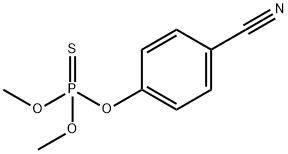
CYANOPHOS
Synonym(s):O-(4-Cyanophenyl) O,O-dimethyl phosphorothioate
- CAS NO.:2636-26-2
- Empirical Formula: C9H10NO3PS
- Molecular Weight: 243.22
- MDL number: MFCD00055485
- EINECS: 220-130-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:15:30
What is CYANOPHOS?
Description
Cyanophos is an amber liquid, decomposes at 119–120 ?C, vp 105 mPa (20 ?C). Solubility in water is 46 mg/L (30 ?C). It is soluble in most organic solvents. Log Kow = 2.65. Cyanophos is effective in controlling a variety of insect pests including rice stem borers. Major formulation types are dustable powder, emulsifiable concentrate, wettable powder, and ultra low volume liquid.
Chemical properties
Cyanophos is a yellow to reddish-yellow or amber liquid.
The Uses of CYANOPHOS
Cyanophos is used to control a number of chewing and sucking pests in cotton, fruit and vegetables and public health pests.
The Uses of CYANOPHOS
Insecticide.
The Uses of CYANOPHOS
Cyanophos is a cholinesterase inhibitor used as an insecticide and avicide.
Definition
ChEBI: Cyanophos is an organothiophosphate insecticide and an organic thiophosphate. It has a role as an agrochemical and an EC 3.1.1.7 (acetylcholinesterase) inhibitor. It is functionally related to a 4-cyanophenol.
General Description
Yellow to reddish-yellow transparent liquid. Used as an insecticide against rice stem borers and house flies. Not registered as a pesticide in the U.S.
Reactivity Profile
Organophosphates, such as CYANOPHOS, are susceptible to formation of highly toxic and flammable phosphine gas in the presence of strong reducing agents such as hydrides. Partial oxidation by oxidizing agents may result in the release of toxic phosphorus oxides.
Health Hazard
CYANOPHOS is an organophosphorus insecticide. It is a cholinesterase inhibitor. Death may occur after a massive oral dose; with smaller accidental doses, onset of illness may be delayed.
Health Hazard
Exhibits acute, delayed, and chronic poisoning; highly toxic cholinesterase inhibitor;ingestion of small doses or skin absorption may produce delayed effects; massiveoral dose can be fatal; toxic symptomsinclude headache, dizziness, blurred vision,pinpoint pupils, vomiting, abdominal painand seizures; respiratory symptoms includeshortness of breath, respiratory depression,and respiratory paralysis.
LD50 oral (rat): 18 mg/kg.
Fire Hazard
(Non-Specific -- Organophosphorus Pesticide, Liquid, n.o.s.) Container may explode in heat of fire. Fire and runoff from fire control water may produce irritating or poisonous gases. Unstable. Rapidly decomposes under alkaline conditions and upon exposure to light.
Potential Exposure
A potential danger to those involved in the manufacture, formulation, and application of this insecticide which is used against rice stem borers and house flies. It is not registered as a pesticide in the United States. Incompatibilities: Alkaline materials and exposure to light can cause rapid decomposition. Contact with oxidizers may cause the release of phosphorous oxides. Contact with strong reducing agents, such as hydrides, may cause the formation of flammable and toxic phosphine gas.
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts theskin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediatelywith soap and water. Speed in removing material from skinis of extreme importance. Shampoo hair promptly if contaminated. Seek medical attention immediately. If thischemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure, beginrescue breathing (using universal precautions, includingresuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR ifheart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medicalfacility. When this chemical has been swallowed, get medical attention. Give large quantities of water and inducevomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit.Effects may be delayed; keep victim under observation
Metabolic pathway
The metabolism of cyanophos in plants and mammals is similar with deactivation via demethylation to desmethylcyanophos being important routes in both systems. Activation via oxidative desulfuration to cyanophos oxon, which is itself demethylated, also occurs in both plants and mammals. 4-Cyanophenol is an important metabolite which probably occurs principally by hydrolysis of the oxon in plants but in mammals is produced by oxidative dearylation of cyanophos also. In mammals it is conjugated as the sulfate ester as a major liver and urinary metabolite but conjugates of 4-cyanophenol have not been reported in plants.
Metabolism
The main biodegradation pathways in mammals are demethylation and aryl ester bond cleavage; the liberated cyanophenol is excreted in the form of the sulfate ester, formed by conjugation. The metabolism in plants is similar to that in mammals except the cyanophenol conjugation.
storage
Color Code—Blue: Health Hazard/Poison: Storein a secure poison location. Cyanophos is stable to storagefor 2 years or more under normal conditions. Prior to working with this chemical you should be trained on its properhandling and storage. Store in tightly closed containers in acool, well-ventilated area.
Shipping
UN3278 Organophosphorus compound, liquid, toxic, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Hazard Technical Name Required, Potential Inhalation Hazard (Special Provision 5). UN3018 Organophosphorus pesticides, liquid, toxic, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials.
Degradation
The photodecomposition of [14C-cyano]cyanophos in acetone (a photosensitising solvent) irradiated by unfiltered UV light yielded cyanophos oxon (2), desmethylcyanophos oxon (3), 4-cyanophenol (4), 4-cyanobenzoic acid (5), 2-hydroxy-5-cyanobenzoic acid (6), CO2 and HCN. When cyanophos was exposed to sunlight in aqueous solution or as thin films on soil or silica gel TLC plates, which represent conditions more relevant to photolysis in the environment, only cyanophos oxon (2), desmethylcyanophos oxon (3) and 4-cyanophenol (4) were detected (Mikami et al., 1976) (Scheme 1).
Toxicity evaluation
It has a low mammalian toxicity: acute oral LD50 for rats is 710–730 mg/kg. Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats is >1500 mg/m3 air.
Incompatibilities
A potential danger to those involved in the manufacture, formulation, and application of this insecticide which is used against rice stem borers and house flies. It is not registered as a pesticide in the United States. Incompatibilities: Alkaline materials and exposure to light can cause rapid decomposition. Contact with oxidizers may cause the release of phosphorous oxides. Contact with strong reducing agents, such as hydrides, may cause the formation of flammable and toxic phosphine gas.
Waste Disposal
In accordance with 40CFR165 recommendations for the disposal of pesticides and pesticide containers. Must be disposed properly by fol- lowing package label directions or by contacting your local or federal environmental control agency, or by contacting your regional EPA office.
Properties of CYANOPHOS
| Melting point: | 14-15° |
| Boiling point: | bp0.09 119-120° (dec) |
| Density | 1.255-1.265 g/cm3(Temp: 25 °C) |
| vapor pressure | 1.05 x 10-1 Pa (20 °C) |
| refractive index | nD32.5 1.5404 |
| Flash point: | >100 °C |
| storage temp. | 0-6°C
|
| form | liquid |
| Water Solubility | 46 mg l-1 (30 °C) |
| Specific Gravity | 1.255~1.265 |
| Merck | 13,2283 |
| BRN | 2695901 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Cyanophos (2636-26-2) |
Safety information for CYANOPHOS
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. |
Computed Descriptors for CYANOPHOS
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid DIETHYL AMINOMALONATE HYDROCHLORIDE 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran





You may like
-
 Cyanophos CAS 2636-26-2View Details
Cyanophos CAS 2636-26-2View Details
2636-26-2 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 -
 733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8