Cuprous thiocyanate
Synonym(s):Cuprous thiocyanate
- CAS NO.:1111-67-7
- Empirical Formula: CHCuNS
- Molecular Weight: 122.63
- MDL number: MFCD00010980
- EINECS: 214-183-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-02-23 21:28:46
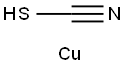
What is Cuprous thiocyanate?
Chemical properties
Copper(I) thiocyanate, CuSCN, [1111-67-7], MW 121.62, is a white powder when pure, but often the material of commerce is yellow. It is soluble in ammonia solution, alkali thiocyanate solutions, and diethyl ether, but it is only slightly soluble in water and dilute mineral acids. It is stable in air in the absence of moisture, but it slowly decomposes in the presence of moisture in air. It is used as an antifouling pigment.
Characteristics
Copper thiocyanate (CuSCN) is also a wide bandgap (3.6?eV) semiconductor and has a work function of about ?5.3?eV. The conductivity ranges between 10-2 and 10-3 S?cm-1, good stability, shows good transparency throughout the visible and near infrared spectrum. It has good chemical stability. It can be deposited through a solution processing approach at low temperature, making it compatible with flexible substrates. By using copper thiocyanate (CuSCN) instead of P3HT as the HTL, a higher device PCE was achieved.
The Uses of Cuprous thiocyanate
In marine antifouling paints; in primer compositions for explosives industry.
The Uses of Cuprous thiocyanate
It is used as flame retardant. It is a good inorganic pigment, and is used as the antifouling paint for protecting the underwater surfaces of ships against vegetation. Manufacturing industrial chemicals, pharmaceuticals and also used in freezing solutions, electroplating , steel picking, printing, and corrosion inhibitor against acid gases.
The Uses of Cuprous thiocyanate
The product can be prepared from Cu(CH3COO)2·H2O, AgNO3, NH4NCS and im(im = imidazole). The structure and optical properties were reported. It is an air- and light-stable source of Cu(I).
Preparation
Copper(I) thiocyanate is prepared by the reaction of alkali metal thiocyanates with copper(I) chloride at 8090°C or by the reaction of copper(II) sulfate solutions with alkali metal thiocyanate in the presence of sulfite. It can also be prepared by precipitation from copper(II) salt solutions with hydrogen thiocyanate.
General Description
We are committed to bringing you Greener Alternative Products,which adhere to one or more of The 12 Principles of Greener Chemistry. This product is an enabling product used as a Hole Transport Material for high-performance solar cells and thus has been enhanced for energy efficiency. Click here for more information.
Potential Exposure
Used as a microbiocide and algaecide in antifouling paints. Used as a laboratory chemical and for making other chemicals. Some formulations may be designated Restricted Use Pesticide (RUP).
Shipping
UN3439 Nitriles, solid, toxic, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required
Structure and conformation
At least two polymorphs of cuprous thiocyanate have been characterized by X-ray crystallography. They both feature copper(I) in a characteristic tetrahedral coordination geometry. The sulfur end of the SCN- ligand is triply bridging so that the coordination sphere for copper is CuS3N.
Incompatibilities
Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides
Waste Disposal
Copper-containing soluble wastes can be concentrated through the use of ion exchange, reverse osmosis, or evaporators to the point where copper can be electrolytically removed and sent to a reclaiming firm. If recovery is not feasible, the copper can be precipitated through the use of caustics and the sludge deposited in a chemical waste landfill. Copper-containing wastes can be concentrated to the point where copper can be electrolytically removed and reclaimed. If recovery is not feasible, the copper can be precipitated by alkali; the cyanide destroyed by alkaline oxidation yielding a sludge which can be sent to a chemical waste landfill. In accordance with 40CFR165, follow recommendations for the disposal of pesticides and pesticide containers. Must be disposed properly by following package label directions or by contacting your local or federal environmental control agency, or by contacting your regional EPA office
Properties of Cuprous thiocyanate
| Melting point: | 1084°C |
| Density | 2.84 |
| vapor pressure | 0Pa at 20-50℃ |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,Room Temperature |
| solubility | insoluble in H2O, dilute acid solutions,ethanol, acetone; soluble in ethyl ether |
| form | Powder |
| color | Off-white |
| Specific Gravity | 2.843 |
| Water Solubility | Practically insoluble in water, alcohol. Soluble in NH{4}OH, ether |
| Merck | 14,2669 |
| Solubility Product Constant (Ksp) | pKsp: 12.75 |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 1 mg/m3 NIOSH: IDLH 100 mg/m3; TWA 1 mg/m3 |
| Stability: | Stable. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 1111-67-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Cuprous thiocyanate (1111-67-7) |
Safety information for Cuprous thiocyanate
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P273:Avoid release to the environment. P391:Collect spillage. Hazardous to the aquatic environment P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for Cuprous thiocyanate
| InChIKey | PDZKZMQQDCHTNF-UHFFFAOYSA-M |
New Products
2-Propanamine, 1-chloro-, hydrochloride (9CI) 3-Pyridineacetonitrile, α-hydroxy- 3-Iodophenylacetic acid 3-(hexyloxy)-4-(pyridin-3-yl)-1,2,5-thiadiazole 2-Hexyn-1-ol Dibenzo-18-crown-6 2-Hexanone, 98% Sodium molybdate dihydrate,98% 2,3-Dimethylphenol, 98% 4,4'-Oxydianiline Isoquinoline, 96% 2-Amino-4,6-difluorobenzoic acid, 95% (R)-2-Methylpyrolidine-2-carboxylic acid (De Mepro) Ramipril Sacubitril- Valsartan Boc-his(trt)-OH Fmoc-L-Glu-OtBu Boc-L-Tyr(tBu)-OH N N Dimethylformamide Dimethyl Acetal (Dmf Dma) Semi carbazide Hydrochloride 1-Ethyl-3-(3-Dimethylaminopropyl)-Carbodiimide Hydrochloride [EDC Hcl] Trans-4-Aminocyclohexanol [4tac] 2-[1-(Mercaptomethyl)Cyclopropyl]Acetic Acid 2-Chloromethyl-4-methyl-quinazolineRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


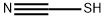

You may like
-
 Copper(I) thiocyanate CAS 1111-67-7View Details
Copper(I) thiocyanate CAS 1111-67-7View Details
1111-67-7 -
 Copper(I) thiocyanate CAS 1111-67-7View Details
Copper(I) thiocyanate CAS 1111-67-7View Details
1111-67-7 -
 Copper(I) thiocyanate 98.00% CAS 1111-67-7View Details
Copper(I) thiocyanate 98.00% CAS 1111-67-7View Details
1111-67-7 -
 Copper(I) thiocyanate, 98%+ CAS 1111-67-7View Details
Copper(I) thiocyanate, 98%+ CAS 1111-67-7View Details
1111-67-7 -
 Copper(I) thiocyanate, 99% CAS 1111-67-7View Details
Copper(I) thiocyanate, 99% CAS 1111-67-7View Details
1111-67-7 -
 Copper(I) Thiocyanate CAS 1111-67-7View Details
Copper(I) Thiocyanate CAS 1111-67-7View Details
1111-67-7 -
 Cuprous thiocyanate CASView Details
Cuprous thiocyanate CASView Details -
 Copper(I) thiocyanate CAS 1111-67-7View Details
Copper(I) thiocyanate CAS 1111-67-7View Details
1111-67-7
