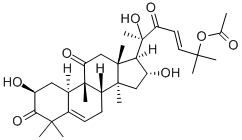
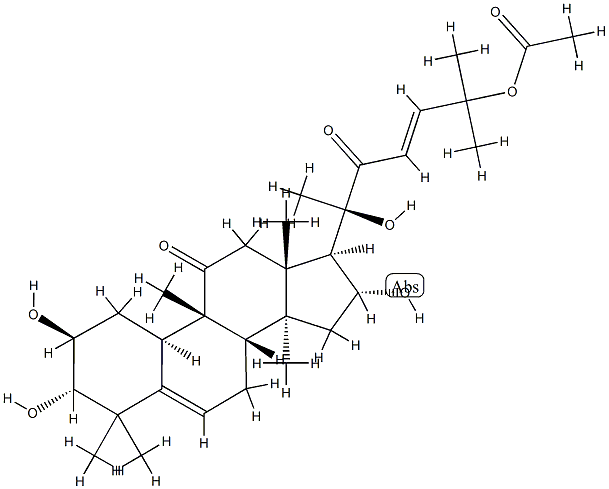
CUCURBITACIN B
Synonym(s):(2β,9β,10α,16α,23E)-25-(acetyloxy)-2,16,20-trihydroxy-9-methyl-19-Norlanosta-5,23-diene-3,11,22-trione
- CAS NO.:6199-67-3
- Empirical Formula: C32H46O8
- Molecular Weight: 558.7
- MDL number: MFCD07778083
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-03 16:17:04
What is CUCURBITACIN B?
Description
Cucurbitacin B is a tetracyclic triterpenoid that has been shown to have a strong antitumor activity.
Description
Cucurbitacins are tetracyclic terpenes with steroidal structures that are isolated from plants of the family Cucurbitaceae such as pumpkins, gourds, and cucumbers. Ancient peoples used cucurbits medicinally, but they also recognized their toxic properties. Medicinal uses included emetics, narcotics, and antimalarials.
Twenty cucurbitacins have been isolated from the ≈965 known species (in ≈95 genera) of Cucurbitaceae. By the 1950s, the research groups of P. R. Enslin (South African Council for Scientific and Industrial Research, Pretoria) and David Lavie (Weizmann Institute of Science, Rehovot, Israel) had isolated 17 cucurbitacins and studied their properties. Lavie’s group showed that cucurbitacin E (also called α-elaterin) has antitumor properties.
The two most common cucurbitacins are B and E. Cucurbitacin B, whose structure is shown, is extremely toxic when ingested (see hazard information box); E is not as toxic but is still harmful if swallowed.
Cucurbitacins are also known as “bitter principles” of cucurbits. In a recent article, Logan Kistler at the University of Warwick (Coventry, UK), George H. Perry at Penn State (University Park), and colleagues at several other institutions reported that, despite the fruits'' bitter taste, prehistoric animals such as mastodons and mammoths ate wild cucurbits and distributed their seeds in their excrement. As the ancient beasts died out, the cucurbits also faded because their primary means of seed dispersal was gone.
Humans came to the rescue. They found that they could eat cucurbit seeds, probably by washing off the bitter constituents. Later, they domesticated squashes and gourds and, by selecting the less bitter seeds, were able to produce more palatable cucurbits. Thus, humans and cucurbits evolved together.
Chemical properties
White solid
The Uses of CUCURBITACIN B
Cucurbitacin B hydrate has been used:
- as a signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (stat3) inhibitor to determine its effect on the expression of human lysosomal acid lipase (hLAL) in myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs).
- as an ecdysone receptor (EcR) antagonist injection to lower the levels of 20-hydoxyecdysone (20E) signaling in butterflies.
- to determine its effect on the cell viability of pancreatic cancer cell lines.
Definition
ChEBI: A cucurbitacin in which a lanostane skeleton is multi-substituted with hydroxy, methyl and oxo substituents, with unsaturation at positions 5 and 23; a hydroxy function at C-25 is acetylated.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Cucurbitacin B is a triterpenoid constituent of Cucurbitaceae plant species. Cucurbitacin B inhibits proliferation in a wide variety of tumor cell lines (IC50 15-30 nM) by inducing apoptosis and inducing cell cycle arrest at G2/M phase. Although the mechanism of action is unclear, Cucurbitacin B inhibits STAT 3 phosphorylation and expression levels and has been shown to block JAK2 activity. Curcubitacin B also inhibits the transcriptional activity of HIF1a and Nf-KB. Curcubitacin B is structurally similar to the JAK inhibitor Curcubitacin I.
Properties of CUCURBITACIN B
| Melting point: | 184-186° |
| Boiling point: | 546.74°C (rough estimate) |
| alpha | D25 +88° (c = 1.55 in ethanol) |
| Density | 1.0953 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.4900 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | Keep in dark place,Sealed in dry,2-8°C |
| solubility | DMSO: soluble10mg/mL, clear |
| form | powder |
| pka | 12.60±0.29(Predicted) |
| appearance | white crystals |
| color | white to beige |
| λmax | 290nm(EtOH)(lit.) |
| Merck | 14,2614 |
| Stability: | Hygroscopic |
Safety information for CUCURBITACIN B
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H300:Acute toxicity,oral |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. P405:Store locked up. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for CUCURBITACIN B
| InChIKey | IXQKXEUSCPEQRD-ALLWXVAWSA-N |
New Products
4-Fluorophenylacetic acid 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate (6-METHYL-[1,3]DITHIOLO[4,5-b]QUINOXALIN-2-ONE INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran




You may like
-
 Cucurbitacin B CAS 6199-67-3View Details
Cucurbitacin B CAS 6199-67-3View Details
6199-67-3 -
 Cucurbitacin B 98% (HPLC) CAS 6199-67-3View Details
Cucurbitacin B 98% (HPLC) CAS 6199-67-3View Details
6199-67-3 -
 Cucurbitacin B hydrate CAS 6199-67-3View Details
Cucurbitacin B hydrate CAS 6199-67-3View Details
6199-67-3 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1