Disopyramid phosphate
Synonym(s):α-Diisopropylaminoethyl-α-phenylpyridine-2-acetamide;Disopyramide phosphate salt
- CAS NO.:22059-60-5
- Empirical Formula: C21H32N3O5P
- Molecular Weight: 437.47
- MDL number: MFCD00069254
- EINECS: 244-756-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-10-23 13:36:13
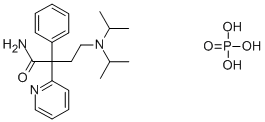
What is Disopyramid phosphate ?
Originator
Rythmodan,Cassenne,France,1969
The Uses of Disopyramid phosphate
Cardiac depressant (anti-arrhythmic).
The Uses of Disopyramid phosphate
Disopyramide Phosphate is an antiarrhythmic (class IA). Sodium channel blocker.
The Uses of Disopyramid phosphate
Disopyramide phosphate salt has been used as an internal standard for plasma sample analysis by mass spectrometry. It might be used as a test compound in a teratogenicity study.
What are the applications of Application
Disopyramide phosphate salt is a sodium channel blocker
Definition
ChEBI: Disopyramide phosphate is an organoammonium phosphate. It is functionally related to a disopyramide.
Manufacturing Process
To a solution of 35.3 parts of phenylacetonitrile and 47.6 parts of 2-
bromopyridine in 175 parts of dry toluene is added 53.4 parts of sodamide
slowly with stirring over a period of 45 minutes. The resultant mixture is
stirred at 100°C for 2 hours before it is cooled and the excess sodamide is
decomposed by the addition of water. The toluene layer is separated and
washed with water to remove excess alkali. The toluene solution is extracted
with 6 N hydrochloric acid and the acid extract is made alkaline and then
extracted with toluene. The toluene solution is dried over sodium sulfate and
the solvent is evaporated. Recrystallization of the residue from alcohol-hexane
gives α-phenyl-2-pyridineacetonitrile melting at about 87-88°C.
To a solution of 41 parts of α-phenyl-2-pyridineacetonitrile in 350 parts of dry
toluene is added 9.2 parts of sodamide and the mixture is stirred and heated
at 90°C for 30 minutes. Heating is stopped and a solution of 38.5 parts of 2-
diisopropylaminoethyl chloride in 110 parts of dry toluene is added slowly over
a period of 30 minutes. The mixture is stirred and refluxed for 6 hours before
it is cooled and decomposed by the addition of water. The toluene layer is
separated and washed with water and extracted with 6 N hydrochloric acid.
The acid extract is made alkaline and extracted with toluene. The toluene
solution is washed with water and dried and the solvent is evaporated.
Distillation of the residue gives 4-diisopropylamino-2-phenyl-2-(2-pyridyl)-
butyronitrile boiling at about 145°-160°C at 0.3 mm pressure.
A solution of 27.2 parts of 4-diisopropylamino-2-phenyl-2-(2-
pyridyl)butyronitrile in 200 parts of concentrated sulfuric acid is heated on a
steam bath for 4 hours and then poured onto ice. The resultant mixture is
alkalized with 10 N sodium hydroxide, and the pH is adjusted to 6 by the
addition of acetic acid. The solution is washed once with benzene before it is
alkalized again with 10 N sodium hydroxide solution. The resultant mixture is
extracted with benzene, and the solvent is evaporated from the benzene
extract. The resultant residue is dissolved in ethanol and the alcohol solution
is treated with charcoal and filtered. Evaporation of the solvent leaves a
residue which is recrystallized from hexane to give 4-diisopropylamino-2-
phenyl-2-(2-pyridyl)butyramide melting at about 94.5-95°C. It may be
converted to the phosphate with phosphoric acid.
brand name
Norpace (Searle).
Therapeutic Function
Antiarrhythmic
General Description
Disopyramide phosphate, -[2(diisopropylamino)ethyl]- -phenyl-2-pyridineacetamidephosphate (Norpace), is an oral and intravenousclass IA antiarrhythmic agent. It is quite similar to quinidineand procainamide in its electrophysiological properties, inthat it decreases phase 4 diastolic depolarization, decreasesconduction velocity, and has vagolytic properties.31 It is usedclinically in the treatment of refractory, life-threatening ventriculartachyarrhythmias. Oral administration of the drugproduces peak plasma levels within 2 hours. The drug isbound approximately 50% to plasma protein and has a halflifeof 6.7 hours in humans. More than 50% is excretedunchanged in the urine. Therefore, patients with renal insufficiencyshould be monitored carefully for evidence ofoverdose. Disopyramide phosphate commonly exhibits sideeffects of dry mouth, constipation, urinary retention, andother cholinergic blocking actions because of its structuralsimilarity to anticholinergic drugs.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Class IA antiarrhythmic; sodium channel blocker
Properties of Disopyramid phosphate
| Melting point: | 202-204°C |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | DMSO (Slightly, Heated, Sonicated), Methanol (Slightly), Water (Slightly) |
| form | neat |
| color | White to Off-White |
Safety information for Disopyramid phosphate
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral |
Computed Descriptors for Disopyramid phosphate
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid DIETHYL AMINOMALONATE HYDROCHLORIDE 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Disopyramide phosphate CAS 22059-60-5View Details
Disopyramide phosphate CAS 22059-60-5View Details
22059-60-5 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 -
 733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8