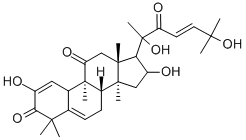
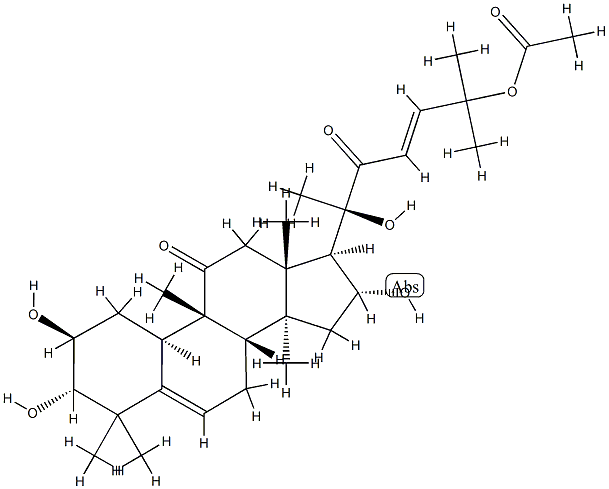
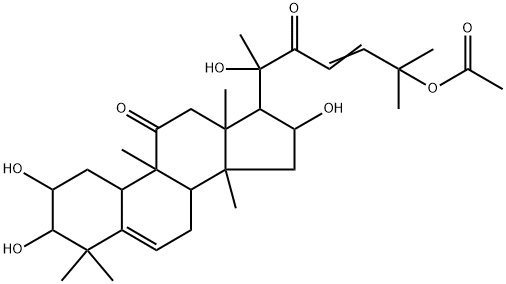
Cucurbitacin E
Synonym(s):α-Elaterin;α-Elaterine
- CAS NO.:18444-66-1
- Empirical Formula: C32H44O8
- Molecular Weight: 556.69
- MDL number: MFCD00135936
- EINECS: 242-325-2
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 20:33:22
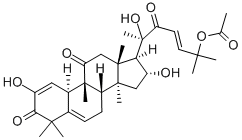
What is Cucurbitacin E?
Description
Cucurbitacin E is a plant-derived triterpene that has diverse biological activities. At a concentration of 10 pM, it reduces MPP+-induced death of neuronal PC12 cells through inhibition of autophagy in vitro. Cucurbitacin E inhibits growth of T24 bladder, MDA-MB-468 and MCF-7 breast, PC3 prostate, and colorectal cancer cell lines (IC50s = 50-1,000 nM) through induction of G2/M arrest and apoptosis. It increases bilirubin binding to human serum albumin (HSA) in human plasma in a dose-dependent manner. Cucurbitacin E also inhibits depolymerization of actin filaments isolated from rabbit skeletal muscle actin and in HeLa cells.
Chemical properties
white to beige powder
The Uses of Cucurbitacin E
Cucurbitacin E is a biochemical compound from the family of Cucurbitacins. Cucurbitacin E is a highly oxidated steroid consisting of a tetracyclic triterpene. Cucurbitacin E is known to possess broad spectrum of potential anti-inflammatory, antitumor andantioxidant effects.
The Uses of Cucurbitacin E
Cucurbitacin E has been used as a cofilin inhibitor. It is also used as a F-actin stabilizer to prevent membrane-associated periodic skeleton (MPS) loss and protect from axonal fragmentation.
Definition
ChEBI: A cucurbitacin in which a lanostane skeleton is multi-substituted with hydroxy, methyl and oxo substituents, with unsaturation at positions 1, 5 and 23.
General Description
This substance is a primary reference substance with assigned absolute purity (considering chromatographic purity, water, residual solvents, inorganic impurities). The exact value can be found on the certificate. Produced by PhytoLab GmbH & Co. KG.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Cucurbitacin E is a potent inhibitor of actin depolymerization. Cucurbitacin E is more active than jasplakinolide, and has a different mechanism of action, binding to a different site. Cucurbitacin E binds specifically to filamentous actin (F-actin) forming a covalent bond at residue Cys257, but not to monomeric actin (G-actin), stabilizing F-actin, without affecting actin polymerization or nucleation.
Properties of Cucurbitacin E
| Melting point: | 228-234°C |
| Boiling point: | 545.56°C (rough estimate) |
| alpha | D -59° (c = 0.7 in chloroform) |
| Density | 1.1059 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.4900 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | -20°C |
| solubility | DMSO: soluble15mg/mL, clear |
| form | powder |
| pka | 8.51±0.70(Predicted) |
| color | white to beige |
| optical activity | [α]/D -60 to -75°, c = 0.7 (CDCl3) |
Safety information for Cucurbitacin E
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral |
Computed Descriptors for Cucurbitacin E
| InChIKey | NDYMQXYDSVBNLL-MUYMLXPFSA-N |
New Products
4-Fluorophenylacetic acid 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate (6-METHYL-[1,3]DITHIOLO[4,5-b]QUINOXALIN-2-ONE INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Cucurbitacin E CAS 18444-66-1View Details
Cucurbitacin E CAS 18444-66-1View Details
18444-66-1 -
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1