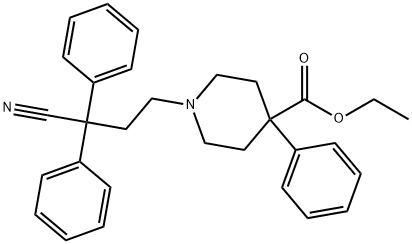
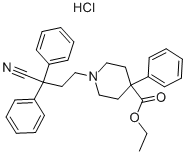
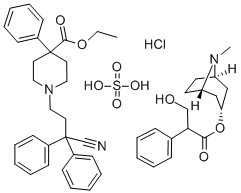
Difenoxinum
- CAS NO.:28782-42-5
- Empirical Formula: C28H28N2O2
- Molecular Weight: 424.53
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2023-05-15 10:44:02
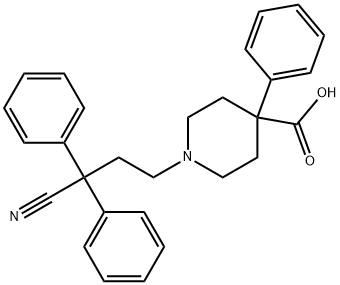
What is Difenoxinum?
Absorption
A high percentage of Motofen(R) is absorbed, and absorption occurs rapidly. Peak plasma concentrations are achieved within 40-60 minutes. [Lexicomp, 2013]
Originator
Lyspafena,Cilag Chemie,W. Germany,1980
The Uses of Difenoxinum
The active metabolite of Diphenoxylate. Antiperistaltic; antidiarrheal. This is a controlled substance (opiate).
Indications
Motofen(R) is a combination of atropine, an anticholinergic drug, and difenoxin, an antidiarrheal drug. It has been used in many countries for many years as a second line opioid-agonist antidiarrheal, which exists an intermediate between loperamide and paragoric. [2]
Diarrhea which is a result of cyclic or diarrhea predominant Inflammatory Bowel Syndrome may not be treated effectively with difenoxin, diphenoxylate, or loperamide. As such, diarrhea and cramping which does not respond to non-centrally acting derivatives or belladonna derivatives such as atropine are often treated with conservative doses of codeine. In patients with acute ulcerative colitis, as induction of toxic megacolon is possible, and thus use of Motofen(R) is cautioned.
Motofen(R) has been assigned pregnancy category C by the FDA, and is to be used only when the potential benefits outweigh the potential risk to the fetus. The safety of use during lactation is unknown and thus not recommended.
Background
Difenoxin is a 4-phenylpiperidine which is closely related to the opioid analgesic meperidine. Difenoxin alone is a USA Schedule I controlled drug, as it may be habit forming. However, it is listed as a Schedule IV controlled drug if combined with atropine, which is added to decrease deliberate misuse. Motofen(R) is a brand mixture which combines atropine sulfate and difenoxin hydrochloride. It is approved by the FDA to treat acute and chronic diarrhea.
Difenoxin is an active metabolite of the anti-diarrheal drug, diphenoxylate, which is also used in combination with atropine in the brand mixture Lomotil(R). It works mostly in the periphery and activates opioid receptors in the intestine rather than the central nervous system (CNS). [3] Difenoxin is also closely related to loperamide, but unlike loperamide it is still capable of crossing the blood brain barrier to produce weak sedative and analgesic effects. However, the antidiarrheal potency of difenoxin is much greater than its CNS effects, which makes it an attractive alternative to other opioids.
Definition
ChEBI: A piperidinemonocarboxylic acid that is 4-phenylpiperidine-4-carboxylic acid in which the hydrogen attached to the nitrogen atom is substituted by a 3-cyano-3,3-diphenylpropyl group.
Manufacturing Process
To a stirred solution of 5.52 parts of t-potassiurn butanolate in 60 parts of dimethylsulfoxide are added 1.7 parts of ethyl-1-(3-cyano-3,3- diphenylpropyl)-4-phenylisonipecotate hydrochloride and the whole is stirred on an oil bath (90°C) for 4 hours. The reaction mixture is cooled (30°C) and poured onto 180 parts of water with stirring. After two extractions with benzene, the aqueous phase is acidified with glacial acetic acid to pH 6.5 with stirring. The precipitated product is filtered off, washed with water, dried, dissolved in 50 parts of 0.4 N potassium hydroxide and precipitated again with glacial acetic acid. The crude free base is filtered off and dissolved in a mixture of 2-propanol and chloroform and gaseous hydrogen chloride is introduced into the solution. The whole is filtered and the filtrate is evaporated. The residue is mixed with benzene and the latter is evaporated again. The residue is recrystallized from 2-propanol, yielding 1-(3-cyano-3,3- diphenylpropyl)-4-phenylisonipecotic acid hydrochloride.
brand name
Dioctin;Lyspafen;Lyspofenac;Motofen.
Therapeutic Function
Antiperistaltic
World Health Organization (WHO)
Difenoxin is the principal metabolite of diphenoxylate. See WHO comment for diphenoxylate.
Pharmacokinetics
Difenoxin acts as a potent antidiarrheal by slowing the movement of the intestines. It also crosses the blood brain barrier to a slight degree to exert weak sedative and analgesic effects.
Adverse reactions thus include dizziness, drowsiness, lightheadedness and headache, in addition to gastrointestal side effects such as nausea, vomiting, dry mouth and epigastric distress. [Lexicomp, 2013]
Metabolism
Metabolism occurs by hydroxylation to form an inactive metabolite. [Lexicomp, 2013]
Properties of Difenoxinum
| Boiling point: | 632.7±55.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.175±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| solubility | soluble in DMSO, Methanol |
| pka | 3.55±0.20(Predicted) |
| form | Powder |
| color | Brown |
Safety information for Difenoxinum
Computed Descriptors for Difenoxinum
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE DIETHYL AMINOMALONATE HYDROCHLORIDE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 -
 733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8