating the potency of eliglustat metabolites, it was determined that none of them were active. Genz-399240 (M24) was identified as the major metabolite of eliglustat, while the rest of the metabolites contributed to less than 10% of total drug-related exposures. Genz-399240 (M24) did not show any major off-target effects; therefore, a transporter substrate specificity characterization was not performed.
Properties of Eliglustat
| Melting point: | 87-92°C |
| Boiling point: | 615.5±55.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.123±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Chloroform (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 13.45±0.20(Predicted) |
| color | White to Off-White |
Safety information for Eliglustat
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H225:Flammable liquids H304:Aspiration hazard H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P233:Keep container tightly closed. P240:Ground/bond container and receiving equipment. P241:Use explosion-proof electrical/ventilating/lighting/…/equipment. P242:Use only non-sparking tools. P243:Take precautionary measures against static discharge. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P331:Do NOT induce vomiting. P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. P303+P361+P353:IF ON SKIN (or hair): Remove/Take off Immediately all contaminated clothing. Rinse SKIN with water/shower. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P332+P313:IF SKIN irritation occurs: Get medical advice/attention. P337+P313:IF eye irritation persists: Get medical advice/attention. P370+P378:In case of fire: Use … for extinction. P405:Store locked up. P403+P235:Store in a well-ventilated place. Keep cool. |
Computed Descriptors for Eliglustat
Eliglustat manufacturer
Opulant Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Vijaya Pharma And Life Science
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 491833-29-5 Eliglustat Free Base 98%View Details
491833-29-5 Eliglustat Free Base 98%View Details
491833-29-5 -
 Eliglustat 98%View Details
Eliglustat 98%View Details -
 Eliglustat 98%View Details
Eliglustat 98%View Details
491833-29-5 -
 Eliglustat 491833-29-5 98%View Details
Eliglustat 491833-29-5 98%View Details
491833-29-5 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1