Dicofol
Synonym(s):2,2,2-Trichloro-1,1-bis(4-chlorophenyl)ethanol
- CAS NO.:115-32-2
- Empirical Formula: C14H9Cl5O
- Molecular Weight: 370.49
- MDL number: MFCD00055271
- EINECS: 204-082-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-06-13 14:48:16
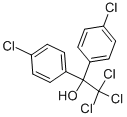
What is Dicofol?
Description
Dicofol is a white or brown waxy solid.Molecular weight=370.48; Flash point=120℃. HazardIdentification (based on NFPA-704 M Rating System):Health 2, Flammability 1, Reactivity 0. Slightly soluble inwater.
Chemical properties
Pure dicofol is available as a white or grey powder or colourless crystal solid, while the technical dicofol is a red-brown or amber viscous liquid with an odour like fresh-cut hay. Dicofol undergoes decomposition on burning or on contact with acids, acid fumes, or bases producing toxic and corrosive fumes including hydrogen chloride.
Dicofol is combustible and incompatible with strong oxidising agents. Dicofol is soluble in most aliphatic and aromatic solvents and most common organic solvents but practically insoluble in water and hydrolyses in basic solution.
Chemical properties
Pure dicofol is available as a white or gray powder or colorless solid crystals while the technical dicofol is a red-brown or amber viscous liquid with an odor like fresh-cut hay. Dicofol undergoes decomposition on burning or on contact with acids, acid fumes or bases, producing toxic and corrosive fumes including hydrogen chloride. Dicofol is a persistent OCP used as an acaricide and miticide. It is structurally similar to DDT. Dicofol is combustible and incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. It is soluble in most aliphatic and aromatic solvents and most common organic solvents, but practically insoluble in water and hydrolyzes in basic solution. It is used on a wide variety of fruit, vegetables, ornamental and fi eld crops. Dicofol is manufactured from DDT. Dicofol is corrosive to some metals. It is used for foliar applications, mostly on cotton, apples, and citrus crops. Other crops include strawberries, mint, beans, peppers, tomatoes, pecans, walnuts, stonefruit, cucurbits, and non-residential lawns/ornamentals.
Chemical properties
Dicofol is a white or brown waxy solid
The Uses of Dicofol
Acaricide, organochlorine pesticide. Dicofol is a non-systemic acaricide/miticide currently registered in the US and Canada for use on a wide variety of crops.
The Uses of Dicofol
Nonsystemic acaricide to control mites in citrus fruits, grapes, cotton, pome and stone fruit.
Definition
ChEBI: A tertiary alcohol that is DDT in which the benzylic hydrogen has been replaced by a hydroxy group.
General Description
Dicofol or kelthane is a white crystalline, wettable powder dissolved in a liquid carrier, (water). The primary hazard is the threat to the environment. Immediate steps should be taken to limit its spread to the environment. Since Dicofol is a liquid Dicofol can easily penetrate the soil and contaminate groundwater and nearby streams. Dicofol can cause illness by inhalation, skin absorption, and/or ingestion. Dicofol is used as a pesticide.
Air & Water Reactions
Hydrolyzed in alkaline media to dichlorobenzophenone and chloroform. Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Dicofol is an organochlorine bridged diphenyl. Halogenated aliphatic compounds are moderately or very reactive. Reactivity generally decreases with increased degree of substitution of halogen for hydrogen atoms. Halogenated aliphatics are incompatible with strong oxidizing and reducing agents. Also, they are incompatible with many amines, nitrides, azo/diazo compounds, alkali metals, and epoxides. Dicofol hydrolyzes in alkali. Dicofol is slightly corrosive to metals. Contact with steel at elevated temperatures causes formation of toxic gases. .
Health Hazard
Inhalation or ingestion causes nausea, headache, weight loss, convulsions, possible kidney and liver damage. Contact with eyes causes irritation.
Health Hazard
Exposures to dicofol cause adverse health effects and poisoning. Occupational workers suffer harmful effects on inhalation, ingestion and through skin contact. The symptoms of poisoning include, but are not limited to, nausea, dizziness, weakness, and vomiting from ingestion or respiratory exposure, skin irritation or rash from dermal exposure. Dicofol-poisoned occupational workers show skin sensitization, conjunctivitis of the eyes, and pathomorphological changes in the liver, kidneys, and CNS. After exposures to high concentrations of dicofol, workers show nervousness, hyperactivity, headache, nausea, vomiting, unusual sensations, fatigue, convulsions, coma, respiratory failure, and death. However, published literature is limited and more data is required on occupational workers as well as the general population.
Agricultural Uses
Insecticide, Acaricide: Not approved for use in EU countries. Severely Restricted for use in EU (containing>78% p,p'-dicofol or 1 g/kg of DDT and DDT-related compounds). Dicofol is an organochlorine miticide/pesticide used for foliar applications, mostly on cotton, apples, and citrus crops. Other crops include: strawberries, mint, beans, peppers, tomatoes, pecans, walnuts, stonefruit, cucurbits, and nonresidential lawns/ornamentals. Formulations registered for use on food/feed crops include emulsifiable concentrates, and wettable powder formulations. These formulations may be applied as concentrated or dilute sprays using aircraft, duster, groundboom, and sprayer. Dicofol is manufactured from DDT. In 1986, use of dicofol was temporarily canceled by the U.S. EPA because of concerns raised by high levels of DDT contamination. However, it was reinstated when it was shown that modern manufacturing processes can produce technical-grade dicofol which contains <0.1% DDT.
Trade name
ACARIN®[C]; CALLIFOL®; CARBAX®; CEKUDIFOL®; DECOFOL®; DICOMITE®; DIFOL®; FERRIAMICIDE®; FUMITE DICOFOL®; FW 293®; HIFOL®; KELTANE®; KELTHANE®; P,P'- KELTHANE®; KELTHANETHANOL®; MILBOL®; MITIGAN®; TIKTOK®; VAPCOTHION®, dicofol
Potential Exposure
A potential danger to those involved in manufacture, formulation and application of this organochlorine pesticide. Used as acaricide (miticide) in agricultural and nonagricultural applications. Similar in structure to DDT.
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts theskin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediatelywith soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. Ifthis chemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure,begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR ifheart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medicalfacility. When this chemical has been swallowed, get medical attention. Give large quantities of water and inducevomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit.
Environmental Fate
Plant. The major metabolite reported on apples is 4,4′-dichlorobenzophenone. On apples, dicofol concentrations decreased from 702 ppm to 436 ppm after 15 days. 4,4′Dichlorobenzophenone increased from 25.5 ppm at time of spraying to 25.5 ppm 15 days after spraying (Archer, 1974). Four days after spraying cucumbers with dicofol, residues decreased from 0.95–1.6 ppm to 0.4–1.5 ppm. No residues were detected 8 days after spraying (Nazer and Masoud, 1986). A half-life of 6 days was reported for dicofol in alfalfa (Akesson and Yates, 1964).
Chemical/Physical. When dicofol was exposed to sunlight for 20 days, a 10% yield of 4,4′-dichlorobenzophenone was obtained. Solvents containing dicofol and exposed to UV light resulted in the formation of chlorobenzilic acid esters (Vaidyanathasw
Metabolic pathway
Dicofol(1) is an analogue of DDT. However, the replacement of a hydrogen atom at position 1 by a hydroxyl group results in a fundamental change in chemical properties and increases the lability of the molecule. It breaks readily down to 4,4’-dichlorobenzophenone (2) thermally or on hydrolysis and this compound is a major metabolite in mammals and plants.
Storage
Color Code—Blue: Health Hazard/Poison: Storein a secure poison location. Prior to working with dicofolyou should be trained on its proper handling and storage.Store in tightly closed containers in a cool, well-ventilatedarea away from alkaline pesticides, strong acids, acidfumes, and steel. Where possible, automatically transfermaterial from drums or other storage containers to processcontainers. A regulated, marked area should be establishedwhere this chemical is handled, used, or stored in compliance with OSHA Standard 1910.1045.
Shipping
UN2996 Organochlorine pesticides, liquid, toxic, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials. UN3082 Environmentally hazardous substances, liquid, n.o. s., Hazard class: 9; Labels: 9-Miscellaneous hazardous material, Technical Name Required.
Degradation
Dicofol is stable to acids but unstable in alkaline media in which it is
hydrolysed to 4,4’-dichlorobenzophenone(2) and chloroform (DT50 values
at pH 5, 7 and 9 are 85 days, 64-99 hours and 26 minutes, respectively).
The isomer, 2,2,2-trichloro-1-(2-chlorophenyl)-1-(4-chlorophenyl)ethanol
(o,p’-dicofol), is hydrolysed more rapidly.
Dicofol is degraded by light to 4,4’-dichlorobenzophenone (2) (PM).
Incompatibilities
Incompatible with alkaline pesticides, strong acids; acid fumes; aliphatic amines; isocyanates. Halogenated aliphatic compounds are moderately or very reactive. Halogenated organics generally become less reactive as more of their hydrogen atoms are replaced with halogen atoms. Halogenated aliphatics are incompatible with strong oxidizing and reducing agents. Also, they are incompatible with many amines, nitrides, azo/diazo compounds, alkali metals, and epoxides. Dicofol hydrolyzes in alkali. It is slightly corrosive to metals. Contact with steel at elevated temperatures causes formation of toxic gases
Waste Disposal
In accordance with 40CFR165, follow recommendations for the disposal of pesticides and pesticide containers. Must be disposed properly by following package label directions or by contacting your local or federal environmental control agency, or by contacting your regional EPA office.
Properties of Dicofol
| Melting point: | 78.5°C |
| Boiling point: | 225°C |
| Density | 1.45 |
| vapor pressure | 5.3 x 10-5 Pa |
| refractive index | 1.6000 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 11 °C |
| storage temp. | APPROX 4°C
|
| solubility | DMSO: Slightly soluble |
| form | A solid |
| pka | 10.70±0.29(Predicted) |
| Water Solubility | Slightly soluble. <0.01 g/100 mL at 22 ºC |
| Merck | 13,3113 |
| Stability: | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. Hydrolyzes in basic solution. Corrodes some metals. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 115-32-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| IARC | 3 (Vol. 30, Sup 7) 1987 |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Acetic acid, [3,5-diiodo-4-(4-hydroxy-3-iodophenoxy) phenyl]-, 2-[diethylamino]ethyl ester, hydrochloride(115-32-2) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Dicofol (115-32-2) |
Safety information for Dicofol
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H317:Sensitisation, Skin H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. |
Computed Descriptors for Dicofol
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Dicofol CAS 115-32-2View Details
Dicofol CAS 115-32-2View Details
115-32-2 -
 Dicofol CAS 115-32-2View Details
Dicofol CAS 115-32-2View Details
115-32-2 -
 Liquid Dicofol 18.5% EC (DICOTOP-X), 500 mlView Details
Liquid Dicofol 18.5% EC (DICOTOP-X), 500 mlView Details
115-32-2 -
 3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 -
 4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
5305-40-8
