Dichlorosilane
- CAS NO.:4109-96-0
- Empirical Formula: Cl2H2Si
- Molecular Weight: 101.01
- MDL number: MFCD00011600
- EINECS: 223-888-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-06 13:21:43
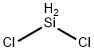
What is Dichlorosilane?
Description
Dichlorosilane is a highly flammable, corrosive, and toxic gas at room temperature and atmospheric pressure. It causes severe bums on contact with eyes, skin, and mucous membranes. With water or moisture, it hydrolyzes rapidly to yield silica and silicon oxyhydride along with hydrochloric acid. It is shipped as a liquefied gas in low pressure cylinders at its vapor pressure of 9.1 psig (62.7 kPa) at 70°F (21.1℃. It can form flammable mixtures with air and oxidizing agents.
Chemical properties
colourless gas
The Uses of Dichlorosilane
Dichlorosilane is primarily used in the electronics industry for such applications as growth of epitaxial or polycrystalline silicon and chemical vapor deposition of silicon dioxide and silicon nitride.
What are the applications of Application
Gives improved yields in reduction of imines over that of trichlorosilane.Easier to handle form of dichlorosilane.
General Description
Dichlorosilane is a flammable and poisonous gas, with a strong repulsive odor. Dichlorosilane is easily ignited in air, reacts with oxidizing agents, is very toxic by inhalation, and is a strong irritant to skin, eyes and mucous membranes. Under prolonged exposure to fire or intense heat the container may rupture violently or rocket.
Air & Water Reactions
Highly flammable. Based on the properties of similar materials, there is the possibility that the reaction of Dichlorosilane with water may be vigorous or violent. Products of the reaction include hydrogen chloride. The reaction generates heat and this heat may be sufficient to ignite the product. The chlorosilicon hydrides(ClxSiHy) are spontaneously flammable in air, NFPA 1991.
Reactivity Profile
Chlorosilanes, such as Dichlorosilane, are compounds in which silicon is bonded to from one to four chlorine atoms with other bonds to hydrogen and/or alkyl groups. Chlorosilanes react with water, moist air, or steam to produce heat and toxic, corrosive fumes of hydrogen chloride. They may also produce flammable gaseous H2. They can serve as chlorination agents. Chlorosilanes react vigorously with both organic and inorganic acids and with bases to generate toxic or flammable gases.
Hazard
Dichlorosilane is toxic by inhalation and skin absorption. Hydrogen chloride causes severe eye and skin burns and is irritating to the skin, eyes, and respiratory system. The four-digit UN identification number is 2189. The NFPA 704 designation is health 4, flammability 4, and reactivity 2. The white area at the bottom of the diamond contains a W with a slash through it, indicating water reactivity.
Health Hazard
TOXIC; may be fatal if inhaled or absorbed through skin. Contact with gas or liquefied gas may cause burns, severe injury and/or frostbite. Fire will produce irritating, corrosive and/or toxic gases. Runoff from fire control may cause pollution.
Fire Hazard
Flammable; may be ignited by heat, sparks or flames. May form explosive mixtures with air. Vapors from liquefied gas are initially heavier than air and spread along ground. Vapors may travel to source of ignition and flash back. Some of these materials may react violently with water. Cylinders exposed to fire may vent and release toxic and flammable gas through pressure relief devices. Containers may explode when heated. Ruptured cylinders may rocket. Runoff may create fire or explosion hazard.
Flammability and Explosibility
Extremely flammable liquified gas
Materials Uses
Dichlorosilane, in the complete absence of water, can be safely stored in mild steel equipment. In the presence of even small traces of water, dichlorosilane becomes extremely corrosive since the Si-CI bonds react rapidly with water, generating hydrogen chloride.br/> Because of reactivity with water, dichlorosilane should always be handled in dry equipment with a dry inert gas such as nitrogen. For transfer service, dry inert gas is preferred to pumping. Some examples of other common compatible materials used include: Viton, Teflon, Kel-F, nickel, Monel, and some types of stainless steel.
Safety Profile
Moderately toxic by inhalation. Ignites spontaneously in air. Confined mixtures with air are spontaneously explosive. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of Cl-. See also CHLOROSILANES.
Physiological effects
Dichlorosilane hydrolyzes and oxidizes readily
to release hydrogen chloride; therefore, the
symptoms, effects, and treatment will be similar
to those for hydrogen chloride. Dichlorosilane
will cause severe bums on contact with eyes,
skin, and mucous membranes.
If dichlorosilane is inhaled, immediately remove
the victim to fresh air. If breathing is difficult,
give oxygen. Prompt treatment by a physician
is required even if no symptoms of exposure
are evident since the symptoms may be
delayed.
storage
Since dichlorosilane is a highly flammable, corrosive,
and toxic liquefied gas, appropriate precautions
must be taken in its storage and handling.
During the handling of chlorosilanes, the
use of such protective equipment as goggles,
neoprene or natural rubber gloves, and protective
clothing is essential. SCBAs, as well as
both safety showers and eyewash fountains,
should be available for emergency use.
Cylinders should be assigned a definite area
for storage. The area should be dry, cool, well
ventilated, fire resistant, and away from ignition
sources. Keep cylinders protected from excessive
temperature rise by storing them away from
radiators or other heat sources. Storage conditions
should comply with local and state regulations.
Cylinders may be stored in the open, but must
be protected against extremes of weather and
from the dampness of the ground to prevent
rusting. During the summer, cylinders stored in
the open should be shaded against the continuous
direct rays of the sun in those localities
where extreme temperatures prevail.
Waste Disposal
Dichlorosilane should not be discharged directly
into surface waters or sewer systems since an
acidic waste product is formed. The disposal
can be accomplished by controlled introduction
of the product into water. The exothermic reactions
of dichlorosilane with water (hydrolysis)
result in the formation of hydrochloric acid and
an insoluble silicon containing solid or fluid. In
order to prevent air pollution, the quantity of
water must be sufticient to dissolve all of the
hydrogen chloride that will be formed. The ratio
of water to dichlorosilane should be at least 10
to 1. The corrosive and exothermic nature of the
reaction should be t;onsidered in selecting materials
of construction for the equipment used in
this procedure.
The hydrochloric acid formed should then be
neutralized with an alkali agent such as aqueous
ammonia, sodium hydroxide, lime slurry, etc.,
and should be added as an aqueous solution
with agitation to the acidic medium. Consideration must be given to the additional heat that
will be produced by the neutralization.
Silicon-containing solids should be washed to
remove residual acid. Discard any product, residue,
disposable container, or liner in an environmentally
acceptable manner. Disposal of
dichlorosilane by neutralizing, scrubbing, incineration,
or by other means, may be subject to
permitting by federal, state or provincial regulations.
Persons involved with disposal of dichiorosilane
should check with the environmental
authorities having jurisdiction to determine
the applicability of permitting regulations
to disposal activities.
GRADES AVAILABLE
Dichlorosilane is primarily sold in ultra-
high-purity grades for use in the electronics
industry. A typical specification usually quantifies
the acceptable levels of hydrocarbons and
metals.
Gas purity guidelines have been developed
and published by Semiconductor Equipment
and Materials International and can be found in
the book of Book ofSEMI Standards [1].
Properties of Dichlorosilane
| Melting point: | −122 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 8.3 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 1,22 g/cm3 |
| vapor density | 3.5 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 1254 mm Hg ( 20 °C) |
| Flash point: | -37°C |
| solubility | reacts with H2O |
| form | colorless gas |
| Specific Gravity | 0.76 |
| color | colorless gas; flammable |
| explosive limit | 99% |
| Water Solubility | decomposes |
| Hydrolytic Sensitivity | 9: reacts extremely rapidly with atmospheric moisture - may be pyrophoric - glove box or sealed system required |
| Stability: | Stable. Extremely flammable; note very wide explosion limits. Reacts violently with water, alcohols, strong oxidizing agents, bases. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 4109-96-0(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Dichlorosilane (4109-96-0) |
Safety information for Dichlorosilane
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H220:Flammable gases H280:Gases under pressure H314:Skin corrosion/irritation H331:Acute toxicity,inhalation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P310:Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P410+P403:Protect from sunlight. Store in a well-ventilated place. |
Computed Descriptors for Dichlorosilane
New Products
Methyl (R)-1-Boc-4,4-difluoropyrrolidine-2-carboxylate 2,2-Difluoropropylamine hydrochloride tert-butyl 3-bromoazetidine-1-carboxylate (R)-1-Boc-3-hydroxypyrrolidine DIFLUOROACETIC ANHYDRIDE 2,2-Difluoropropionic acid Diallylamine, 99% Calcium hydroxide, 95% Aluminum oxide, basic 2-Bromophenylacetonitrile, 97% L-tert-Leucine,97% N-Hydroxy-2-methylpropanimidamide 4-(3,4-Dichlorophenyl)-3,4-Dihydro-N-Methyl-1-(2H)-Naphthalenimine (Schiff Base) 2-AMINO-3,5-DIBROMO BENZALDEHYDE [ADBA] L-Glutamic Acid Dimethyl Ester Hcl 10-Methoxy-5H-dibenz[b,f]azepine 5-Cyanophthalide N, N-Carbonyldiimidazole (CDI) Dibenzoyl Peroxide Titanium Dioxide 2-(Methylthio) Benzonitrile Sodium Acetate Anhydrous Allopurinol 1,5-DibromopentaneRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
![Cis-2-(Bromomethyl)-2-(2,4-Dichlorophenyl)-1,3-Dioxolane-4-Ylmethyl Benzoate [CBB] 61397-56-6 99%](https://img.chemicalbook.in//Content/image/CP5.jpg) Cis-2-(Bromomethyl)-2-(2,4-Dichlorophenyl)-1,3-Dioxolane-4-Ylmethyl Benzoate [CBB] 61397-56-6 99%View Details
Cis-2-(Bromomethyl)-2-(2,4-Dichlorophenyl)-1,3-Dioxolane-4-Ylmethyl Benzoate [CBB] 61397-56-6 99%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 287930-77-2 / 142569-70-8 99%View Details
287930-77-2 / 142569-70-8 99%View Details
287930-77-2 / 142569-70-8 -
![2033-24-1 2,2-Dimethyl-1,3-Dioxane-4,6-Dione [Meldrum Acid] 98%](https://img.chemicalbook.in//Content/image/CP5.jpg) 2033-24-1 2,2-Dimethyl-1,3-Dioxane-4,6-Dione [Meldrum Acid] 98%View Details
2033-24-1 2,2-Dimethyl-1,3-Dioxane-4,6-Dione [Meldrum Acid] 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 Ethyl-2-Chloroacetoacetate 609-15-4View Details
Ethyl-2-Chloroacetoacetate 609-15-4View Details
609-15-4 -
 CIS- BROMO BENZOATEView Details
CIS- BROMO BENZOATEView Details
61397-56-6 -
 609-15-4View Details
609-15-4View Details
609-15-4 -
![1-(6-Methylpyridin-3-Yl)-2-[4-(Methylsulfonyl)Phenyl]Ethanone [Ketosulfone] 99%](https://img.chemicalbook.in//Content/image/CP5.jpg) 1-(6-Methylpyridin-3-Yl)-2-[4-(Methylsulfonyl)Phenyl]Ethanone [Ketosulfone] 99%View Details
1-(6-Methylpyridin-3-Yl)-2-[4-(Methylsulfonyl)Phenyl]Ethanone [Ketosulfone] 99%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 27143-07-3View Details
27143-07-3View Details
27143-07-3
