Darifenacin
- CAS NO.:133099-04-4
- Empirical Formula: C28H30N2O2
- Molecular Weight: 426.55
- MDL number: MFCD00896313
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 15:53:33
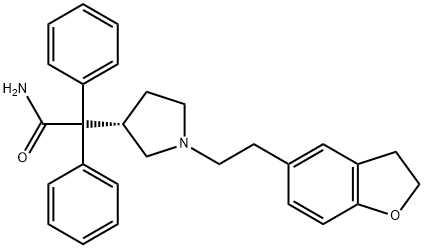
What is Darifenacin?
Absorption
The mean oral bioavailability at steady state is estimated to be 15% and 19% for 7.5 mg and 15 mg tablets, respectively.
Toxicity
Overdosage can potentially result in severe central anticholinergic effects.
Description
Darifenacin is a novel muscarinic M3 selective antagonist for the once-daily oral treatment of urinary incontinence and overactive bladder. The majority of overactive bladder symptoms are thought to result from the overactivity of the detrusor muscle, which is primarily mediated by acetylcholine-induced stimulation of muscarinic M3 receptors in the bladder. Consequently, antimuscarinic agents have become the mainstay of overactive bladder treatment. Darifenacin has a higher level of M3 selectivity than the previously marketed antimuscarinic agents. It has Ki values of 16nM for M1, 50 nM for M2, and 1.6 nM for M3 receptors. It is slightly more M3 selective than solifenacin (M1:Ki=25 nM, M2:Ki=126 nM, M3:Ki=10 nM), which was launched in 2004. Darifenacin is significantly more selective than other muscarinics such as tolterodine, oxybutynin, and trospium, which are all essentially equipotent against M1, M2, and M3 receptors. In addition,darifenacin demonstrates greater effect on tissues in which the predominant receptor type is M3 rather than M1 or M2. In vitro darifenacin inhibits carbacholinduced contractions with greater potency in isolated guinea-pig bladder (M3) than in guinea-pig atria (M2) or dog saphenous vein (M1). In animal models, it shows greater selectivity for inhibition of detrusor contraction over salivation or tachycardia.Darifenacin is supplied as a controlled release formulation, and the recommended dosage is 7.5 mg once, daily. Darifenacin is rapidly and completely absorbed from the GI tract after oral administration, with maximum plasma levels achieved after about 7 h. The elimination half-life is approximately 3 h, but because of the controlled release characteristics of the formulation, the drug is suitable for once-daily dosing. Steady-state plasma levels are achieved within 6 days of commencing treatment. Darifenacin exhibits high-protein binding (98%), a volume of distribution of 163 L, and a clearance of 40 L/h. It has low oral bioavailability (15–19%) due to extensive first-pass metabolism by CYP3A4 and CYP2D6, but this can be saturated after multiple administrations. The major circulating metabolites are produced by monohydroxylation and N-dealkylation; however, none contribute significantly to the overall clinical effect of darifenacin. Approximately 58% of the dose is excreted in urine and 44% in feces; only a small percentage (3%) of the excreted dose is unchanged darifenacin.
Originator
Pfizer (US)
The Uses of Darifenacin
Treatment for an overactive bladder.
Indications
For the treatment of overactive bladder with symptoms of urge urinary incontinence, urgency and frequency.
Background
Darifenacin (Enablex?, Novartis) is a medication used to treat urinary incontinence.
Darifenacin blocks M3 muscarinic acetylcholine receptors, which mediate bladder muscle contractions. This block reduces the urgency to urinate and so it should not be used in people with urinary retention.
It is unknown if M3 receptor selectivity is clinically advantageous in overactive bladder syndrome treatments.
Definition
ChEBI: 2-[(3S)-1-Ethylpyrrolidin-3-yl]-2,2-diphenylacetamide in which one of the hydrogens at the 2-position of the ethyl group is substituted by a 2,3-dihydro-1-benzofuran-5-yl group. It is a selective antagonist for the M3 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor, which is primarily responsible for bladder muscle contractions, and is used as the hydrobromide salt in the management of urinary incontinence.
brand name
Enablex (Novartis);Emselex.
Pharmacokinetics
Darifenacin is a competitive muscarinic receptor antagonist. In vitro studies using human recombinant muscarinic receptor subtypes show that darifenacin has greater affinity for the M3 receptor than for the other known muscarinic receptors (9 and 12-fold greater affinity for M3 compared to M1 and M5, respectively, and 59-fold greater affinity for M3 compared to both M2 and M4). Muscarinic receptors play an important role in several major cholinergically mediated functions, including contractions of the urinary bladder smooth muscle and stimulation of salivary secretion. Adverse drug effects such as dry mouth, constipation and abnormal vision may be mediated through effects on M3 receptors in these organs.
Clinical Use
Symptomatic treatment of urinary incontinence,
frequency or urgency
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Anti-arrhythmics: increased risk of antimuscarinic
side effects with disopyramide
Antifungals: concentration increased by ketoconazole
- avoid; avoid with itraconazole.
Antivirals: avoid with fosamprenavir, atazanavir,
indinavir, lopinavir, ritonavir, saquinavir and
tipranavir.
Calcium-channel blockers: avoid with verapamil
Ciclosporin: avoid concomitant use.
Metabolism
Hepatic. Primarily mediated by the cytochrome P450 enzymes CYP2D6 and CYP3A4.
Metabolism
After an oral dose, darifenacin is subject to extensive first-pass metabolism and has a bioavailability of about 15-19%. Darifenacin is metabolised in the liver by the cytochrome P450 isoenzymes CYP2D6 and CYP3A4. Most of a dose is excreted as metabolites in the urine and faeces.
Properties of Darifenacin
| Boiling point: | 614.3±55.0 °C(Predicted) |
| alpha | 25D -20.6° (c = 1.0 in methylene chloride) |
| Density | 1.192±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Soluble in DMSO |
| form | Powder |
| pka | pKa (25°): 9.2 |
| color | White to off-white |
Safety information for Darifenacin
Computed Descriptors for Darifenacin
Darifenacin manufacturer
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran



You may like
-
 133099-04-4 Darifenacin 98%View Details
133099-04-4 Darifenacin 98%View Details
133099-04-4 -
 133099-04-4 99%View Details
133099-04-4 99%View Details
133099-04-4 -
 Darifenacin 99%View Details
Darifenacin 99%View Details -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1