D-PANTOTHENIC ACID
- CAS NO.:79-83-4
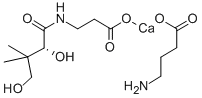
- Empirical Formula: C9H17NO5
- Molecular Weight: 219.24
- MDL number: MFCD00020513
- EINECS: 201-229-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:08:57
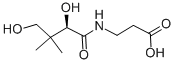
What is D-PANTOTHENIC ACID?
Absorption
Dietary pantothenic acid is primarily in the form of CoA or ACP and must be converted into free pantothenic acid for absorption. CoA and ACP are hydrolyzed into 4'-phosphopantetheine which is then dephosphorylated into pantetheine and subsequently hydrolyzed again to free pantothenic acid by Pantetheinase in the intestinal lumen. Free pantothenic acid is absorbed into intestinal cells via a saturable, sodium-dependent active transport system with passive diffusion acting as a secondary pathway. As intake increases up to 10-fold absorption rate can decrease to as low as 10% due to transporter saturation.
Toxicity
No Tolerable Upper Level Intake (UL) has been established for the vitamin.
Description
Pantothenic acid, or vitamin B5, is a B vitamin that plays a role in the breakdown of fats and carbohydrates for energy and is critical to the manufacture of red blood cells.
Physical properties
Pantothenic acid is composed of β-alanine joined to 2,4-dihydroxy-3,3- dimethylbutyric acid via an amide linkage. The molecule has an asymmetric center, and only the R-enantiomer, usually called D-(+)pantothenic acid, is biologically active and occurs naturally. Appearance: pantothenic acid is a yellow, viscous oil. Its calcium and other salts, however, are colorless crystalline substances; calcium pantothenate is the main product of commerce. Solubility: neither form is soluble in organic solvents, but each is soluble in water and ethanol. Stability: aqueous solu tions of pantothenic acid are unstable when heated under acidic or alkaline conditions
Originator
Panto-250 , Bio-Tech Pharmacal
The Uses of D-PANTOTHENIC ACID
Labelled Pantothenic Acid
The Uses of D-PANTOTHENIC ACID
Vitamin B5 is water-soluble. It is required for proper growth and maintenance of the body and is involved in body processes such as energy release from carbohydrates and metabolism of fatty acids. It is relatively stable through storage and is found in liver, eggs, and meat.
The Uses of D-PANTOTHENIC ACID
Pantothenic Acid is a member of the B complex vitamins; essential vitamin for the biosynthesis of coenzyme A in mammalian cells. Occurs ubiquitously in all animal and plant tissue. The richest common source is liver, but jelly of the queen bee contains 6 times as much as liver. Rice bran and molasses are other good sources.
Indications
Studied for the treatment of many uses such as treatment of testicular torsion, diabetic ulceration, wound healing, acne, obesity, diabetic peripheral polyneuropathy. It has also been investigated for its hypolipidemic effects and as cholesterol lowering agent.
Background
Pantothenic acid, also called pantothenate or vitamin B5 (a B vitamin), is a water-soluble vitamin discovered by Roger J. Williams in 1919. For many animals, pantothenic acid is an essential nutrient as it is required to synthesize coenzyme-A (CoA), as well as to synthesize and metabolize proteins, carbohydrates, and fats. Pantothenic acid is the amide between pantoic acid and β-alanine and commonly found as its alcohol analog, the provitamin panthenol, and as calcium pantothenate. Small quantities of pantothenic acid are found in nearly every food, with high amounts in whole-grain cereals, legumes, eggs, meat, royal jelly, avocado, and yogurt. Pantothenic acid is an ingredient in some hair and skin care products. Only the dextrorotatory (D) isomer of pantothenic acid possesses biological activity. while the levorotatory (L) form may antagonize the effects of the dextrorotatory isomer.
Definition
ChEBI: (R)-pantothenic acid is a pantothenic acid having R-configuration. It has a role as an antidote to curare poisoning, a human blood serum metabolite and a geroprotector. It is a vitamin B5 and a pantothenic acid. It is a conjugate acid of a (R)-pantothenate.
Manufacturing Process
Isobutylaldehyde reacted with formaldehyde in the presence potassium chromate as a result 2,2-dimethyl-3-hydroxy-propanal was obtained.
The 2,2-dimethyl-3-hydroxy-propanal was treated by sodium cyanide so 2,4dihydroxy-3,3-dimethyl-butironitrile was prepared.
The 2,4-dihydroxy-3,3-dimethyl-butironitrile was treated hydrochloric acid and D,L-3-hydroxy-4,4-dimethyl-dihydro-furan-2-one (D,L-pantolacton) was obtained. The racemic mixture of D- and L-pantolactons was a division of Dand L- isomers by the adding of α-phenylethylamine. So D-pantolacton was isolated.
Acrylic acid contacted with NH3and β-alanine was obtained.
D-Pantalacton reacted with β-alanine as a result 3-(2,4-dihydroxy-3,3dimethyl-butyrylamino)-propanoic acid was produced
brand name
Calpan (BASF); Pantholin (Lilly).
Therapeutic Function
Vitamin
Pharmacokinetics
Pantothenic acid is used in the synthesis of coenzyme A (CoA). CoA is thought to act as a carrier molecule, allowing the entry of acyl groups into cells. This is of critical importance as these acyl groups are used as substrates in the tricarboxylic acid cycle to generate energy and in the synthesis of fatty acids, cholesterol, and acetylcholine. Additionally, CoA is part of acyl carrier protein (ACP), which is required in the synthesis of fatty acids in addition to CoAs use as a substrate.
Pantothenic acid in the form of CoA is also required for acylation and acetylation, which, for example, are involved in signal transduction and enzyme activation and deactivation, respectively.
Since pantothenic acid participates in a wide array of key biological roles, it may have numerous wide-ranging effects.
Safety Profile
Moderately toxic by subcutaneous and intraperitoneal routes. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic vapors of NOx.
Metabolism
Not Available
Properties of D-PANTOTHENIC ACID
| Melting point: | 178-179℃ |
| Boiling point: | 360.05°C (rough estimate) |
| alpha | D25 +37.5° |
| Density | 1.266 |
| refractive index | 1.4315 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,Room Temperature |
| solubility | DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly), Water (Slightly) |
| pka | 4.30±0.10(Predicted) |
| form | Oil to Gel |
| color | Colourless |
| Stability: | Hygroscopic |
| InChI | InChI=1/C9H17NO5/c1-9(2,5-11)7(14)8(15)10-4-3-6(12)13/h7,11,14H,3-5H2,1-2H3,(H,10,15)(H,12,13)/t7-/s3 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | D-Pantothenic acid (79-83-4) |
Safety information for D-PANTOTHENIC ACID
Computed Descriptors for D-PANTOTHENIC ACID
| InChIKey | GHOKWGTUZJEAQD-KPOCXSGKNA-N |
| SMILES | [C@H](O)(C(=O)NCCC(=O)O)C(C)(C)CO |&1:0,r| |
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran




You may like
-
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 42831-50-5 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 98%View Details
42831-50-5 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 98%View Details
42831-50-5 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1