Dalbavancin
Synonym(s):;Ristomycin A aglycone;
- CAS NO.:171500-79-1
- Empirical Formula: C88H100Cl2N10O28
- Molecular Weight: 1816.71
- MDL number: MFCD09837770
- EINECS: 206-141-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-27 09:38:02
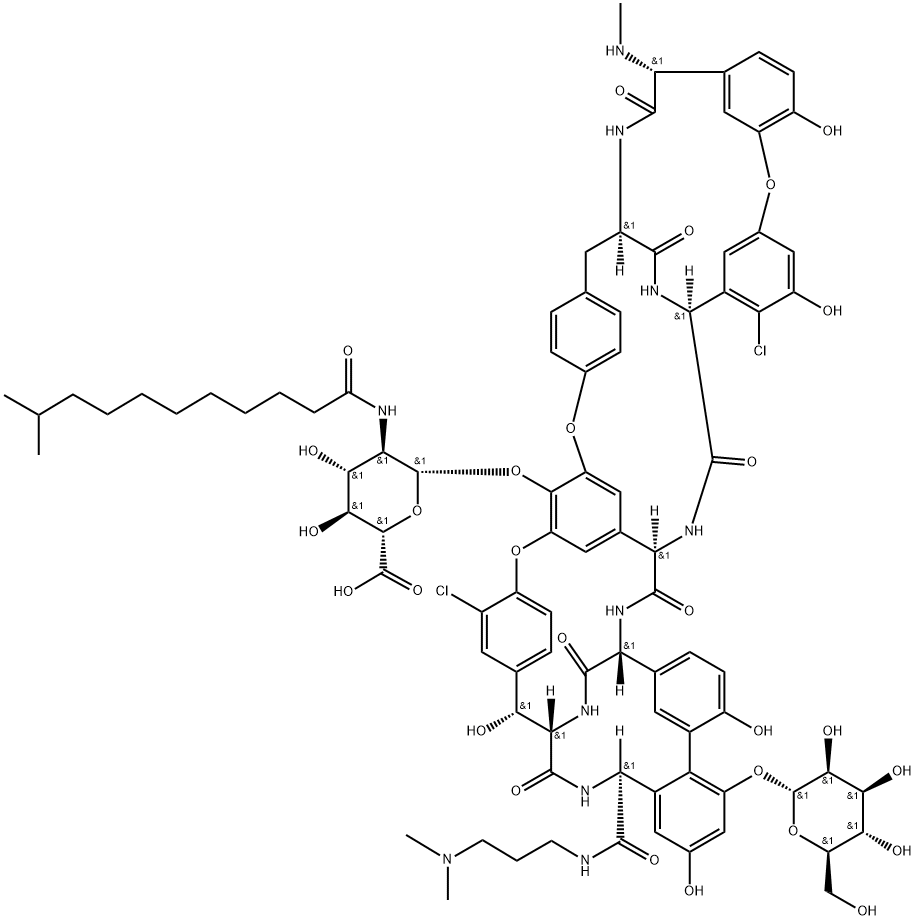
What is Dalbavancin?
Absorption
In healthy subjects, dalbavancin AUC0-24h and Cmax both increased proportionally to dose following single intravenous (IV) dalbavancin doses ranging from 140 mg to 1500 mg, indicating linear pharmacokinetics .
No apparent accumulation of dalbavancin was observed following multiple IV infusions administered once weekly for up to eight weeks, with 1000 mg on Day 1 followed by up to seven weekly 500 mg doses, in healthy adults with normal renal function .
Toxicity
Treatment with antibacterial agents can alter the normal flora of the colon leading to growth of C. difficile and commonly occurs in the development of C. difficile-associated diarrhea . Other common side effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, headache, rash, and pruritis . Side effects that occurred in less than 2% of patients during clinical trials include blood and lymphatic system disorders, gastrointestinal disorders, hepatotoxicity, anaphylactoid reactions, hepatic enzyme elevation, hypoglycaemia, dizziness, bronchospasm, urticaria, and vascular disorders . There have been no adequate or well-controlled studies to conclude that use of dalbavancin is safe during pregnancy or breastfeeding .
The Uses of Dalbavancin
Dalbavancin is a semi-synthetic glycopeptide prepared from A40926 by introducing a positively charged lipophilic moiety in a previously unexplored region of the natural glycopeptide. This modification provides a longer in vivo half life, and improved in vitro activity against a variety of Gram positive and multi-drug resistant isolates such as MRSA and MRSE.
The Uses of Dalbavancin
Dalbavancin is a second-generation lipoglycopeptide antibiotic. It is a semisynthetic lipoglycopeptide that was designed to improve upon the natural glycopeptides currently available, vancomycin and teicoplanin.
What are the applications of Application
Dalbavancin is a semi-synthetic glycopeptide prepared from A40926
Background
Dalbavancin is a second-generation lipoglycopeptide antibiotic that was designed to improve on the natural glycopeptides currently available, such as vancomycin and teicoplanin . Modifications from these older glycoprotein classes facilitated a similar mechanism of action for dalbavancin but with increased activity and once-weekly dosing . Its use is indicated for the treatment of acute bacterial skin and skin structure infections (ABSSSI) caused by the following gram-positive microorganisms: Staphylococcus aureus (including methicillin-susceptible and methicillin-resistant strains), S. pyogenes, S. agalactiae, S. dysgalactiae, the S. anginosus group (including S. anginosus, S. intermedius, and S. constellatus), and Enterococcus faecalis (vancomycin susceptible strains) . Dalbavancin acts by interfering with bacterial cell wall synthesis by binding to the D-alanyl-D-alanine terminus of nascent cell wall peptidoglycan and preventing cross-linking .
Indications
Dalbavancin for injection is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with acute bacterial skin and skin structure infections (ABSSSI), caused by susceptible isolates of the following gram-positive microorganisms: Staphylococcus aureus (including methicillin-susceptible and methicillin-resistant strains), Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus agalactiae, Streptococcus dysgalactiae, Streptococcus anginosus group (including Streptococcus anginosus, Streptococcus intermedius, Streptococcus constellatus) and Enterococcus faecalis (vancomycin susceptible strains) .
Dalbavancin is not active against gram-negative bacteria; therefore, combination therapy may be clinically indicated if the ABSSSI is polymicrobial and includes a suspected or documented gram-negative pathogen .
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of dalbavancin and other antibacterial drugs, dalbavancin should be used only to treat infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria . When culture and susceptibility information are available, they should be considered in selecting or modifying antibacterial therapy . In the absence of such data, local epidemiology and susceptibility patterns may contribute to the empiric selection of therapy .
Definition
ChEBI: A semisynthetic glycopeptide used for the treatment of acute bacterial skin and skin structure infections caused or suspected to be caused by susceptible isolates of designated Gram-positive microorganisms including MRSA.
Pharmacokinetics
The antibacterial activity of dalbavancin appears to best correlate with the ratio of area under the concentration-time curve to minimal inhibitory concentration (AUC/MIC) for Staphylococcus aureus based on animal models of infection . An exposure-response analysis of a single study in patients with complicated skin and skin structure infections supports the two-dose regimen for which dalbavancin injection is administered .
Subsequently, the recommended dosage regimen of dalbavancin in patients with normal renal function is 1500 mg, administered either as a single dose, or 1000 mg followed one week later by 500 mg [FDA Label, F2356. Dalbavancin should be administered over 30 minutes by intravenous infusion .
Furthermore, inn a randomized, positive- and placebo-controlled, thorough QT/QTc study, 200 healthy subjects received either dalbavancin 1000 mg intravenous (IV), dalbavancin 1500 mg IV, oral moxifloxacin 400 mg, or placebo. Neither dalbavancin 1000 mg nor dalbavancin 1500 mg had any clinically relevant adverse effect on cardiac repolarization .
Metabolism
Dalbavancin is not a substrate, inhibitor, or inducer of CYP450 isoenzymes . Subsequently, metabolites have not been observed in significant amounts in human plasma . The metabolites hydroxy-dalbavancin and mannosyl aglycone have been detected in urine (< 25% of administered dose) . The metabolic pathways responsible for producing these metabolites have not been identified; however, due to the relatively minor contribution of metabolism to the overall elimination of dalbavancin, drug-drug interactions via inhibition or induction of metabolism of dalbavancin are not anticipated . Hydroxy-dalbavancin and mannosyl aglycone show significantly less antibacterial activity compared to dalbavancin .
Properties of Dalbavancin
| Melting point: | >160°C (dec.) |
| Density | 1.59 |
| storage temp. | -20°C |
| solubility | Aqueous Base (Slightly), DMSO (Slightly, Heated), Water (Slightly) |
| pka | 2.73±0.70(Predicted) |
| form | powder |
| color | white to beige |
Safety information for Dalbavancin
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Dalbavancin
Dalbavancin manufacturer
New Products
1-Amino-1-cyclohexanecarboxylic acid Cycloleucine 6-Bromo-3-iodo-1-methyl-1H-indazole 3-(2,4-Dimethoxybenzyl)dihydropyrimidine-2,4(1H,3H)-dione 7-Bromo-1H-indazole ELECTROLYTIC IRON POWDER 2-Methyl-2-phenylpropyl acetate 1-Aminocyclobutanecarboxylic acid 1-(2-Ethoxyethyl)-2-(piperidin-4-yl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazole hydrochloride Decanonitrile tert-butyl 4-(1H-benzo[d]iMidazol-2-yl)piperidine-1-carboxylate 4-Ethylbenzylamine Methyl 5-bromo-2-chloro-3-nitrobenzoate N-(5-Amino-2-methylphenyl)acetamide 2-Chloro-3-nitropyridine 5-Bromo-2,3-dimethoxypyridine methyl 6-chloro-2-(chloromethyl)nicotinate 2-methoxy-4-methyl-5-nitro pyridine 2-iodo-5-bromo pyridine 2-amino-4-methyl-5-nitro pyridine 5-Fluoro-2-Oxindole methyl L-alaninate hydrochloride diethyl L-glutamate hydrochloride Ethyl tosylcarbamateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Dalbavancin 99%View Details
Dalbavancin 99%View Details -
 Dalbavancin CAS 171500-79-1View Details
Dalbavancin CAS 171500-79-1View Details
171500-79-1 -
 Ethoxymethylenemalononitrile 99% HPLCView Details
Ethoxymethylenemalononitrile 99% HPLCView Details
123-06-8 -
 Diethyl Disulfide 99% HPLCView Details
Diethyl Disulfide 99% HPLCView Details
110-81-6 -
 6285-05-8. 1-(4-chlorophenyl) propan-1-one 98%View Details
6285-05-8. 1-(4-chlorophenyl) propan-1-one 98%View Details
6285-05-8. -
 4-chloro-3,5-dinitropyridine 98%View Details
4-chloro-3,5-dinitropyridine 98%View Details -
 401-95-6 99% HPLCView Details
401-95-6 99% HPLCView Details
401-95-6 -
 171663-13-1 tert-Butyl 3-bromobenzylcarbamate 98%View Details
171663-13-1 tert-Butyl 3-bromobenzylcarbamate 98%View Details
171663-13-1