Edoxaban (tosylate Monohydrate)
- CAS NO.:1229194-11-9
- Empirical Formula: C31H38ClN7O7S2
- Molecular Weight: 720.26
- MDL number: MFCD28400751
- EINECS: 1592732-453-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-17 08:48:38
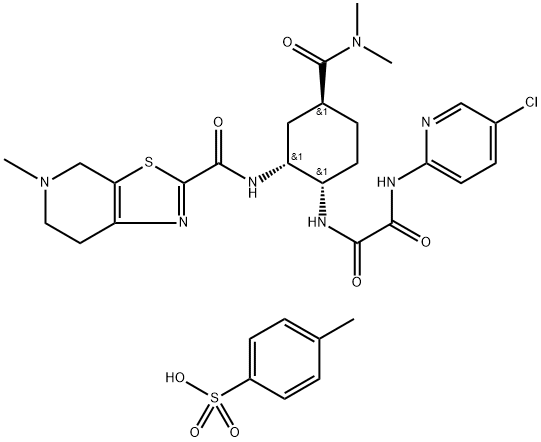
What is Edoxaban (tosylate Monohydrate)?
The Uses of Edoxaban (tosylate Monohydrate)
Edoxaban is an anticoagulant drug which acts as a direct factor Xa inhibitor.
Definition
ChEBI: A hydrate that is the monohydrate of the tosylate salt of edoxaban. Used for the treatment of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism.
Biological Activity
factor xa (fxa), a key serine protease, is a promising target enzyme for the prophylaxis and treatment of thromboembolic diseases. edoxaban tosylate monohydrate is a novel antithrombotic agent that directly inhibits fxa activity.
Clinical Use
Daichi Sankyo’s edoxaban tosilate is an orally administered coagulation factor Xa inhibitor that was approved and launched in Japan for the preventive treatment of venous thromboembolic events (VTE) in patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty, total hip arthroplasty, or hip fracture surgery. Edoxaban has been shown to have a rapid onset of anticoagulant effect due to short Tmax (1–2 h) after dosing and sustained for up to 24 h post-dose. Marketed under the brand name Lixiana, it is currently in phase III studies in the US for the prevention of stroke and systemic embolic events in patients with atrial fibrillation (AF) and venous thromboembolism (VTE).
in vitro
edoxaban tosylate monohydrate (du-176b) inhibited fxa with ki values of 0.561 nm for free fxa, 2.98 nm for prothrombinase, and exhibited >10 000-fold selectivity for fxa. du-176b doubled prothrombin time and activated partial thromboplastin time in human plasma. du-176b did not impair platelet aggregation by adp, collagen or u46619 [1].
in vivo
du-176b dose-dependently inhibited thrombus formation in rat and rabbit thrombosis models, although bleeding time in rats was not significantly prolonged at an antithrombotic dose [1].
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Analgesics: increased risk of bleeding with NSAIDs
and high dose aspirin; increased risk of haemorrhage
with IV diclofenac and ketorolac - avoid
Anti-arrhythmics: concentration increased by
dronedarone (reduce edoxaban dose)
Antibacterials: concentration increased by
erythromycin (reduce edoxaban dose); concentration
reduced by rifampicin.
Anticoagulants: increased risk of haemorrhage with
other anticoagulants - avoid.
Antidepressants: concentration possibly reduced by
St John’s wort.
Antiepileptics: concentration possibly reduced
by carbamazepine, fosphenytoin, phenobarbital,
phenytoin and primidone.
Antifungals: concentration increased by ketoconazole
(reduce edoxaban dose).
Ciclosporin: concentration of edoxaban increased
(reduce edoxaban dose).
Metabolism
Unchanged edoxaban is main form in plasma.
Edoxaban is metabolised via hydrolysis (mediated
by carboxylesterase 1), conjugation or oxidation by
CYP3A4/5 (<10%). Edoxaban has 3 active metabolites,
the predominant metabolite (M-4), formed by hydrolysis,
is active and reaches less than 10% of the exposure of the
parent compound in healthy subjects. Exposure to the
other metabolites is less than 5%. Edoxaban is a substrate
for the efflux transporter P-glycoprotein (P-gp), but
not a substrate for uptake transporters such as organic
anion transporter polypeptide OATP1B1, organic
anion transporters OAT1 or OAT3 or organic cation
transporter OCT2. Its active metabolite is a substrate for
OATP1B1.
Renal clearance accounts for approximately 35% of the
administered dose. Metabolism and biliary/intestinal
excretion account for the remaining clearance.
References
[1] furugohri t, isobe k, honda y, kamisato-matsumoto c, sugiyama n, nagahara t, morishima y, shibano t. du-176b, a potent and orally active factor xa inhibitor: in vitro and in vivo pharmacological profiles. j thromb haemost. 2008;6(9):1542-9.
[2] bathala ms, masumoto h, oguma t, he l, lowrie c, mendell j. pharmacokinetics, biotransformation, and mass balance of edoxaban, a selective, direct factor xa inhibitor, in humans. drug metab dispos. 2012;40(12):2250-5.
Properties of Edoxaban (tosylate Monohydrate)
| Melting point: | >252°C (dec.) |
| storage temp. | Hygroscopic, Refrigerator, under inert atmosphere |
| solubility | Chloroform (Very Slightly), DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly, Sonicated) |
| form | Solid |
| color | White to Off-White |
| Stability: | Hygroscopic |
Safety information for Edoxaban (tosylate Monohydrate)
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Edoxaban (tosylate Monohydrate)
| InChIKey | ZLFZITWZOYXXAW-BUZWFPPCNA-N |
| SMILES | S(C1C=CC(C)=CC=1)(O)(=O)=O.N([C@@H]1C[C@@H](C(=O)N(C)C)CC[C@@H]1NC(=O)C(=O)NC1N=CC(Cl)=CC=1)C(C1SC2CN(C)CCC=2N=1)=O |&1:12,14,22,r| |
Edoxaban (tosylate Monohydrate) manufacturer
CVR Life sciences Pvt Ltd
Honour Lab Limited
Mehta API Pvt. Ltd.
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 1229194-11-9 Edoxaban tosylate monohydrate 99%View Details
1229194-11-9 Edoxaban tosylate monohydrate 99%View Details
1229194-11-9 -
 Edoxaban tosylate monohydrate 98%View Details
Edoxaban tosylate monohydrate 98%View Details -
 Edoxaban tosylate monohydrate 98%View Details
Edoxaban tosylate monohydrate 98%View Details
1229194-11-9 -
 Edoxaban tosylate monohydrate 1229194-11-9 98%View Details
Edoxaban tosylate monohydrate 1229194-11-9 98%View Details
1229194-11-9 -
 Edoxaban tosylate hydrate 95% CAS 1229194-11-9View Details
Edoxaban tosylate hydrate 95% CAS 1229194-11-9View Details
1229194-11-9 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1