Calcium D-Pantothenate
Synonym(s):(R)-(+)-N-(2,4-Dihydroxy-3,3-dimethyl-1-oxobutyl)-β-alanine hemicalcium salt;D -Pantothenic acid hemicalcium salt;Calcium D -pantothenate;Vitamin B5
- CAS NO.:137-08-6
- Empirical Formula: C9H17NO5.1/2Ca
- Molecular Weight: 476.53
- MDL number: MFCD00002766
- EINECS: 205-278-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:08:52
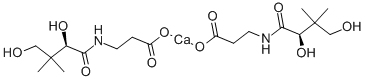
What is Calcium D-Pantothenate?
Chemical properties
Calcium D-Pantothenate is white crystalline powder
Originator
Calcium D-Pantothenate,Arocor Holdings Inc.
History
Pantothenic acid (PA), also known as vitamin B5, is essential to all forms of life. Its name is derived from the Greek word pantos that means “everywhere”, which is appropriate for this widely, distributed vitamin.
The Uses of Calcium D-Pantothenate
D-(+)-Pantothenic acid calcium salt is a member of the B complex vitamins; essential vitamin for the biosynthesis of coenzyme A in mammalian cells. Occurs ubiquitously in all animal and plant tissue. The richest common source is liver, but jelly of the queen bee contains 6 times as much as liver. Rice bran and molasses are other good sources.
The Uses of Calcium D-Pantothenate
calcium pantothenate is used as an emollient and to enrich creams and lotions in hair care preparations. This is the calcium salt of pantothenic acid found in liver, rice, bran, and molasses. It is also found in large amounts in royal jelly.
The Uses of Calcium D-Pantothenate
Calcium Pantothenate is a nutrient and dietary supplement which is the calcium chloride double salt of . It is a white powder of bitter taste and has a solubility of 1 g in 3 ml of water. It is used in special dietary foods.
What are the applications of Application
Calcium D-(+)-pantothenate is a precursor for coenzyme A biosynthesis
Definition
ChEBI: Calcium pantothenate is a polymer.
Definition
Calcium pantothenate, also known as calcium D-pantothenate or calcium pantothenic acid, is a naturally occurring form of pantothenic acid, an essential vitamin found in various foods. Calcium pantothenate is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) in the United States and in Europe. The US FDA requires infant formulas have at least 300 micrograms (mcg) per 100 calories of prepared formula.
Reactions
Pantothenic acid is a constituent of coenzyme A, which participates in numerous enzyme reactions. CoA was discovered as an essential cofactor for the acetylation of sulfanilamide in the liver and of choline in the brain.
Manufacturing Process
A mixture of 288 g (4 mols) of isobutyraldehyde, 288 g of methanol was
cooled to 10°C and 170 g (2 mols) of 36.6% formalin containing 8.5 g (3%
based on isobutyraldehyde) of sodium hydroxide was added dropwise over a
55 minute period to produce alpha,alpha-dimethyl-beta-hydroxy-propionaldehyde. The mixture was stirred for an additional 2 hours at 10-15°C
and then contacted with acetic acid to neutralize the catalyst. The excess
isobutyraldehyde and methanol were stripped off at a kettle temperature of
50°C at 25 mm. To the residual α,α-dimethyl-beta-hydroxypropionaldehyde a
mixture of 260 ml of methanol and 2 g (0.75%) sodium cyanide was added
and the solution cooled to 10°C before adding 59.4 g (2.2 mols) of hydrogen
cyanide dropwise over a 35 minute period to produce α,γ-dihydroxy-β,β-
dimethylbutyronitrile. The mixture was stirred at 10°C for one hour period and
then contacted with acetic acid to neutralize the catalyst before stripping off
the excess methanol to a kettle temperature of 45°C at 18 mm. The crude
cyanohydrin was then hydrolysed by heating with 4 mols of concentrated
hydrochloric acid at 80°C for 2 hours, then diluting with an equal volume of
water and heating at 100°C for an additional 8 hours. The aqueous mixture
was extracted continuously with ethylene dichloride. The solvent was removed, and pantolactone (B. P. 131°C/19 mm, M.P. 61-77°C, 96.5% purity
by saponification) was obtained by distillation in 71.5% yield based on
formaldehyde and 55% efficiency based on isobutyraldehyde.
26 grams of racemic pantolactone (0.2 mol) and 1.1 grams of sodium
methoxide (0.02 mol) contained in 30 ml of methanol, were added to 78.8
grams of 1-brucine (0.2 mol) contained in 156 ml of methanol. The resulting
mixture was refluxed for 1.5 hours and allowed to stand at room temperature
overnight. After centrifuging, washing with methanol and drying, 65.4 grams
of D-(-)-pantolactone 1-brucine (62% of theory based upon all of the racemic
pantolactone) melting at 203° to 206°C were obtained. Upon chilling the
mother liquor, 13.46 grams of additional complex melting at 175° to 177°C
were obtained.
D-(-)-Pantolactone was obtained from the complex in the following manner.
The 65.4 grams of complex obtained above were treated with 65 ml of
chloroform and 5.35 grams of sodium hydroxide contained in 35 ml of water
for one hour at room temperature. The aqueous layer was extracted 6 times
with 20 ml portions of chloroform in order to remove the brucine. The sodium
pantoate contained in the aqueous layer was relactonized by treatment with
11 ml of concentrated hydrochloric acid. Extraction of the crude D-(-)-
pantolactone yielded 15.29 grams. This material was then recrystallized from
7 ml of methyl isobutyl ketone and 7 ml hexane thereby yielding 9.77 grams
of D-(-)-pantolactone (37% of theory). The αD25 was -44.8°.
Into a vessel equipped with an agitator and reflux condenser are placed
approximately 52 parts by weight of α-hydroxy-β,β-di-methyl-γ-butyrolactone,
approximately 36 parts by weight of β-alanine, about 40 parts by weight of
diethylamine and about 100 parts by weight of anhydrous methanol. The
mixture is stirred and refluxed for about 12 hours until the reaction is
complete as evidenced by the dissolution of the β-alanine. To this resulting
mass is gradually added 8 parts by weight of calcium metal nodules or pellets
and refluxing continued until the metal is dissolved. The diethylamine and
alcohol are distilled off until the residue becomes viscous. The viscous residue
is dried under vacuum at 100°C. The solid residue recovered, as biologically
assayed, indicated a 91% yield of calcium pantothenate.
brand name
Calpan (BASF); Pantholin (Lilly).
Therapeutic Function
Vitamin
Biological Functions
Calcium D-Pantothenate accelerates the wound healing process by increasing the number of migrating cells, their distance and hence their speed. In addition, cell division is increased and the protein synthesis changed. Hence, higher quantities of pantothenate are locally required to enhance wound healing.
General Description
The first suggestion for the existance of vitamin B5 came from Carter et al. in 1930; although it was never characterized or isolated. This vitamin is synthesized by most green plants and microorganisms. Excellent sources of the vitamin are liver, egg yolk, whole grains, and fortified ready-to-eat cereals. However, as the original name implies, many foods contain sufficient pantothenic acid to supply dietary needs.
Chemically, pantothenic acid is considered to be aβ-alanine derivative of the asymmetric pantoic acid and thus shows asymmetry. Only the naturally occurring D(+)- stereoisomer (with R configuration) is biologically active and the L(-)-stereoisomer (with S configuration) is inactive. When its carboxylate functional group is attached through an amide linkage with β-mercaptoethylamine, it is known as pantetheine (also spelled pantotheine). The biologically active form of pantothenic acid, CoA, is formed when the terminal alcoholic function of pantetheine is attached to ADP 3'-phosphate.
Biochem/physiol Actions
The calcium salts of panthenol are commonly used for pharmaceutical preparations. Pantothenate is a component of coenzyme A and is useful in its synthesis. Pantothenic acid is also involved in the synthesis of heme, cholesterol and fatty acids. Since vitamin B5 is found in all foods, its deficiency is not commonly observed.
Clinical Use
The only therapeutic indication for pantothenic acid is intreatment of a known or suspected deficiency of this vitamin.Because of the ubiquitous nature of pantothenic acid, deficiencystates of this vitamin are only seen experimentally byuse of synthetic diets devoid of the vitamin, by use of thevitamin antagonist, ω-methylpantothenic, or both. In a 1991review, Tahiliani and Beinlich described that the mostcommon symptoms associated with pantothenic acid deficiencywere headache, fatigue, and a sensation of weakness.Sleep disturbances and gastrointestinal disturbances, amongothers, were also noted. The most likely setting for pantothenicacid deficiency is in the setting of alcoholism wherea multiple vitamin deficiency exists confounding the exactrole of the pantothenic acid deficiency as compared to theother vitamins. Because a deficiency of a single B vitamin israre, pantothenic acid is commonly formulated in multivitaminor B-complex preparations.
Safety Profile
Moderately toxic by intraperitoneal, subcutaneous, and intravenous routes. Mildly toxic by ingestion. A vitamin. See also CALCIUM COMPOUNDS. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx.
Purification Methods
The salt crystallises as needles from MeOH, EtOH or isoPrOH (with 0.5mol of isoPrOH). It is moderately hygroscopic. The S-benzylisothiuronium salt has m 151-152o (149o when crystallised from Me2CO). [Kagan et al. J Am Chem Soc 79 3545 1957, Wilson et al. J Am Chem Soc 76 5177 1954, Stiller & Wiley J Am Chem Soc 63 1239 1941, Beilstein 4 IV 2569.]
Properties of Calcium D-Pantothenate
| Melting point: | 190 °C |
| alpha | 26.5 º (c=5, in water) |
| refractive index | 27 ° (C=5, H2O) |
| Flash point: | 145 °C |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | H2O: 50 mg/mL at 25 °C, clear, nearly colorless |
| form | Powder |
| color | White or almost white |
| PH | 6.8-7.2 (25℃, 50mg/mL in H2O) |
| Odor | Odorless |
| optical activity | [α]20/D +27±2°, c = 5% in H2O |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in water. |
| Sensitive | Hygroscopic |
| Merck | 14,7015 |
| BRN | 3769272 |
| Stability: | Stable, but may be moisture or air sensitive. Incompatible with strong acids, strong bases. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 137-08-6(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Calcium pantothenate (137-08-6) |
Safety information for Calcium D-Pantothenate
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Calcium D-Pantothenate
| InChIKey | FAPWYRCQGJNNSJ-UBKPKTQASA-L |
Calcium D-Pantothenate manufacturer
Medi Pharma Drug House
Stabicoat Vitamins
Rivashaa Agrotech Biopharma Pvt. Ltd.
Supreem Pharmaceuticals Mysore Pvt Ltd
Suvan LifeSciences (formerly Sansh Biotech Pvt Ltd)
ARRAKIS INDUSTRIES LLP
Anand Agencies
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 137-08-6 Calcium D-pantothenate 98%View Details
137-08-6 Calcium D-pantothenate 98%View Details
137-08-6 -
 D-Calcium Pantothenate 99%View Details
D-Calcium Pantothenate 99%View Details -
 (+)-Pantothenic Acid Calcium Salt CAS 137-08-6View Details
(+)-Pantothenic Acid Calcium Salt CAS 137-08-6View Details
137-08-6 -
 Pandy's reagent CAS 137-08-6View Details
Pandy's reagent CAS 137-08-6View Details
137-08-6 -
 Calcium D-(+)-pantothenate CAS 137-08-6View Details
Calcium D-(+)-pantothenate CAS 137-08-6View Details
137-08-6 -
 Calcium D-Pantothenate CAS 137-08-6View Details
Calcium D-Pantothenate CAS 137-08-6View Details
137-08-6 -
 Calcium D-pantothenate 98.00% CAS 137-08-6View Details
Calcium D-pantothenate 98.00% CAS 137-08-6View Details
137-08-6 -
 Polypep® Low Viscosity CASView Details
Polypep® Low Viscosity CASView Details