D-α-Tocopherol succinate
Synonym(s):D -α-Tocopherol succinate;Vitamin E succinate
- CAS NO.:4345-03-3
- Empirical Formula: C33H54O5
- Molecular Weight: 530.78
- MDL number: MFCD00072055
- EINECS: 224-403-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-27 09:38:02
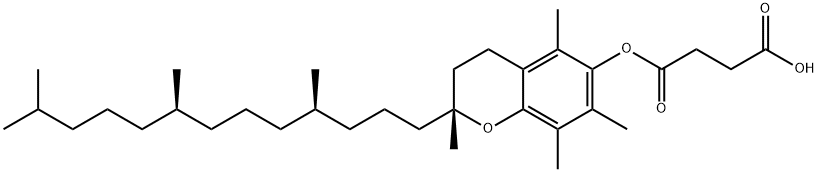
What is D-α-Tocopherol succinate?
Absorption
In addition to any following information, owing to alpha-Tocopherol succinate's closely related chemical nature with alpha-Tocopherol acetate, please also refer to the drug information page for alpha-Tocopherol acetate for further data.
It is generally believed that alpha-tocopherol succinate is ultimately de-esterified or cleaved to provide alpha-tocopherol once administered to the human body . It is consequently expected that pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics similar to that of alpha-tocopherol to be followed .
50 to 80% absorbed from gastrointestinal tract.
Toxicity
In addition to any following information, owing to alpha-Tocopherol succinate's closely related chemical nature with alpha-Tocopherol acetate, please also refer to the drug information page for alpha-Tocopherol acetate for further data.
It is generally believed that alpha-tocopherol succinate is ultimately de-esterified or cleaved to provide alpha-tocopherol once administered to the human body . It is consequently expected that pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics similar to that of alpha-tocopherol to be followed .
Description
Tocopherol succinate (4345-03-3) is a potent antioxidant. Protects mice from gamma-radiation by induction of granulocyte-colony stimulating factor.1,2?Tocopherol succinate induces apoptosis in human gastric cancer cells3?and inhibits proliferation of mesothelioma cells by down-regulation of fibroblast growth factor receptor-14. Induces apoptosis in neuroblastoma cells.5
Chemical properties
Off-White to Pale Yellow Solid
The Uses of D-α-Tocopherol succinate
A potent novel antineoplastic agent with high selectivity and cooperativity with tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (Apo2 ligand). It inhibits proliferation of mesothelioma cells by selective down-regulation of fibroblast growth factor receptors. Furthermore, it has been shown to enhance the anti-tumor effect of dendritic cell vaccines.
The Uses of D-α-Tocopherol succinate
A potent antioxidant tocopherol
The Uses of D-α-Tocopherol succinate
A potent novel antineoplastic agent with high selectivity and cooperativity with tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (Apo2 ligand). It inhibits proliferation of mesothelioma cells by selective down-regulation of fibroblast growth factor receptors. Furthermore, it has been shown to enhance the anti-tumor effect of dendritic cell vaccines.
What are the applications of Application
D-α-Tocopheryl Succinate is a potent antioxidant tocopherol
Indications
The primary health-related use for which alpha-tocopherol succinate is formally indicated is as a dietary supplement for patients who demonstrate a genuine vitamin E deficiency. At the same time, vitamin E deficiency is generally quite rare but may occur in premature babies of very low birth weight (< 1500 grams), individuals with fat-malabsorption disorders (as fat is required for the digestive tract to absorb vitamin E), or individuals with abetalipoproteinemia - a rare, inherited disorder that causes poor absorption of dietary fat - who require extremely large doses of supplemental vitamin E daily (around 100 mg/kg or 5-10 g/day) . In all such cases, alpha-tocopherol is largely the preferred form of vitamin E to be administered.
Elsewhere, vitamin E's chemical profile as a fat-soluble antioxidant that is capable of neutralizing free radicals in the body continues to generate ongoing interest and study regarding how and whether or not the vitamin can help prevent or delay various chronic diseases associated with free radicals or other potential biological effects that vitamin E possesses like cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, ocular conditions, immune illnesses, cancer, and more . None of these ongoing studies have yet to elucidate any formally significant evidence, however .
Similarly, more effective clinical trials are necessary to confirm what has only been accrued as preliminary data when it comes to studies proposing the demonstration of alpha-tocopherol succinate's capability to act as an anti-cancer therapy or as a regulator of inflammation .
Background
Alpha-tocopherol is the primary form of vitamin E that is preferentially used by the human body to meet appropriate dietary requirements. In particular, the RRR-alpha-tocopherol (or sometimes called the d-alpha-tocopherol stereoisomer) stereoisomer is considered the natural formation of alpha-tocopherol and generally exhibits the greatest bioavailability out of all of the alpha-tocopherol stereoisomers. Moreover, manufacturers typically convert the phenol component of the vitamin to esters using acetic or succinic acid, making a compound such as alpha-tocopherol succinate more stable and easier to use in vitamin supplements .
Alpha-tocopherol succinate is subsequently most commonly indicated for dietary supplementation in individuals who may demonstrate a genuine deficiency in vitamin E. Vitamin E itself is naturally found in various foods, added to others, or used in commercially available products as a dietary supplement. The recommended dietary allowances (RDAs) for vitamin E alpha-tocopherol are: males = 4 mg (6 IU) females = 4 mg (6 IU) in ages 0-6 months, males = 5 mg (7.5 IU) females = 5 mg (7.5 IU) in ages 7-12 months, males = 6 mg (9 IU) females = 6 mg (9 IU) in ages 1-3 years, males = 7 mg (10.4 IU) females = 7 mg (10.4 IU) in ages 4-8 years, males = 11 mg (16.4 IU) females = 11 mg (16.4 IU) in ages 9-13 years, males = 15 mg (22.4 IU) females = 15 mg (22.4 IU) pregnancy = 15 mg (22.4 IU) lactation = 19 mg (28.4 IU) in ages 14+ years . Most individuals obtain adequate vitamin E intake from their diets; genuine vitamin E deficiency is considered to be rare.
Nevertheless, vitamin E is known to be a fat-soluble antioxidant that has the capability to neutralize endogenous free radicals. This biologic action of vitamin E consequently continues to generate ongoing interest and study in whether or not its antioxidant abilities may be used to help assist in preventing or treating a number of different conditions like cardiovascular disease, ocular conditions, diabetes, cancer and more. At the moment, however, there exists a lack of formal data and evidence to support any such additional indications for vitamin E use.
Moreover, although it is generally believed that alpha-tocopherol succinate would naturally demonstrate such general vitamin E-tocopherol pharmacodynamics after undergoing a logical de-esterification in the gut , there is ongoing research that proposes that the alpha-tocopherol succinate compound itself is capable of eliciting anti-cancer and inflammation mediation activities that are unique from the alpha-tocopherol form and other alpha-tocopherol esters .
Definition
ChEBI: Tocopherol succinate is a tocol and a hemisuccinate.
General Description
White powder.
Air & Water Reactions
Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Vitamin E succinate is an ester. Esters react with acids to liberate heat along with alcohols and acids. Strong oxidizing acids may cause a vigorous reaction that is sufficiently exothermic to ignite the reaction products. Heat is also generated by the interaction of esters with caustic solutions. Flammable hydrogen is generated by mixing esters with alkali metals and hydrides.
Fire Hazard
Flash point data for Vitamin E succinate are not available; however, Vitamin E succinate is probably combustible.
Flammability and Explosibility
Not classified
Biochem/physiol Actions
Tocopherol exhibits antioxidant property by protecting the cells and membranes from oxidative stress. In plants, high levels of α-tocopherol leads to plant stress tolerance whereas low levels is associated with oxidative stress. In humans, tocopherol prevents cancer, premature aging, atherosclerosis, arthritis caused due to free radicals. Vitamin E succinate (VES) is an anti-tumor analog of vitamin E.
Pharmacokinetics
Of the eight separate variants of vitamin E, alpha-tocopherol is the predominant form of vitamin E in human and animal tissues, and it has the highest bioavailability . This is because the liver preferentially resecretes only alpha-tocopherol by way of the hepatic alpha-tocopherol transfer protein (alpha-TTP); the liver metabolizes and excretes all the other vitamin E variants, which is why blood and cellular concentrations of other forms of vitamin E other than alpha-tocopherol are ultimately lower .
Furthermore, the term alpha-tocopherol generally refers to a group of eight possible stereoisomers which is often called all-rac-tocopherol for being a racemic mixture of all eight stereoisomers . Of the eight stereoisomers, the RRR-alpha-tocopherol - or sometimes referred to as the d-alpha-tocopherol - stereoisomer is the naturally occurring form of alpha-tocopherol that is perhaps best recognized by the alpha-TTP and has been reported to demonstrate approximately twice the systemic availability of all-rac-tocopherol .
As a result, often times (but certainly not always) the discussion of vitamin E - at least within the context of using the vitamin for health-related indications - is generally in reference to the use of RRR- or d-alpha-tocopherol.
Subsequently, without further evidence to suggest otherwise, alpha-tocpherol succinate is generally believed to undergo a logical de-esterification in the gastrointestinal tract before being subsequently absorbed as free tocopherol .
Safety Profile
When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes.
Metabolism
In addition to any following information, owing to alpha-Tocopherol succinate's closely related chemical nature with alpha-Tocopherol acetate, please also refer to the drug information page for alpha-Tocopherol acetate for further data.
It is generally believed that alpha-tocopherol succinate is ultimately de-esterified or cleaved to provide alpha-tocopherol once administered to the human body . It is consequently expected that pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics similar to that of alpha-tocopherol to be followed .
Hepatic.
References
1) Singh?et al. (2010),?Alpha-tocopherol succinate protects mice from gamma-radiation by induction of granulocyte-colony stimulating factor; Int. J. Radiation Biol.,?86?12 2) Singh?et al. (2009),?Tocopherol succinate: a promising radiation countermeasure; Immunopharmacol.,?9?1423 3) Wu?et al. (2004),?c-Jun N-terminal kinase is required for vitamin E succinate-induced apoptosis in human gastric cancer cells; J. Gastroenterol.,?10?1110 4) Stapelberg?et al. (2004),?alpha-Tocopheryl succinate inhibits proliferation of mesothelioma cells by selective down-regulation of fibroblast growth factor receptors; Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.,?318?636 5) Swettenham?et al. (2005),?Alpha-tocopheryl succinate selectively induces apoptosis in neuroblastoma cells: potential therapy of malignancies of the nervous system; J. Neurochem.,?94?1448
Properties of D-α-Tocopherol succinate
| Melting point: | ~76 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 625.8±55.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.002±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| vapor pressure | 0Pa at 20℃ |
| storage temp. | -20°C |
| solubility | Practically insoluble in water, very soluble in methylene chloride, soluble in acetone and in anhydrous ethanol. |
| form | neat |
| pka | 4.35±0.17(Predicted) |
| form | Solid |
| color | White or off-white |
| Odor | Little or no odor |
| λmax | 286nm(EtOH)(lit.) |
| Merck | 14,9495 |
| BRN | 4038233 |
| Stability: | Stable for 2 years from date of purchase as supplied. Solutions in DMSO or ethanol may be stored at -20° for up to 1 month. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 4345-03-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | D-.alpha.-Tocopheryl acid succinate (4345-03-3) |
Safety information for D-α-Tocopherol succinate
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P304+P340:IF INHALED: Remove victim to fresh air and Keep at rest in a position comfortable for breathing. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for D-α-Tocopherol succinate
New Products
4-Piperidinemethanol Ethyl 2,4-Dihydroxy-6-methylnicotinate Ethyl isonicotinate 3-pyridine methanol N-Methyl 4-chloro-pyridine-2-carboxamide 2-Fluoro-6-iodobenzoic acid 2-((2,6-difluorobenzyl)(ethoxycarbonyl)amino)-4-((dimethylamino)methyl)-5-(4-nitrophenyl)thiophene-3-carboxylic acid Ethyl2-oxo-2,3,9,10-tetrahydro-1H-pyrido[3',4':4,5]pyrrolo[1,2,3-de]quinoxaline-8(7H)-carboxylate Elinzanetant tert-butyl 2-(4-amino-6-chloropyrimidin-5-yloxy)ethylmethylcarbamate Phenylazomalononitrile 5,6 Dimethoxy-1-indanone 3-Iodophenylacetic acid 2-Hexyn-1-ol Dibenzo-18-crown-6 2-Propanamine, 1-chloro-, hydrochloride (9CI) 3-Pyridineacetonitrile, α-hydroxy- 3-(hexyloxy)-4-(pyridin-3-yl)-1,2,5-thiadiazole N Ethylmethylamine Ethyl Methanesulfonate N N' DimethylEthylenediamine Lead II Bromide Variamine Blue B Diazonium salt N N N'Trimethyl ethylenediamineRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 D-α-Tocopherol succinate CAS 4345-03-3View Details
D-α-Tocopherol succinate CAS 4345-03-3View Details
4345-03-3 -
 D-α-Tocopherol Succinate CAS 4345-03-3View Details
D-α-Tocopherol Succinate CAS 4345-03-3View Details
4345-03-3 -
 Tocopheryl Acid Succinate, a CAS 4345-03-3View Details
Tocopheryl Acid Succinate, a CAS 4345-03-3View Details
4345-03-3 -
 D-α-Tocopherol succinate CAS 4345-03-3View Details
D-α-Tocopherol succinate CAS 4345-03-3View Details
4345-03-3 -
 Alpha tocopheryl acid succinate CAS 4345-03-3View Details
Alpha tocopheryl acid succinate CAS 4345-03-3View Details
4345-03-3 -
 D-α-Tocopherol succinate CAS 4345-03-3View Details
D-α-Tocopherol succinate CAS 4345-03-3View Details
4345-03-3 -
 5162-90-3 2-Amino-3-(1,2-dihydro-2-oxoquinoline-4-yl)propanoic acid 97%View Details
5162-90-3 2-Amino-3-(1,2-dihydro-2-oxoquinoline-4-yl)propanoic acid 97%View Details
5162-90-3 -
 4-(4-Chlorobenzyl)-2-(1-methylazepan-4-yl)phthalazin-1(2H)-one hydrochloride 98 %View Details
4-(4-Chlorobenzyl)-2-(1-methylazepan-4-yl)phthalazin-1(2H)-one hydrochloride 98 %View Details
79307-93-0
