DIALLATE
- CAS NO.:2303-16-4
- Empirical Formula: C10H17Cl2NOS
- Molecular Weight: 270.22
- MDL number: MFCD00869632
- EINECS: 218-961-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:08:52
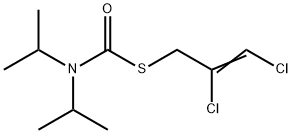
What is DIALLATE?
Description
Diallate is a brown liquid. Molecularweight = 270.21; Boiling point =150℃ at 9 mmHg;Freezing/Melting point = 25-30℃. Hazard Identification(based on NFPA-704 M Rating System): Health 2,Flammability 0, Reactivity 0. Slightly soluble in water;solubility = 14 mg/L at 25℃.
Chemical properties
Diallate is a brown liquid.
The Uses of DIALLATE
Diallate is a pesticide used to treat fruits and vegetables. Environmental wastewater pollutant.Environmental toxin on US EPA Toxic Release Inventory list (TRI) list.
The Uses of DIALLATE
Herbicide.
The Uses of DIALLATE
Preemergent, selective herbicide used to control wild oats and blackgrass in barley, corn, flax, lentils, peas, potatoes, soybeans and sugar beets.
Definition
ChEBI: Diallat is a tertiary amine.
General Description
Used as an herbicide.
Air & Water Reactions
Thio and dithiocarbamates slowly decompose in aqueous solution to form carbon disulfide and methylamine or other amines. Such decompositions are accelerated by acids.
Reactivity Profile
DIALLATE is a thiocarbamate ester. Flammable gases are generated by the combination of thiocarbamates and dithiocarbamates with aldehydes, nitrides, and hydrides. Thiocarbamates and dithiocarbamates are incompatible with acids, peroxides, and acid halides.
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion. Moderately toxic by skin contact. Questionable carcinogen with experimental carcinogenic and tumorigenic data. Mutation data reported. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of Cl-, NOx, and SOx. See also CARBAMATES and ALLYL COMPOUNDS.
Potential Exposure
A thiocarbamate herbicide. The slow release of poisonous gases from hydrolysis of many thio and dithiocarbamates requires the use of respirators during handling. Poisoning can also occur by ingestion and absorption through the skin. Diallate is potential danger to those involved in the manufacture, formulation and applica- tion of this re-emergence herbicide.
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seekmedical attention immediately. If this chemical contactsthe skin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediately with soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical has been inhaled, remove fromexposure, begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing hasstopped and CPR if heart action has stopped. Transferpromptly to a medical facility. When this chemical hasbeen swallowed, get medical attention. Give large quantities of water and induce vomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit.
Environmental Fate
Soil. Soil metabolites include 2,3-dichloroallyl alcohol, 2,3-dichloroallyl mercaptan
(Hartley and Kidd, 1987) and carbon dioxide (Smith, 1988). The formation of the alcohol
occurs via hydrolysis of the ester linkage and transthiolation of the allylic group (Kaufman,
1967). In an agricultural soil, 14CO2 was the only biodegradation identified; however, bound
residue and traces of benzene and water-soluble radioactivity were also detected in large
amounts (Anderson and Domsch, 1980). The reported half-lives in soil range from 2 to 4
weeks to (Smith and Fitzpatrick, 1970) to approximately 30 days (Hartley and Kidd, 1987).
Diallate did not migrate deeper than 5 cm on test field plots (Smith, 1970). In four
microbially-active agricultural soils, the half-life was 4 weeks but in sterilized soil the
half-life was 20 weeks (Anderson and Domsch, 1976).
Plant. In plants, diallate is metabolized and carbon dioxide is released (Hartley and
Kidd, 1987). Diallate undergoes cis/trans isomerization and oxidative cleavage when
irradiated at 300 nm forming 2,3-dichloroacrolein and 2-chloroacrolein as products (Ruzo
and Casida, 1985).
Photolytic. Irradiation of diallate was also conducted in oxygenated chloroform or
water until a 10% conversion was obtained. Products formed included acetaldehyde, 2,3-
dichloroacrolein and trace amounts of 2-chloroacrolein (Ruzo and Casida, 1985).
Chemical/Physical. Emits toxic fumes of chlorine, nitrogen and sulfur oxides when
heated to decomposition (Sax and Lewis, 1987). Though no products were reported, the
calculated hydrolysis half-life at 25°C and pH 7 is 6.6 years (Ellington et al., 1988).
storage
Color Code—Blue: Health Hazard/Poison: Storein a secure poison location. Prior to working with diallateyou should be trained on its proper handling and storage.Store in tightly closed containers in a cool, well-ventilatedarea away from alkalies. Where possible, automaticallypump liquid from drums or other storage containers to process containers. A regulated, marked area should be established where this chemical is handled, used, or stored incompliance with OSHA Standard 1910.1045.
Shipping
UN2992 Carbamate pesticides, liquid, toxic, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials.
Incompatibilities
hiocarbamate esters are combustible. They react violently with powerful oxidizers such as calcium hypochlorite. Poisonous gases are generated by the thermal decomposition of thiocarbamate compounds, including carbon disulfide, oxides of sulfur, oxides of nitro- gen, hydrogen sulfide, ammonia, and methylamine. Many materials in this group slowly decompose in aqueous solu- tion to form carbon disulfide and methylamine or other amines. Such decompositions are accelerated by acids. Flammable gases are generated by the combination of thiocarbamates with aldehydes, nitrides, and hydrides. Thiocarbamates are incompatible with acids, peroxides, and acid halides.
Waste Disposal
Land burial is acceptable for small quantities. Larger quantities can be incinerated . In accordance with 40CFR165, follow recommendations for the disposal of pesticides and pesticide containers. Must be disposed properly by following package label directions or by contacting your local or federal environmental control agency, or by contacting your regional EPA office. Consult with environmental regulatory agencies for guidance on acceptable disposal practices. Generators of waste containing this contaminant (≥100 kg/mo) must conform with EPA regulations governing storage, transportation, treatment, and waste disposal.
Properties of DIALLATE
| Melting point: | 25-30℃ |
| Boiling point: | bp9 150° |
| Density | 1.1556 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.6000 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | >100 °C |
| storage temp. | 0-6°C |
| form | Viscous Liquid |
| pka | -1.63±0.70(Predicted) |
| color | Colorless to light yellow |
| Water Solubility | 40mg/L(room temperature) |
| IARC | 3 (Vol. 30, Sup 7) 1987 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Diallate (2303-16-4) |
Safety information for DIALLATE
Computed Descriptors for DIALLATE
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE DIETHYL AMINOMALONATE HYDROCHLORIDE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran



You may like
-
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 -
 733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8