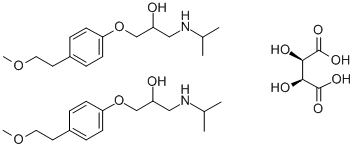
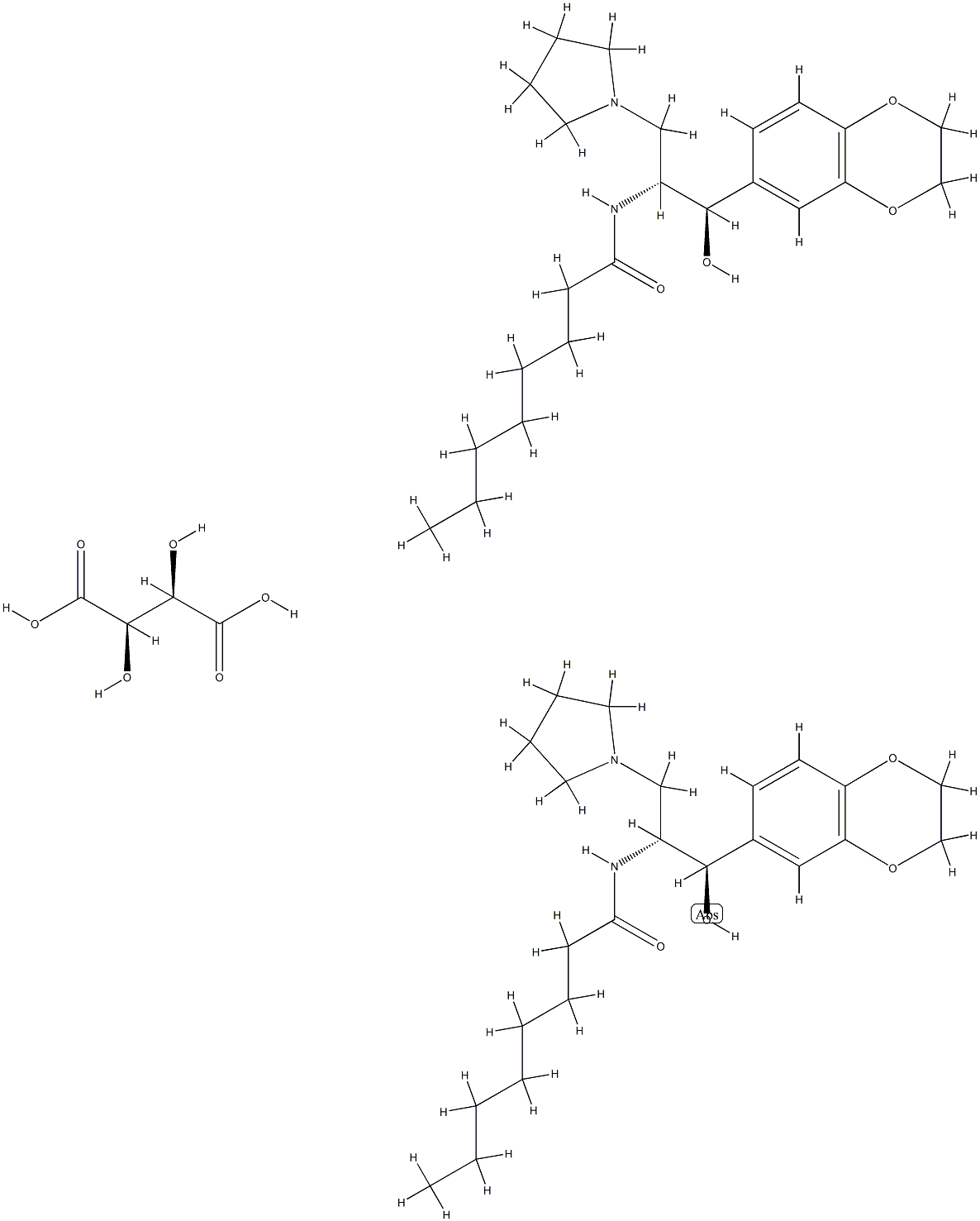
Eliglustat hemitartrate
- CAS NO.:928659-70-5
- Empirical Formula: C50H78N4O14
- Molecular Weight: 959.17272
- MDL number: MFCD22665712
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-28 10:29:14
What is Eliglustat hemitartrate?
Description
Eliglustat tartrate, developed and marketed by Genzyme Corporation (a subsidiary of Sanofi), was approved by the US FDA in August 2014 for the treatment of nonneuropathic (type 1) Gaucher disease (GD1) in both treatment-naive and treatment-experienced adult patients. It is the first oral treatment to be approved for first-line use in patients with Gaucher disease type 1, which is a rare lysosomal storage disease characterized by accumulation of lipid glucosylceramide (GL-1) due to insufficient production of the enzyme glucosylceramidase. Clinical complications include hepatosplenomegaly, anemia, thrombocytopenia, and bone involvement. Eliglustat is a specific inhibitor of glucosylceramide synthase with an IC50 of 10 ng/mL and acts as substrate reduction therapy for GD1; it has demonstrated non-inferiority to enzyme replacement therapy, which is the current standard of care, in Phase III trials.
The Uses of Eliglustat hemitartrate
Eliglustat Tartrate functions as an oral agent for treatment of Gaucher disease type 1, and lysosomal storage disorders in human. It also inhibits UDP-glucosylceramide synthase in mice thereby preventing Gaucher disease-associated with B-cell malignancy.
Definition
ChEBI: A tartrate that is the hemitartrate salt of eliglustat. A ceramide glucosyltransferase inhibitor used (as its tartrate salt) for treatment of Gaucher's disease.
Synthesis
Condensation of commercially available S-(+)-2-phenyl glycinol (87) with phenyl bromoacetate (88) in acetonitrile in the presence of N,N-diisopropylethylamine (DIPEA) provided morpholin-2-one 89 upon treatment with HCl. Neutralization with NaHCO3 followed by coupling with aldehyde 90 in refluxing EtOAc/toluene yielded oxazine adduct 91, which was isolated as a precipitate from methyl-tert-butyl ether (MTBE). The stereochemistry of the three new stereocenters in 91 can be rationalized through the cycloaddition of an ylide intermediate in the sterically-preferred S-configuration (generated by the reaction of the morpholinone 89 with aldehyde 90) with a second equivalent of the aldehyde. With the morpholinone in a chair conformation in which the phenyl group is equatorial, endo axial approach of the dipolarophile to the less-hindered face of the ylide and subsequent ring flip of the morpholinone ring to a boat conformation positions all exocyclic aryl substituents in a pseudoequatorial configuration. Opening of oxazine 91 with pyrrolidine in refluxing THF followed by addition of HCl in refluxing MeOH gave amide 92, which was reduced to amine 93 using LiAlH4 in refluxing THF. Subsequent hydrogenation with Pd(OH)2 in EtOH cleaved the phenylethanol group to give the free amine, which was converted to dioxalate salt 94 by treatment with oxalic acid in methyl isobutylketone (MIBK). Subjection of aminoethanol 94 to aqueous sodium hydroxide followed by coupling with palmitic acid Nhydroxysuccinimide (NHS)-ester (95) gave eliglustat as the corresponding freebase (96) in 9.5% overall yield from 87. Salt formation with L-tartaric acid (0.5 equiv) then provided eliglustat tartrate (XII).

Properties of Eliglustat hemitartrate
| Melting point: | >133°C (dec.) |
| storage temp. | -20°C Freezer, Under inert atmosphere |
| solubility | DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | Solid |
| color | White |
Safety information for Eliglustat hemitartrate
Computed Descriptors for Eliglustat hemitartrate
Eliglustat hemitartrate manufacturer
Biophore India Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Vijaya Pharma And Life Science
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 928659-70-5 Eliglustat Hemitartrate 98%View Details
928659-70-5 Eliglustat Hemitartrate 98%View Details
928659-70-5 -
 928659-70-5 98%View Details
928659-70-5 98%View Details
928659-70-5 -
 Eliglustat tartrate 98%View Details
Eliglustat tartrate 98%View Details
928659-70-5 -
 Eliglustat tartrate 928659-70-5 98%View Details
Eliglustat tartrate 928659-70-5 98%View Details
928659-70-5 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1