DIPHENAMID
Synonym(s):N,N-Dimethyl-2,2-diphenylacetamide
- CAS NO.:957-51-7
- Empirical Formula: C16H17NO
- Molecular Weight: 239.31
- MDL number: MFCD00008321
- EINECS: 213-482-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:07:02
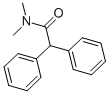
What is DIPHENAMID?
Description
Diphenamid is a white crystalline solid in various forms. Molecular weight= 239.34; Freezing/Meltingpoint = 135℃; Vapor pressure= 2.8 3 10 2 8 mmHg at20℃. Hazard Identification (based on NFPA-704 M RatingSystem): Health 1, Flammability 0, Reactivity 0. Veryslightly soluble in water
Chemical properties
white or off-white powder
The Uses of DIPHENAMID
Diphenamid is a pesticide found in representative agricultural produce (brown rice, orange, spinach and potatoes).
The Uses of DIPHENAMID
Herbicide.
The Uses of DIPHENAMID
Selective preemergence herbicide used to control many broad-leaved weeds and most grass weeds in okra, cotton, peanuts tomatoes, sweet potatoes, potatoes, tobacco, fruits, turf and ornamentals.
Definition
ChEBI: Diphenamid is a diarylmethane.
General Description
Colorless to off-white crystals. Used as an herbicide.
Reactivity Profile
DIPHENAMID is an amide. Amides/imides react with azo and diazo compounds to generate toxic gases. Flammable gases are formed by the reaction of organic amides/imides with strong reducing agents. Amides are very weak bases (weaker than water). Imides are less basic yet and in fact react with strong bases to form salts. That is, they can react as acids. Mixing amides with dehydrating agents such as P2O5 or SOCl2 generates the corresponding nitrile. The combustion of these compounds generates mixed oxides of nitrogen (NOx). DIPHENAMID is decomposed by strong base or acid.
Agricultural Uses
Herbicide: This material is used as a pre-emergent and selective herbicide for tomatoes, peanuts, alfalfa, soybeans, cotton and other crops. Not approved for use in the U.S. or EU countries. There are 18 global suppliers.
Trade name
DIF 4®; DYMID®[C]; ENIDE®[C]; FDN®; FENAM®; L 34314®; LILLY 34314®; RIDEON®; U 4513®; ZARUR®
Potential Exposure
AgriculturalChemical; Mutagen. This material is used as a preemergentand selective herbicide for tomatoes, peanuts, alfalfa, soybeans, cotton, and other crops.
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts theskin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediatelywith soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. Ifthis chemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure,begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPRif heart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to amedical facility. When this chemical has been swallowed,get medical attention. Give large quantities of water andinduce vomiting. Do not make an unconscious personvomit.
Environmental Fate
Soil. Degradation of diphenamid in soils was reported to form desmethyldiphenamid via monodemethylation and a bidemethylated product of diphenamid (Somasundaram and Coats, 1991). The persistence of diphenamid under warm-moist soil conditions ranged from 3 to 6 months (Ashton and Monaco, 1991).
Groundwater. According to the U.S. EPA (1986), diphenamid has a high potential to leach to groundwater.
Plant. In strawberries, diphenamide was transformed via N-demethylation yielding Nmethyl-2,2-diphenylacetamide (Golab et al., 1966).
Photolytic. N-Methyl-2,2-diphenylacetamide and benzoic acid were reported as major photoproducts following the UV irradiation of diphenamid in distilled water (Cessna and Muir, 1991).
Chemical/Physical. Emits toxic fumes of nitrogen oxides when heated to decomposition (Sax and Lewis, 1987).
storage
Color Code—Blue: Health Hazard/Poison: Storein a secure poison location. Color Code—White: Corrosiveor Contact Hazard; Store separately in a corrosion-resistantlocation. Prior to working with this chemical you should betrained on its proper handling and storage. Store in tightlyclosed containers in a cool, well-ventilated area away fromstrong oxidizers, strong acids, strong alkalies.
Shipping
The name of this material is not in the DOT listof materials for label and packaging standards. However,based on regulations, it may be classified as anEnvironmentally hazardous substances, solid, n.o.s. Thischemical requires a shipping label of “CLASS 9.” It falls inHazard Class 9 and Packing Group III.[20, 21]
Properties of DIPHENAMID
| Melting point: | 132-136 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 381.97°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.1700 |
| refractive index | 1.5500 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | 0-6°C |
| form | Huff Powder |
| pka | -0.68±0.70(Predicted) |
| color | White |
| Water Solubility | 239.9mg/L(25 ºC) |
| Merck | 13,3339 |
| BRN | 2052009 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, strong bases. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 957-51-7 |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Fenam(957-51-7) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Diphenamid (957-51-7) |
Safety information for DIPHENAMID
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H412:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for DIPHENAMID
New Products
4-Fluorophenylacetic acid 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate (6-METHYL-[1,3]DITHIOLO[4,5-b]QUINOXALIN-2-ONE INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 42831-50-5 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 98%View Details
42831-50-5 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 98%View Details
42831-50-5 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1