D-Glyceraldehyde
- CAS NO.:453-17-8
- Empirical Formula: C3H6O3
- Molecular Weight: 90.08
- MDL number: MFCD00064378
- EINECS: 207-217-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-08-28 13:53:23
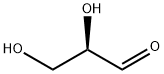
What is D-Glyceraldehyde ?
Description
D-(+)-Glyceraldehyde is an intermediate in carbohydrate metabolism. It is phosphorylated by triose kinase to produce D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate, an intermediate in glycolysis, gluconeogenesis, photosynthesis, and other metabolic pathways.
Description
D-Glyceraldehyde, a triose and the simplest aldose (aldehyde sugar), is an intermediate in fructose metabolism. It occurs in all living organisms, including humans. Its enantiomer, L-glyceraldehyde1, is related to the natural amino acids; but it does not occur in nature.
Racemic glyceraldehyde, along with dihydroxyacetone2, can be synthesized via the hydrogen peroxide oxidation of glycerol. Further oxidation of rac-glyceraldehyde produces rac-glyceric acid3 and eventually one- and two-carbon compounds.
D-Glyceraldehyde is an important starting material for the classic Kiliani–Fischer synthesis, which is used to build larger sugars from smaller ones. In this synthesis, D-glyceraldehyde reacts with cyanide ion to add a carbon atom at the aldehyde position. The nitrile group is then hydrolyzed and catalytically hydrogenated to produce the tetroses D-erythrose4 and D-threose5. Further iterations of the Kiliani–Fischer synthesis lead to higher aldoses.
D-Glyceraldehyde is also involved in shortening aldose chains, as exemplified by the Wohl degradation. It essentially accomplishes the reverse of the Kiliani–Fischer synthesis, so that D-erythrose and D-threose can be degraded to D-glyceraldehyde in a three-step process that, like Kiliani–Fischer, proceeds through a nitrile intermediate.
For additional information, see the ScienceDirect topic page on D-glyceraldehyde. And a question for readers: Crystalline D-glyceraldehyde has a relatively high melting point of 145 °C—so why is the article of commerce a viscous syrup?
1. CAS Reg. No. 497-09-6.
2. CAS Reg. No. 96-26-4.
3. CAS Reg. No. 473-81-4.
4. CAS Reg. No. 583-50-6.
5. CAS Reg. No. 95-43-2.
Chemical properties
CLEAR ORANGE SYRUP
The Uses of D-Glyceraldehyde
D-Glyceraldehyde is the simplest of all aldoses and have been shown to be the one of the carbonyl metabolite of dietary fructose.
The Uses of D-Glyceraldehyde
D-(+)-Glyceraldehyde can be utilized as a reactant in the synthesis of:
- (S)-homophenylalanine by ruthenium oxidation of a 3-amino-1,2-diol generated via coupling of an amine, and α-hydroxyaldehyde.
- β- and γ-allenols via metal-catalyzed cyclization. Allenols are used as a key precursor for the preparation of enantiopure dihydropyrans and tetrahydrooxepines.
- Isopropylidene D-glyceraldehyde intermediate, which controls the chirality in the total synthesis of prostaglandins (PGE1).
What are the applications of Application
D-(+)-Glyceraldehyde is an intermediate in carbohydrate metabolism
Definition
ChEBI: The D-enantiomer of glyceraldehyde.
Purification Methods
enantiomer [453-17-8] is a syrup (70 + % H2O) with [] D +14o (c 2, H2O) and the dimethyl acetal has b 124-127 o/14mm and []15 +21o (c 18, H2O). [Beilstein 1 H 845, 1 IV 4114.]
Properties of D-Glyceraldehyde
| Melting point: | 127-129 C |
| Boiling point: | bp17 127-129°; bp10 123-126° |
| alpha | D25 +8.7° (c = 2 in H2O); D15 +21.2° (c = 18) |
| Density | 1.272±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| refractive index | n20/D 1.494 |
| Flash point: | 112 °C |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | DMSO, Methanol (Slightly), Water (Slightly) |
| appearance | colorless crystals or viscous liquid |
| form | liquid (viscous) |
| pka | 12.60±0.20(Predicted) |
| color | Clear Colourless to Light Brown |
| Merck | 13,4494 |
| BRN | 1720474 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 453-17-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Propanal, 2,3-dihydroxy-, (r)-(453-17-8) |
Safety information for D-Glyceraldehyde
Computed Descriptors for D-Glyceraldehyde
D-Glyceraldehyde manufacturer
New Products
4-Fluorophenylacetic acid 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate (6-METHYL-[1,3]DITHIOLO[4,5-b]QUINOXALIN-2-ONE INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 D-(+)-Glyceraldehyde 89% CAS 453-17-8View Details
D-(+)-Glyceraldehyde 89% CAS 453-17-8View Details
453-17-8 -
 D-(+)-Glyceraldehyde CAS 453-17-8View Details
D-(+)-Glyceraldehyde CAS 453-17-8View Details
453-17-8 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1