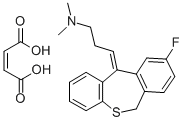
Dothiepin
- CAS NO.:113-53-1
- Empirical Formula: C19H21NS
- Molecular Weight: 295.44
- MDL number: MFCD00242922
- EINECS: 204-031-2
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-10-28 16:00:23
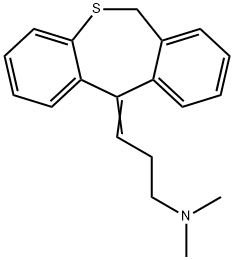
What is Dothiepin?
Absorption
Dosulepin is well absorbed from the intestines to reach the peak plasma concentration of 37.6ng/mL at 2.18 hours (Tmax) following oral administration of 25mg . The steady state concentrations are variable among individuals due to dynamic relationship between the drug dose and plasma concentration .
Toxicity
High mortality is associated with overdose of dosulepin (>5mg/kg) with the onset of toxicity occuring within 4-6 hours. Dosulepin may increase the risk of cardiovascular toxicity (cardiac arrhythmias, conduction disorders, cardiac failure and circulatory collapse) and severe hypotension, especially in the elderly . Withdrawal symptoms are reported in case of sudden cessation of therapy, which include insomnia, irritability, headache, nausea, giddiness, panic-anxiety, extreme motor restlessness and excessive perspiration. There have been reports of increased suicidal thoughts or behaviour with dosulepin treatment. Oral lowest published toxic dose (Toxic Dose Low, TDLo) is 90 mg/kg in infants and 4.5 mg/kg in female adults. Intravenous LD50 in mouse is 31 mg/kg .
Most common adverse effects involve the central nervous system (drowsiness, extrapyramidal symptoms, tremor, confusional states, disorientation, dizziness, paraesthesia, alterations to EEG patterns), anticholinergic effects (dry mouth, sweating, urinary retention), cardiovascular system (hypotension, postural hypotension, tachycardia, palpitations, arrhythmias, conduction defects), endocrine system (altered libido), gastrointestinal system (nausea, vomiting, constipation) and blurred vision .
Chemical properties
Pale Yellow Low Melting Solid
History
Described in the 1960s by the Czech company Sdruzeni Podniku pro Zdravotnickon Vyrobu; SPOFA (Spofa, 1962)
The Uses of Dothiepin
A tricyclic antidepressant.
Indications
Indicated in the treatment of symptoms of depressive illness, especially where an anti-anxiety effect is required.
Background
Dosulepin (INN, BAN) formerly known as dothiepin (USAN), is a tricyclic antidepressant with anxiolytic properties that is used in several European and South Asian countries, as well as Australia, South Africa, and New Zealand. It is not FDA-approved due to low therpeutic index and significant toxicity in overdose. Dosulepin inhibits the reuptake of biogenic amines, increasing available neurotransmitter levels at the synaptic cleft. The use of dosulepsin is only recommended in patients who are intolerant or unresponsive to alternative antidepressant therapies. Dosulepsin is a thio derivative of Amitriptyline with a similar efficacy to that of Amitriptyline, and also exhibits anticholinergic, antihistamine and central sedative properties . Its hydrochloride form is a common active ingredient in different drug formulations.
What are the applications of Application
Dothiepin is a serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor
Definition
ChEBI: Dothiepin is a dibenzothiepine. It has a role as an antidepressant and an anticoronaviral agent.
Synthesis Reference(s)
Synthesis (Spofa, 1962): S-Benzylthiosalicylic acid is treated with polyphosphoric acid and the resulting cyclic ketone is reacted with 3-dimethylaminopropyl magnesium chloride to afford an alcohol which is dehydrated with sulfuric acid. 
Synthesis of dosulepin
Pharmacokinetics
Dosulepin is a tricyclic antidepressant that interacts with various receptors and transporters. It is a monoamine reuptake inhibitor with approximately equal potency for noradrenaline and 5-HT that increases the availability of these neurotransmitters at the central synapses . The metabolites of dosulepin are shown to inhibit 5HT uptake by the human blood platelet .
Clinical Use
Dosulepin (also referred to as dothiepin) is a member of the TCA family and has similar clinical uses as amitrip- tyline, thus providing effective treatment of depression (Goldstein and Claghorn, 1980; Lancaster and Gonzales, 1989; Donovan et al., 1991) and also against pain (Feinmann et al., 1984; Caruso et al., 1987) and tinnitus. Like amitriptyline it has sedative properties, however its anti-muscarinic side-effects are less pronounced. Dosulepin is readily absorbed from the GI tract and extensively demethylated while undergoing a first-pass effect. Metabolic pathways include next to hydroxylation and N-oxidation steps, S-oxidation. Elimination half-lifes vary from 14 to 24 hours interindividually (Maguire et al., 1982; Yu et al., 1986; Ilett et al., 1993).
Metabolism
Dosulepin undergoes extensive hepatic metabolism, to form main metabolites N-demethylated derivative northiaden (desmethyldosulepin or northiaden) and dosulepin S-oxide. Northiaden S-oxide is among 12 basic metabolites that are found in urine. The metabolic pathways of dosulepin is thought to involve N-demethylation, S-oxidation and glucuronic acid conjugation .
Properties of Dothiepin
| Melting point: | 55-57° |
| Boiling point: | bp0.05 171-172° |
| Density | 1.1022 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.5300 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | Refrigerator |
| solubility | Chloroform (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | Thick Oil to Low-Melting Solid |
| pka | 9.35±0.28(Predicted) |
| color | Off-White to Light Yellow |
Safety information for Dothiepin
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H361:Reproductive toxicity H362:Reproductive toxicity, effects on or via lactation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P263:Avoid contact during pregnancy/while nursing. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Dothiepin
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
![3-dibenzo[b,e]thiepin-11(6H)-ylidene-8-methyl-8-azabicyclo[3.2.1]octane hydrochloride](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/27574-25-0.gif)


You may like
-
 113-53-1 Dosulepin 98%View Details
113-53-1 Dosulepin 98%View Details
113-53-1 -
 Dosulepin for system suitability CAS 113-53-1View Details
Dosulepin for system suitability CAS 113-53-1View Details
113-53-1 -
 3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 -
 4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
5305-40-8
